Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersMaintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial in the ongoing pursuit of health and well-being. Among various health concerns, hypertension stands out as one of the most prevalent and potentially debilitating conditions. This article explores the vital role lifestyle changes play in preventing hypertension, emphasizing their profound impact on blood pressure regulation.
As we delve into the topic, it becomes clear that adopting proactive measures is not merely a choice but a necessity for reducing the risk of hypertension and establishing a strong foundation for long-term cardiovascular health.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Your Risk of Hypertension
1. Balanced Diet and Nutrition
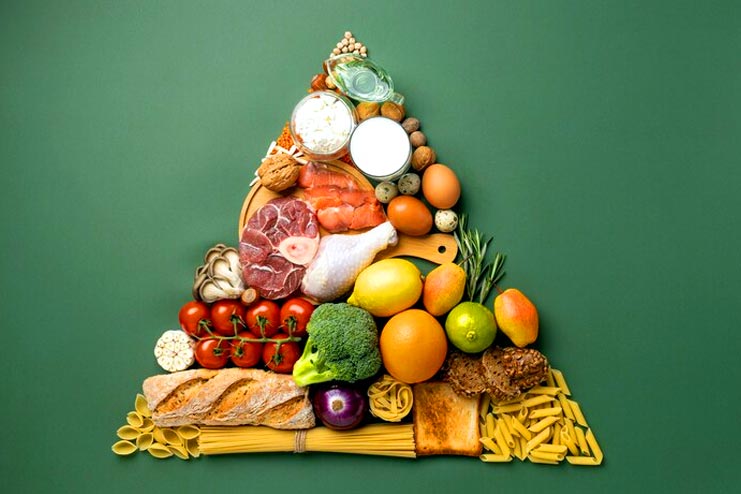

A balanced diet is key to good health and plays a significant role in lowering blood pressure. Understanding the symbiotic relationship between nutrition and blood pressure regulation empowers us to make dietary choices that can significantly enhance long-term cardiovascular health.
Maintaining optimal blood pressure is essential for preventing hypertension, and a well-rounded diet is a powerful tool in this process.
Key Nutrients That Help Prevent Hypertension:
Several nutrients are essential in the fight against hypertension.
- Sodium: a nutrient-rich diet helps regulate sodium levels, lowering blood pressure.
- Potassium: found abundantly in fruits and vegetables, is particularly important as it helps balance the effects of sodium, supporting cardiovascular health.
- Magnesium: found in almonds and leafy greens, helps relax blood vessels, reducing the strain on the heart.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: present in fatty fish like salmon, offer anti-inflammatory benefits that can lower blood pressure.
- Calcium-rich foods: such as dairy products and leafy greens, support healthy blood vessel function, making them crucial for hypertension prevention.
Practical Tips for a Hypertension-Friendly Diet:
Adopting a diet that supports healthy blood pressure requires mindful food choices and practical adjustments. Reducing sodium intake is vital, so opting for fresh, unprocessed foods over packaged ones is a good strategy. A plant-based diet rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables ensures a steady supply of essential nutrients.
2. Regular Physical Activity
3. Stress Reduction
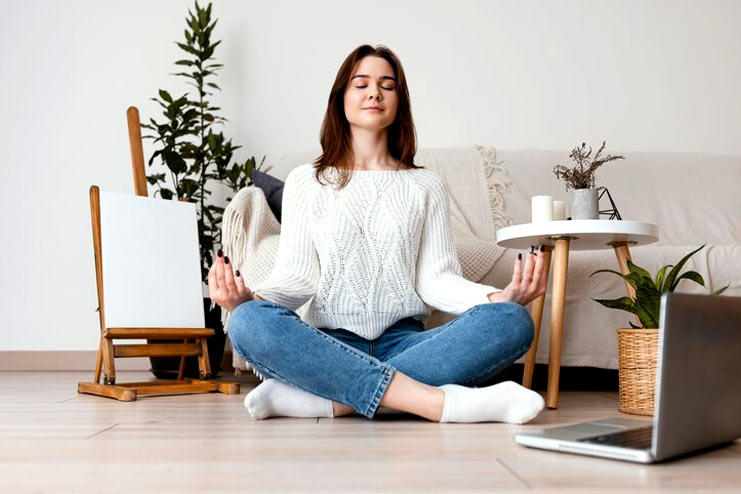

The complex relationship between stress and hypertension underscores the profound impact mental health can have on physical well-being. Chronic stress triggers physiological responses, including the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can contribute to elevated blood pressure over time. Understanding this connection is essential for preventing hypertension holistically.
