Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersPerformance-enhancing training loads may be the aim of competitive athletes but are increasingly becoming a goal for us regular people as well. While training, we may go through several phases, including overreaching and overtraining.
Overreaching frequently causes fatigue after several days of intensive training, but is easily remedied by rest. Overtraining happens when we continue to train past overreaching, which results in maladaptations and decreased competitive performance.
Performance losses result from chronic maladaptations brought on by excessive training combined with other stressors and insufficient recovery time, which can result in “Overtraining Syndrome.”
We can guarantee long-term success in our exercise regimen and maximize post-workout recovery by being aware of and responsive to the signs of overtraining.
In this article we explore seven distinct signs of overtraining and provide preventative measures so you can continue reaching for your fitness goals in a healthy and safe manner.
Also, read: 7 Top-Rated Massage Guns for Post-Workout Recovery
1. Persistent Fatigue
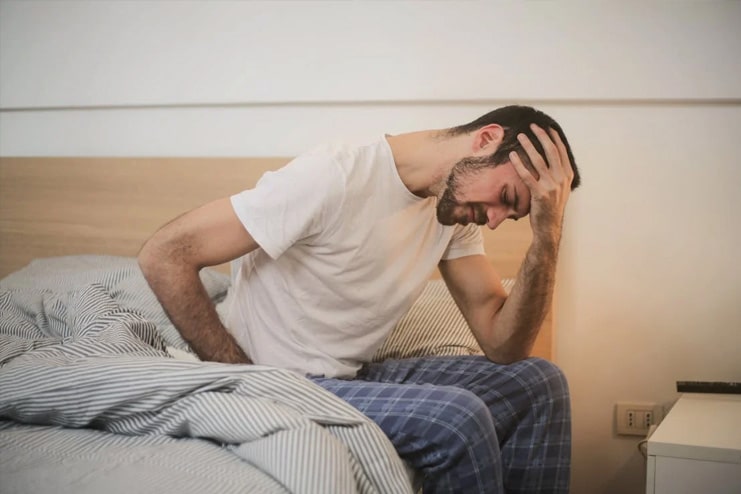

One of the most common symptoms of overtraining is persistent fatigue, characterized by a constant feeling of exhaustion that does not improve even after you’ve taken a break.
Chronic fatigue can impact day to day activities, leaving individuals feeling exhausted and unable to perform at their best. A persistent state of fatigue can also decrease motivation and lower performance during exercise, which further impedes their fitness progress.
Combat fatigue and effectively manage your energy levels by incorporating adequate rest and recovery periods between workouts, eat a balanced diet rich in nutrients, and get sufficient, good quality sleep.
Also, read: 15 Ways To Beat Afternoon Fatigue
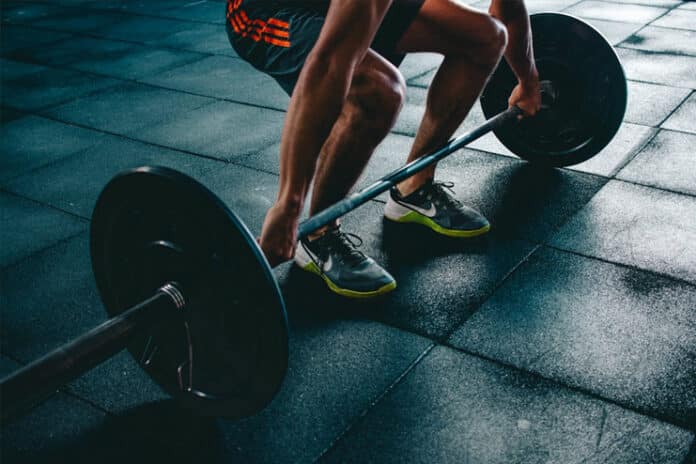
2. Decreased Performance

