Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersStress and high blood pressure are intimately related, and chronic stress is a significant cause of high blood pressure. Stress causes our body to release the chemicals that raise our heart rate and narrow blood vessels, which causes a brief rise in blood pressure. Chronic stress worsens hypertension over time, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Integrating stress-reduction strategies into everyday routines can significantly improve cardiovascular health since stress management is essential for blood pressure control. This article will discuss eight practical stress-reduction methods that generally lower blood pressure and support heart health.
Read More: 6 Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Your Risk of Hypertension
1. Deep Breathing Exercises

We cannot eliminate stress; it is crucial in certain circumstances. Like aerobic exercise builds muscles and enhances heart function, breathing exercises can increase lung efficiency.
Deep breathing is a straightforward yet effective method for lowering blood pressure and stress. Breathing slowly and deliberately relaxes the neurological system, reducing heart rate and fostering calm.
Deep Breathing Exercise Types:
Diaphragmatic Breathing: The diaphragm, or stomach, is the most effective breathing muscle. It is a big, dome-shaped muscle at the base of your lungs. Your abdominal muscles move the diaphragm, offering extra force as you exhale.
- With your head supported and your knees bent, lie on your back on a level surface or bed.
- Grasp your upper chest with one hand and your rib cage with the other.
- Breathe slowly through your nose until your hand rises and your stomach moves out. Try to keep your hand on your chest as still as you can.
- When you exhale through pursed lips, your hand will drop as your stomach moves in due to the tightness of your abdominal muscles.
Box Breathing: One deep breathing method that can help you slow down your breathing is box breathing, often known as square breathing. It reduces stress in your body, calms your nervous system, and diverts your attention as you count to four. Box breathing is a straightforward yet effective relaxation method for returning your breathing pattern to a calm rhythm.
- Place your feet on the floor and sit in a cozy chair with your back supported.
- As you gently count to four, close your eyes and inhale through your nose, feeling the air enter your lungs.
- Hold your breath and try not to cover your mouth or nose as you count slowly to four.
- Exhale slowly for four seconds.
- Repeat steps 1 through 3 at least three times after waiting four seconds.
2. Progressive Muscle Relaxation

Practitioners have successfully used progressive muscle relaxation (PMR), a deep relaxation method, to manage stress and anxiety, alleviate sleeplessness, and reduce the symptoms of several chronic pain conditions.
The basic idea behind progressive muscle relaxation is to tense or tighten one muscle group at a time and release the tension during a relaxation period. Progressive muscle relaxation typically employs systematic desensitization and other cognitive behavioral treatment strategies.
If you only practice the approach, you will have more control over your body’s body’sbody’s anxious response.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation Step-by-Step Guide:
- Choose a comfortable, distraction-free position to sit or lie down in.
- To relax your body, take a deep breath through your nose and release it gradually.
- For roughly five seconds, tense the muscles in your feet. Then, gradually relax them while paying attention to the feeling of relaxation.
- Tense and relax each muscle group in turn.
- Allow your body to feel lighter and more relaxed as you observe the contrast between tension and relaxation.
- To relax more deeply, repeat the sequence twice.
Read More: Passive Smoking And Hypertension – What Study Suggests?
3. Mindfulness Meditation