Effective Stress-Reduction Techniques:
Incorporating stress-reduction strategies is crucial in the battle against hypertension. Practices such as mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation techniques are highly effective in reducing stress and, consequently, controlling blood pressure.
- Mindfulness: encourages present-moment awareness, helping individuals let go of worries about the past or future.
- Meditation: such as guided imagery or focused breathing—offer the mind a space to relax and reset.
- Progressive muscle relaxation and deep breathing exercises can calm the nervous system and lower stress levels.
Practical Tips for Integrating Stress-Reduction into Daily Life:
Incorporating stress-reduction techniques into your routine doesn’t have to be complicated. Small adjustments can significantly impact your overall stress levels. Set aside a few minutes each day for mindfulness or meditation practice. As you become more comfortable, gradually extend the duration and create a peaceful, distraction-free environment to enhance the experience. Regular practice helps solidify these habits, increasing their effectiveness over time.
Stress-reduction practices can also be seamlessly integrated into everyday activities. Use work breaks to practice deep breathing exercises or incorporate mindfulness into activities such as eating, walking, or even commuting. Before bedtime, create a calming atmosphere with relaxing routines, like reading or gentle stretching, to help reduce stress and promote restful sleep.
Engaging in enjoyable activities, such as hobbies or spending time in nature, can also help alleviate stress. Maintaining strong social connections is equally important, as emotional support and meaningful relationships play a vital role in managing stress levels.
Related Article: 9 Side Effects of Hypertension on the Brain
4. Weight Management

The relationship between blood pressure and body weight highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy weight to prevent hypertension. Being overweight, especially in the abdominal area, increases the strain on the heart and disrupts the hormonal and chemical balance that regulates blood pressure, which can lead to the development of hypertension.
Tips for Achieving and Maintaining a Healthy Weight:
Embarking on a weight-loss journey requires a multifaceted approach, combining healthy eating, regular exercise, and lifestyle adjustments. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential for weight management. Focusing on mindful eating, controlling portion sizes, and limiting processed foods and sugary beverages can significantly support weight loss efforts.
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight also requires regular physical activity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-to-intense aerobic exercise per week, 75 minutes of vigorous exercise, and two or more strength training sessions. These activities improve cardiovascular fitness, support weight loss, and lower the risk of hypertension.
Prioritize getting enough sleep, as insufficient rest can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to weight gain and an increased risk of hypertension. Similarly, managing stress is crucial, as chronic stress can trigger unhealthy eating patterns and hinder weight loss efforts.
To effectively manage weight, set realistic and achievable goals. Avoid quick-fix solutions, which are often unsustainable. Instead, focus on gradual, steady progress. Working with healthcare professionals, such as dietitians or personal trainers, can provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific needs and health status.
5. Limit Sodium and Alcohol Intake

Moderation in both sodium and alcohol consumption is crucial for controlling hypertension. Excessive intake of either can significantly elevate blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart-related issues.
The Impact of Excess Sodium on Blood Pressure:
A high-sodium diet is a major contributor to hypertension, as it increases blood volume and puts strain on blood vessels. Elevated sodium levels lead the body to retain water, which raises blood pressure. Many processed foods, restaurant meals, and snacks contain hidden sodium, making it essential to be mindful of what we eat.
To reduce sodium intake, focus on eating fresh, whole foods and cooking at home using flavor-enhancing herbs and spices instead of salt. Practical strategies include reading food labels, choosing low-sodium alternatives, and reducing consumption of processed or packaged foods. By making these simple changes, you can better control sodium levels and support healthy blood pressure.
The Effect of Excessive Alcohol on Blood Pressure:
While moderate alcohol consumption may have some cardiovascular benefits, excessive drinking is a known risk factor for hypertension. Alcohol raises blood pressure and heart rate by stimulating the sympathetic nervous system. Chronic alcohol misuse also contributes to weight gain, which further increases the risk of high blood pressure.
To prevent hypertension, reducing alcohol and sodium intake is key. When it comes to alcohol, moderation is vital. Health guidelines recommend that men limit alcohol intake to two drinks per day, while women should have no more than one. Be mindful of portion sizes, choose drinks with lower alcohol content, and dilute alcoholic beverages with water.