A sudden decrease in performance, such as a decline in strength or endurance, is typically an indication of overtraining. Even with consistent effort, this decrease may manifest as a workout plateau, in which progress either stops or reverses itself.
Strength loss and decreased endurance are two key indicators that the body is not recovering as effectively as it should. Monitoring the progress of your workouts is essential to identifying any changes in performance at an early stage. Keep detailed records of your workouts, so you can recognize patterns and address problems promptly.
To prevent a decline in performance, incorporate rest days into your routine and modify the intensity of your workouts. Ensure adequate recovery time and balance high-intensity workouts with lower-intensity ones to maintain performance levels and avoid the effects of overtraining.
If you pay attention to your body and adjust your workout routines, you can maintain your fitness gains over the long term and improve your overall health.
Read More: 10 Things To Do Before And After Workout – Know The Basics!
3. Chronic Soreness and Pain
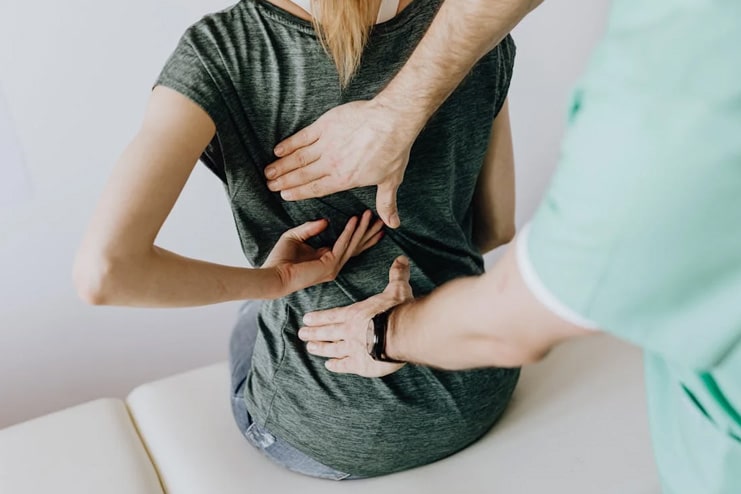

Chronic soreness and muscle pain beyond the typical discomfort experienced after exercising can indicate that you have overtrained your muscles. If muscles and joints do not recover sufficiently, they can develop persistent pain, increasing the likelihood of injuries. Ignoring chronic pain can result in serious complications, such as stress fractures, tendonitis, or other long-term damage.
Injury prevention is necessary to maintain a sustainable fitness routine. Including appropriate recovery techniques into your routine can be of assistance in reducing persistent pain and soreness.
Stretching, foam rolling, and regular massage are all effective methods for promoting muscle recovery and flexibility. These methods improve blood flow to the muscles, lessen muscle tension, and help the body recover more quickly. Prioritize these relaxation strategies to avoid overtraining and preserve the health of your muscles, and continue to make secure progress in your fitness journey.
Suggested Article: Soothe Sore Muscles: 7 Top-Rated Massage Guns for Post-Workout Recovery
4. Frequent Illness
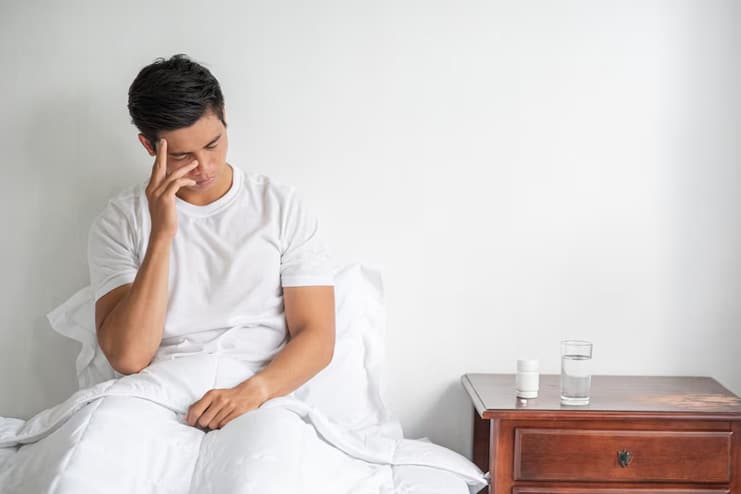

