Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersAlarmingly widespread digestive problems impact millions of people worldwide and can cause disruptions to daily living. Malabsorption is a serious yet often disregarded illness among these worries. When the small intestine cannot appropriately absorb nutrients from our food, malabsorption occurs. It may result in various health issues, from immune system weakness and exhaustion to dietary inadequacies and weight loss.
Comprehending and identifying malabsorption is crucial since prompt identification and management can significantly enhance health results and overall well-being.
What is Malabsorption?
Malabsorption is the term used to describe inability of the small intestine to absorb macronutrients, vitamins, and minerals from meals in an effective manner for the body. Numerous health issues arise due to the body’s inability to obtain the essential nutrients which are necessary for its proper functioning.
A variety of underlying conditions can cause malabsorption. The ingestion of gluten, for instance, is responsible for the damage to the small intestine in patients with celiac disease. This autoimmune condition hinders the body’s capacity to absorb nutrients. For instance, Crohn’s disease is an example of an inflammatory bowel disease. This condition causes persistent inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, which in turn hinders the body’s ability to absorb nutrients. Malabsorption results from chronic pancreatitis, characterized by persistent pancreatic inflammation that impedes the production of digestive enzymes necessary for food digestion. Lactose intolerance, infections, and certain medications are potential causes of this condition.
10 Common Symptoms of Malabsorption
1. Chronic Diarrhea:

Explanation: Chronic diarrhea is characterized by loose, watery, and frequent feces that continue for an extended period of time. This causes dehydration and substantial electrolyte imbalance.
Relationship to Malabsorption: Malabsorption is when the small intestine cannot absorb nutrients, notably lipids, from the digested food. The lipids that have not been digested are removed from the body through the stool, which causes the stool to become very loose and watery. Because of this inadequate nutrient absorption, the body disrupts regular bowel function, ultimately resulting in persistent diarrhea.
Also, read: How to Stop Diarrhea Quickly: 6 Effective Home Remedies to Relieve Diarrhea
2. Bloating and Gas:

Explanation: Bloating is the feeling of fullness and tightness in the abdominal region. Excessive gas is frequently present along with it, which could cause discomfort and noticeable swelling.
Relationship to Malabsorption: When the digestive system is unable to break down and absorb nutrients effectively, undigested food particles ferment in the gut, producing an excessive amount of gas; as a result of the accumulation of this gas, bloating occurs, which is most visible after meals. The poor digestion and fermentation processes highlight the connection between malabsorption and these symptoms.
Also, read:
- 10 Ways Prevent To Stomach Bloating- Causes and Remedies
- 20 Effective Remedies to Relieve Stomach Bloating at Home
3. Abdominal Pain:

Explanation: “Abdominal pain” refers to discomfort experienced within the stomach region regularly. It is typical for cramping to accompany the pain, which can range in the intensity from mild to severe.
Relation to Malabsorption: The relationship between malabsorption and the discomfort that it causes is that malabsorption can cause inflammation or irritation of the intestinal lining, which can be somewhat uncomfortable. In addition to contributing to malabsorption, conditions such as celiac disease and Crohn’s disease frequently produce chronic inflammation, which in turn leads to discomfort in the abdominal region that persists over time.
4. Weight Loss

Explanation: The term “unintended and unexplained weight loss” refers to body weight loss that occurs without any changes to the individual’s diet or exercise routine. It can be concerning and may point to underlying health problems.
Relation to Malabsorption: There is a connection between malabsorption and the fact that when nutrients, particularly fats, and proteins, are not absorbed adequately, the body is unable to get the calories and building blocks required for appropriate weight maintenance. Because of this, the body will use its stores for energy, resulting in unexpected weight loss even though the amount of food consumed is average or even increased.
Also, read:
- 14 Ways To Maintain Weight After Weight Loss – Consistency Is Key
- What Happens To Fat Cells After Weight Loss? Know The Rightful Answers!
5. Fatigue