6. Regular Health Check-ups and Monitoring
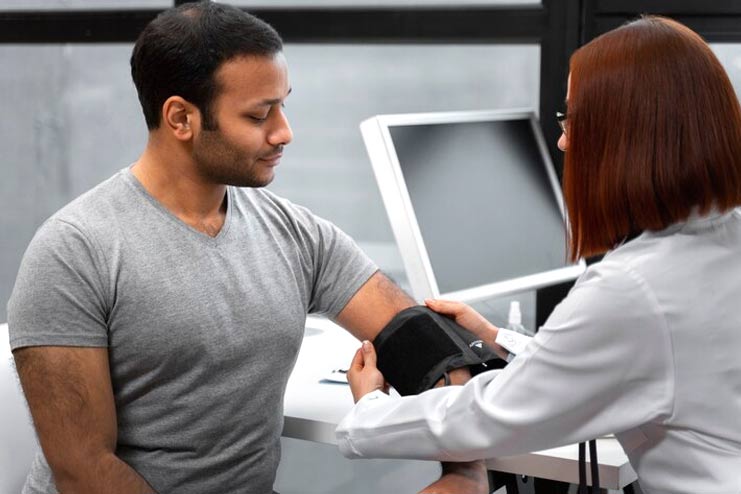
Regular medical checkups are essential for proactive blood pressure control and cardiovascular health. These visits allow for early identification of potential issues, enabling lifestyle changes—such as improving diet and increasing physical activity—before medical intervention is required. Prioritizing checkups ensures timely intervention and supports long-term cardiovascular well-being.
Why Monitoring Blood Pressure Matters:
Routine checkups provide healthcare professionals with the opportunity to assess blood pressure, establish baseline levels, and detect any changes. Consistent monitoring helps identify risk factors, allowing individuals to work with their doctors to develop personalized hypertension prevention and management plans.
Understanding Blood Pressure Trends:
Tracking blood pressure numbers over time is crucial for managing cardiovascular health. Regular monitoring helps individuals spot patterns and potential triggers, empowering them to take timely action. Being aware of these trends enables informed lifestyle choices and the ability to seek treatment early if hypertension develops.
Conclusion
Lifestyle changes become essential allies in the fight against hypertension. Maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, eating a balanced diet, and getting regular exercise all work together to create an effective proactive blood pressure management plan.
Accepting these modifications helps people protect themselves against hypertension while promoting general health. It’s a call to action to lead a heart-healthy lifestyle that lays the way for a robust cardiovascular future and make decisions consistent with long-term health. Accept these shifts, prioritize your health, and embark on a revolutionary journey to a vibrant, well-being-focused life.
Recommended Articles:
Reference
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/diet-in-the-treatment-and-prevention-of-hypertension#:~:text=A%20variety%20of%20dietary%20modifications,%2C%20sweets%2C%20meat%2C%20and%20saturated
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4366416/
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/high-blood-pressure-diet-and-weight-beyond-the-basics#:~:text=Eat%20more%20fruits%20and%20vegetables%20%E2%80%94%20Adding%20more%20fruits%20and%20vegetables,fiber%20may%20decrease%20blood%20pressure.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/in-depth/high-blood-pressure/art-20045206#:~:text=Regular%20exercise%20makes%20the%20heart,This%20lowers%20blood%20pressure.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/hypertensionaha.113.01965
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3901083/
https://www.mindful.org/how-to-manage-stress-with-mindfulness-and-meditation/#:~:text=Research%20published%20in%20the%20Journal,or%20dwelling%20on%20the%20past.
https://academic.oup.com/ajh/article/27/1/122/142278
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.094011
https://www.cdc.gov/bloodpressure/prevent.htm#:~:text=Be%20Physically%20Active,walking%20or%20bicycling%2C%20every%20week.
https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/changes-you-can-make-to-manage-high-blood-pressure/managing-weight-to-control-high-blood-pressure
https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/changes-you-can-make-to-manage-high-blood-pressure/limiting-alcohol-to-manage-high-blood-pressure
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/expert-answers/blood-pressure/faq-20058254
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7903677/
https://www.cdc.gov/bloodpressure/measure.htm#:~:text=It’s%20important%20to%20get%20an,of%20security%20about%20your%20health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7203601/
In this Article





