When the body is subjected to intense and prolonged physical exertion without sufficient rest, it experiences stress, impairing immune function and compromising health, making an individual more prone to experiencing frequent illnesses such as colds and infections. Maintaining a healthy immune system is essential for overall well-being because it helps the body fight off pathogens and supports its ability to function at its highest potential.
Balance physical activity, rest, and proper nutrition to protect and support the immune system. Including sufficient rest periods between workouts is essential so that the body can recover and strengthen its immune system.
Consuming a diet abundant in nutrients supplies the essential vitamins and minerals required to strengthen immune defenses. You can reduce the likelihood of experiencing frequent illness and keep your overall health and fitness in good standing by combining physical activity with rest and maintaining a well-balanced diet.
5. Mood Changes
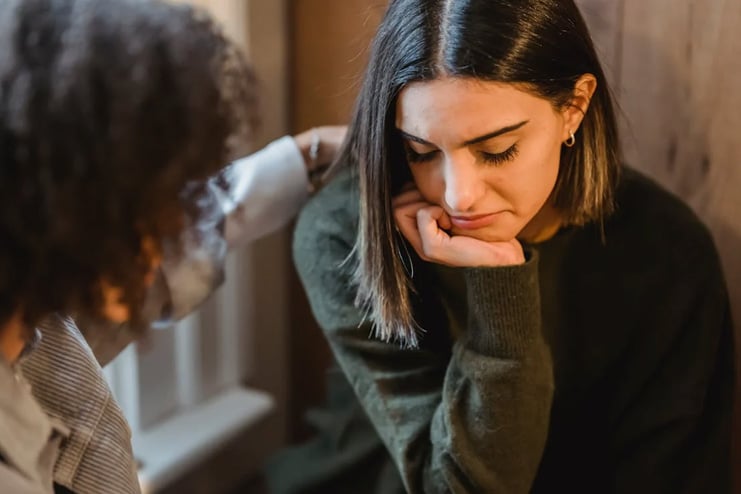

An excessive amount of training can have a significant impact on mental health, causing mood changes such as irritability, anxiety, and depression. Emotional well-being can be impacted by a disturbance in the hormone balance between norepinephrine and epinephrine, as well as by the physical strain that comes from excessive activity without sufficient recovery. When the body is subjected to constant strain, it can result in chronic fatigue and anxiety, which can manifest in negative mood swings and increased irritability.
It is essential to recognize the significance of stress management and mental health maintenance to guarantee a well-balanced and efficient fitness routine. Practicing mindfulness, employing relaxation techniques, and ensuring sufficient rest are all methods to manage stress effectively.
Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises, can help reduce stress levels and help to calm the mind. In addition, getting enough rest is essential because it enables the body and mind to recuperate from the effects of physical exertion, promoting overall mental health and well-being.
You can counteract the adverse effects of overtraining on your mental health and maintain a positive and a balanced lifestyle by incorporating these practices into your routines.
Also, read: 18 Natural Ways To Increase Serotonin
6. Insomnia or Poor Sleep Quality
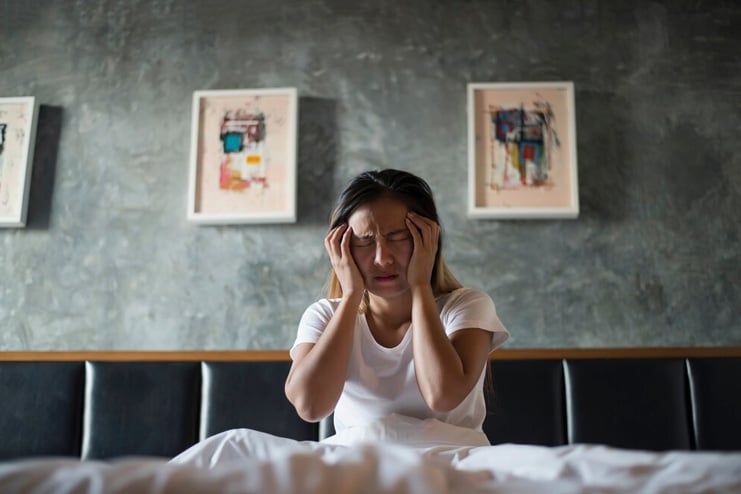