For thousands of years, people have frequently meditated as a spiritual practice. However, mindfulness has gained popularity in recent years to assist people in stress management and enhance their general well-being. Mindfulness meditation is a mental training technique that trains you to slow down your racing thoughts, let go of negativity, and relax your body and mind.
It incorporates mindfulness, a mental state that focuses entirely on “the now” to recognize and accept thoughts, feelings, and sensations without judgment, with meditation.
Mindfulness Meditation’sMeditation’s Advantages:
- Reduces blood pressure swings by lowering stress hormones.
- Enhances emotional control, lowering stress and anxiety.
- It encourages calm breathing and relaxation, which improves heart health.
- Promotes deeper sleep, which enhances cardiovascular health.
Methods for Mindfulness Meditation:
- Locate a peaceful, cozy area. Sit in a chair or on the ground with your head, neck, and back straight but not rigid. Wearing loose-fitting, comfortable attire also helps you stay focused.
- Although it’s not required, setting a timer—ideally with a moderate, silent alarm—may help you concentrate on your meditation and forget the passing of time. It can also help you eliminate excuses for stopping doing something else. It can also ensure you’re not meditating for too long, as many individuals lose the sense of time while meditating.
- The objective is to become more at ease with being the “witness” to your thoughts, not to stop them. Don’t ignore or suppress your thoughts when they arise. Just notice them, stay composed, and anchor yourself with your breathing.
- If you lose yourself in worry, dread, anxiety, or hope, take a moment to notice where your thoughts have gone without judgment and then focus on your breathing.
4. Yoga and Stretching
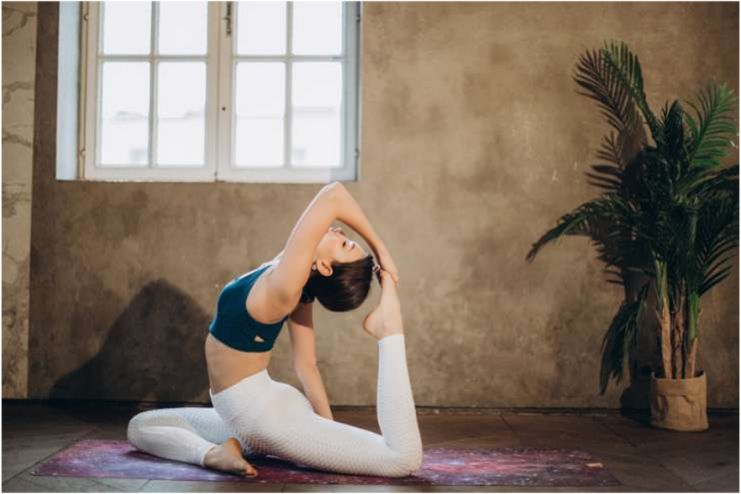

You could believe yoga is unnecessary because you always stretch after working out. Alternatively, you might have started a weekly yoga practice but not been stretching after a run or a bike ride. Stretching and yoga promote healing, but practitioners shouldn’t view them as opposing choices.
You need both to stay in shape and increase your fitness and workout performance. Stretching and yoga are powerful stress-reduction methods that enhance circulation, encourage relaxation, and lower blood pressure.
Yoga lowers cortisol levels and stimulates the parasympathetic nerve system, which results in a calmer body and mind. It does this by combining movement, mindfulness, and breath control.
Stress-Relieving Yoga Pose and Stretches:
- Child’s pose: 30 seconds. Stretch your arms forward while sitting on your heels and lowering your torso towards the floor; allow your forehead to rest gently on the mat. Focus on breathing deeply and relax into the stretch.
- Downward-facing dog pose: 60 seconds in the downward-facing dog stance. Exhale as you extend your arms and legs and raise your hips back and forth.
- Standing forward bend pose: 30 seconds in the forward bend position. Step your feet forward, exhale as you stretch your torso, and gently pull your belly in.
- Extended puppy pose: 30 seconds of prolonged puppy stance. Put both knees on the mat, extend your spine, place your forehead on the mat, walk your hands forward, and bring your hips back toward your heels.
Read More: 9 Side Effects Of Hypertension On The Brain, Heart And Overall Health
5. Biofeedback Therapy
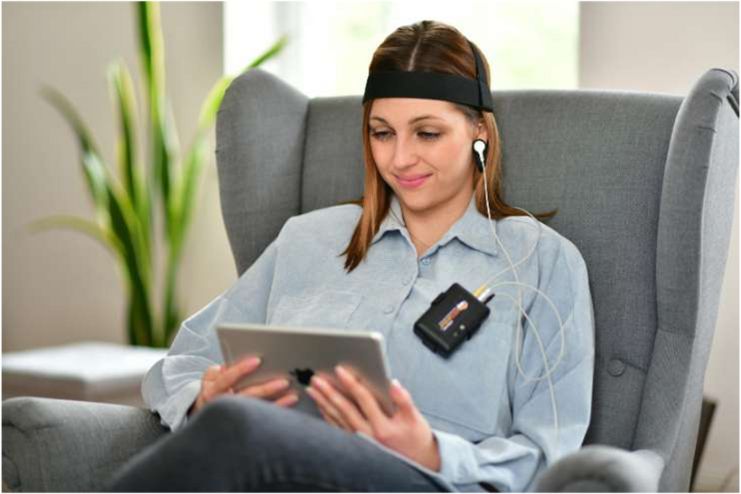