Explanation: A prolonged feeling of exhaustion and a loss of energy not alleviated by rest are the defining characteristics of fatigue. Daily and on one’s quality of life in general, it might have a considerable impact.
Relation to Malabsorption: The absence of essential nutrients such as iron, vitamin B12, and other vitamins and minerals might contribute to fatigue. It is related to malabsorption. Certain nutrients are necessary for cells to operate correctly and produce energy. When the body does not digest them correctly, it leads to low energy levels and persistent fatigue.
Also, read: 15 Ways To Beat Afternoon Fatigue – Tide The Slumber!
6. Sore Tongue
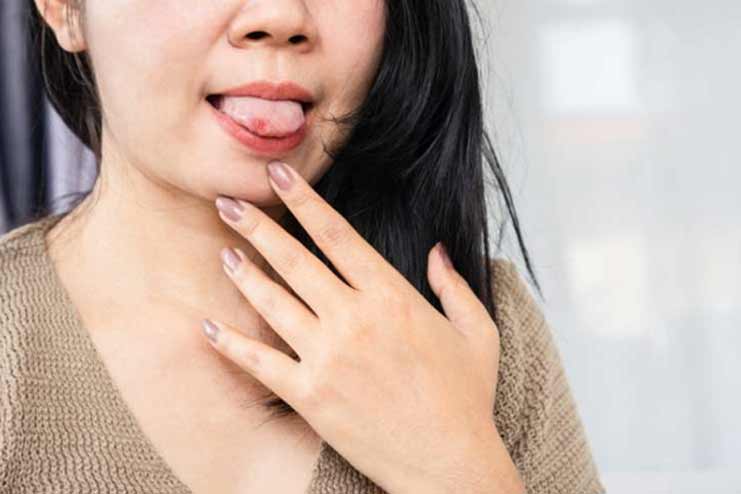

Explanation: Discomfort, soreness, or a burning feeling in the tongue are all symptoms of chronic tongue discomfort. Swelling, color changes, or difficulties communicating and eating may also be present.
Relation to Malabsorption: A connection between malabsorption and shortages in critical vitamins like B12, folic acid, and iron can be shown. Malabsorption can lead to deficiencies in these vitamins. Because of these deficits, glossitis, a tongue inflammation that causes the tongue to become painful and swollen, can occur. This symptom brings to light that the body requires adequate nutrient absorption to keep its tissues in good health.
7. Muscle Wasting
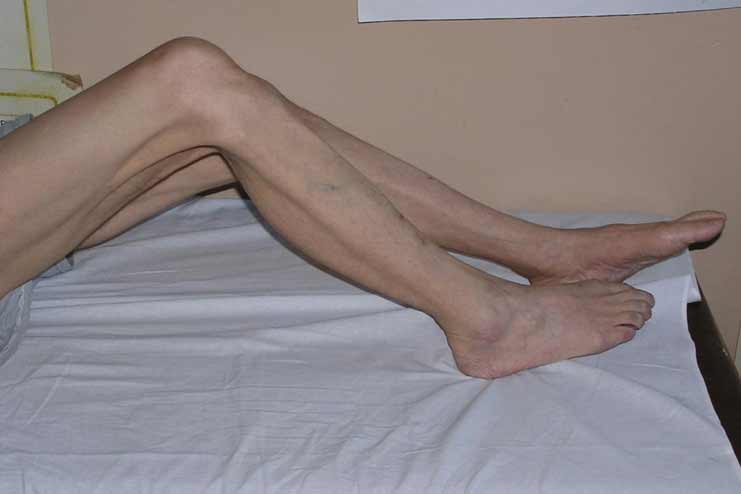
Explanation: The term “muscle wasting” describes the process by which an individual loses muscle mass and strength despite maintaining a regular diet and level of physical activity.
Relation to Malabsorption: Protein is absolutely necessary for the growth and maintenance of muscle strength. When the body is unable to absorb an adequate amount of protein from the food it consumes, it starts to break down its own muscle tissue to satisfy its need for protein. Because of this, there is a discernible decrease in both muscle mass and strength.
8. Anemia
Explanation: Anemia is a disorder that is defined by a low red blood cell count, which leads to symptoms such as weakness, pallor, and shortness of breath.
Relation to Malabsorption: The inability of the small intestine to absorb iron, folate, and vitamin B12, all of which are essential for the synthesis of red blood cells, can be a contributing factor in the development of anemia. These inadequacies make it more difficult for the body to create sufficient quantities of healthy red blood cells, which causes the symptoms associated with anemia.
9. Scaly or Dry Lips
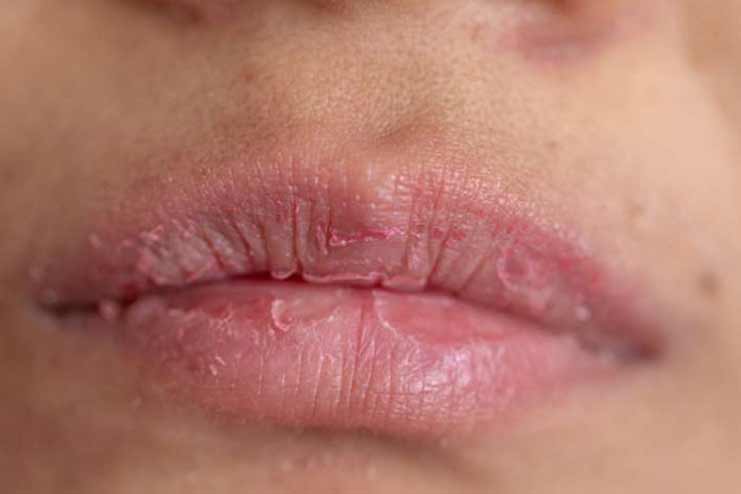
Explanation: Scaly lips are frequently characterized by cracked, flaky, and occasionally painful lips that have the potential to bleed or become infected.
Relationship to Malabsorption: Malabsorption can result in deficits in critical vitamins such as B vitamins, particularly B2 (riboflavin) and B6, which are required for maintaining healthy skin. If these nutrients are not present, the skin of the lips might become dry and scaly, reflecting the general nutritional deficits that the body is experiencing.
10. Greasy Stool