Significant sleep disturbances, such as insomnia and irregular sleep patterns, can be a result of overtraining. Excessive exercise causes physical and mental stress which disrupts the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, making it challenging to fall asleep and to stay asleep.
Getting sufficient good quality sleep is essential for hormone regulation, muscle repair, and general health, and getting too little sleep harms recuperation.
To improve sleep quality and muscle recovery, reduce your caffeine intake, create a calm and comfortable sleeping environment, and establish a regular sleep schedule. Maintaining a regular sleep and wake-up schedule aids in regulating the body’s internal clock. Reducing caffeine consumption can help avoid sleep disturbances, particularly in the hours before bed.
Furthermore, establishing a peaceful, stress-free pre-sleep environment without electronics can enhance sleep quality.
Make sleep a priority to help you recover and feel better overall, reducing the adverse effects of overtraining.
Related Article:
- 12 Breathing Techniques For Sleep To Drive Insomnia Away
- 9 Essential Oils for Sleep That Drives Insomnia Away
- Simple Ways To Tackle Insomnia
7. Loss of Appetite
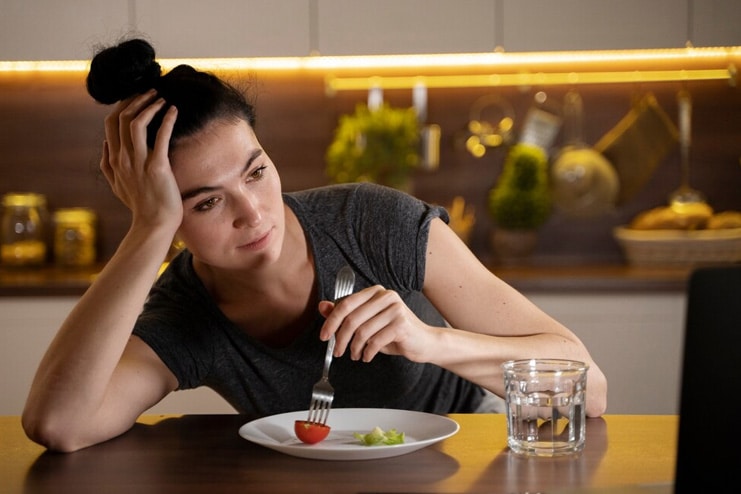

Overtraining can impact hunger levels, causing a loss of appetite and an inadequate intake of nutrients. When the body is subjected to excessive physical stress, it can disrupt standard hunger signals, making it difficult to consume sufficient calories and essential nutrients required for energy, recovery, and muscle repair.
To combat the loss of appetite associated with overtraining, pay attention to your body’s hunger cues, stay hydrated and drink sufficient water, and focus on eating well-balanced meals.
Pay close attention to your body’s signals that indicate hunger and eat only when truly hungry. Consume a wide variety of foods that are rich in nutrients to ensure that the body receives all the vitamins and minerals essential for its proper functioning. And finally, keep yourself hydrated to control your appetite and support the functions of your body as a whole.
Support your energy needs and recovery processes by prioritizing proper nutrition, and reduce the adverse effects of overtraining on your body.
Also, read:
- 15 Foods To Eat When Sick And You Don’t Have An Appetite
- 25 Easy and Effective Ways to Suppress Appetite For a Healthy Living
- 13 Effective Ways To Increase Your Appetite For a Healthier Body
Conclusion
Keeping a balanced exercise schedule and fostering long-term health depends on identifying and treating the symptoms of overtraining. Some signs that the body is overworked are: mood swings, insomnia, loss of appetite, chronic soreness, decreased performance, and persistent fatigue. Healthy habits like adequate recovery periods, a balanced diet, regular sleep, and stress reduction are essential to preventing and combating overtraining.
Stay on your fitness journey and avoid the pitfalls of overtraining by listening to your body and implementing some of these strategies in your daily routine. Remember, attaining the best possible outcomes and maintaining general well-being requires a balanced approach to exercise.
We encourage you to explore our other articles for additional wellness and fitness guidance as you proceed to a more balanced, healthier lifestyle.
In this Article