Your nervous system controls involuntary bodily activities such as blood pressure, skin temperature, and heart rate. You don’t consider speeding up your heartbeat. It simply occurs in reaction to your surroundings, such as when you’re exercising, anxious, or excited.
You can increase your control over these typically involuntary processes by using one method. The technique, known as biofeedback, is used to treat or prevent diseases like high blood pressure, persistent discomfort, migraine headaches, and incontinence.
Advantages of Biofeedback for High Blood Pressure:
- It helps control blood pressure by lessening spikes brought on by stress.
- Promotes relaxation by raising awareness of the things that cause stress.
- Reduces tension by improving muscular relaxation and respiratory control.
Biofeedback Technique Types:
- EMG stands for Electromyogram. It gauges tension and muscular activity and can be used to treat incontinence, headaches, anxiety problems, back discomfort, and muscle retraining following an injury.
- Thermal. It gauges the skin’s temperature and can be used to treat Raynaud’s illness and headaches.
- HRA, or Heart Rate Variability, gauges heart rate. It can also treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), anxiety, asthma, and irregular heartbeats.
- EDA stands for Electrodermal Activity. You can use it for anxiety and pain, and it measures sweating.
6. Guided Imagery and Visualization

Using your imagination to help your body relax is known as imagery or visualization. Your body can react to thoughts that make you angry or nervous by becoming tense and agitated, but it can also respond to serene, pleasant, and comforting thoughts by becoming more relaxed and tranquil.
Closing your eyes and visualizing yourself in a calm, soothing environment is one of the most straightforward techniques to utilize imagery to relax. It could be a location you have visited in the past or one you made up in your head.
The advantages of guided imagery are numerous; studies have demonstrated that the technique can lessen worry and panic, reduce headache frequency, and lessen psychological suffering in cancer patients.
How to Put Guided Imagery Into Practice:
- Make yourself at home in a quiet, private area.
- Take a few deep, steady breaths to focus your concentration and relax.
- Picture yourself in a stunning setting, with everything just how you would like it to be. Some folks see a beach, a forest, a mountain, or a person reclining in a beloved chair in their favorite room.
- Picture yourself feeling relaxed and at ease. Alternatively, see yourself smiling, happy, and enjoying yourself.
- Stay in your scene for five to ten minutes, or until you are at ease, and explore its many sensory elements.
- As you unwind, remind yourself that you may return here anytime to relax.
- Return to your world after opening your eyes once more.
Implementing guided imagery into everyday routines can help people develop a calmer body and mind, enhancing their cardiovascular health and stress management.
Read More: A Detailed List Of Hypertension Causes
Conclusion
Stress management is crucial for preserving normal blood pressure and general wellness. Deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, mindfulness meditation, yoga, biofeedback treatment, and guided imagery are stress-reduction methods considered effective in lowering stress levels, lessening the risk of hypertension, and enhancing cardiovascular health.
Implementing these techniques into regular routines can improve relaxation, foster long-term wellness, and create healthier coping strategies. Minor, deliberate improvements can have a big impact, so consistency is essential. Build a routine that suits you best by including one or two approaches at a time. Making stress management a priority now might result in a healthy, stress-free future
References
- https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/wellness/breathing-exercises
- https://www.nhs.uk/mental-health/self-help/guides-tools-and-activities/breathing-exercises-for-stress
- https://www.michiganmedicine.org/health-lab/easy-way-beat-stress-and-build-healthier-life
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/9445-diaphragmatic-breathing
- https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/breathing-to-reduce-stress
- https://www.webmd.com/balance/what-is-box-breathing
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321805#how-to-do-it
- https://www.webmd.com/sleep-disorders/muscle-relaxation-for-stress-insomnia
- https://www.anxietycanada.com/articles/how-to-do-progressive-muscle-relaxation
- https://www.verywellmind.com/how-do-i-practice-progressive-muscle-relaxation-3024400
- https://mentalhealthyfit.org/thinky/2024/4/8/identifying-and-managing-stress
- https://www.verywellmind.com/mindfulness-meditation-88369
- https://www.apa.org/topics/mindfulness/meditation
- https://www.sleep.com/sleep-health/morning-yoga-stretches
- https://www.prevention.com/fitness/workouts/g30417941/best-yoga-stretches
- https://www.spotebi.com/yoga-sequences/full-body-stretch
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/265802
- https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/biofeedback-therapy-uses-benefits
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/13354-biofeedback
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/265802
- https://positivepsychology.com/guided-imagery-scripts
- https://www.mentalhealth.va.gov/coe/cih-visn2/Documents/Patient_Education_Handouts/Visualization_Guided_Imagery_2013.pdf
- https://www.headspace.com/meditation/guided-imagery
- https://www.mentalhealth.com/library/visualization-and-guided-imagery-for-stress-reduction
- https://healthy.kaiserpermanente.org/health-wellness/health-encyclopedia/he.stress-management-doing-guided-imagery.uz2270
- https://positivepsychology.com/guided-imagery-scripts
In this Article