Explanation: In addition to being referred to as steatorrhea, the condition known as “greasy stool” is characterized by pale, thick feces with an offensive odor. Flushing them away can be challenging because they frequently float.
Relationship to Malabsorption: Glycemic stool is a direct consequence of the inability to absorb fat. When the small intestine is very unable to absorb fats in the appropriate manner, lipids can linger in the digestive tract and be eliminated through the stool. Excess fat is responsible for the greasy look of the stool and its many distinguishing characteristics.
When to See a Doctor
It is essential to know when to seek medical help to receive a quick diagnosis and treatment for malabsorption. If you are experiencing persistent symptoms such as chronic diarrhea, unexplained weight loss, severe exhaustion, or recurrent abdominal discomfort, you should get medical attention before continuing to experience these symptoms. Frequent bloating, gas, and oily stools are some other symptoms that may be present. A medical checkup is also necessary if symptoms such as muscular atrophy, anemia, and a sore or swollen tongue are present.
Each of the underlying illnesses that can cause malabsorption, such as celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, or chronic pancreatitis, calls for a different type of therapeutic approach. A medical practitioner can conduct exhaustive examinations, including blood testing, stool tests, and imaging scans, to correctly identify the root cause.
Managing Malabsorption
Making adjustments to one’s food, receiving medical treatment, and making changes to one’s lifestyle are all necessary components in the management of malabsorption.
Dietary Adjustments: Alterations to Your Diet It is essential to modify your diet to contain simple meals to digest and steer clear of items that worsen your symptoms. As an illustration, people with celiac disease ought to adhere to a diet entirely free of gluten, and people who are lactose intolerant ought to steer clear of dairy products. When addressing deficiencies brought on by malabsorption, incorporating meals that are high in nutrients and even taking supplements can be helpful.
Medical Treatments: Enzyme supplements, such as pancreatic enzymes for chronic pancreatitis, or drugs to control inflammation in disorders such as Crohn’s disease, are examples of medical treatments that may be administered, depending on the underlying cause of the problem. If infections contribute to malabsorption, antibiotics or antiparasitic drugs may sometimes be essential.
Lifestyle Changes: Alterations to Lifestyle: Alterations to one’s way of life might also be helpful in managing symptoms. Regular, moderate exercise can improve digestive health, and stress-reduction techniques like yoga or meditation can lessen gastrointestinal distress. When it comes to adequately managing malabsorption and maintaining optimal health, it is crucial to maintain regular follow-ups with a healthcare professional and check symptoms consistently.
Conclusion
The identification and treatment of malabsorption are necessary to avoid significant problems. Understanding the symptoms and obtaining medical help at the appropriate time can result in an early diagnosis and sound therapy, improving quality of life. You must seek the advice of a medical expert if you are experiencing persistent symptoms such as persistent diarrhea, unexplained weight loss, or significant exhaustion. Significant improvement is possible with early intervention and individualized treatment.
In this Article


















