Affiliate Disclaimer
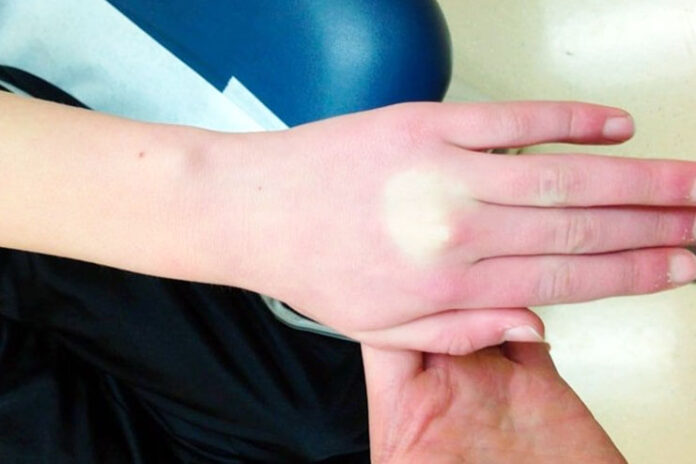
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersBlanching skin occurs when pressure applied to the skin lightens or whitens it temporarily. It indicates that there is a reduction in the amount of blood that is flowing into the area. This reaction occurs when the skin loses its natural color, turning pale when squeezed and reverting to its regular hue as the pressure is released.
Blanching skin can be an indication of underlying diseases such as poor circulation, vascular disorders, or skin infections, and medical diagnostics may be needed to have a thorough understanding of the causes of blanching skin.
The ability to recognize skin blanching can assist medical personnel in accurately diagnosing and managing these illnesses in a timely fashion. .
Causes of Blanching Skin
Skin blanching might be caused by several underlying conditions, including vascular problems, allergic reactions, and systemic disorders.
Vascular Issues: Blanching can be caused by vascular issues such as Raynaud’s disease or Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), which pertain to the circulatory system. Raynaud’s disease causes blood vessels to spasm, restricting blood flow and leading to pale skin, particularly in the fingers and toes. In patients with PAD, arteries become constricted, which reduces blood flow to the limbs and causes blanching, mainly when pressure is applied.
Allergic Reactions: As part of the body’s inflammatory response, blanching can be a symptom of allergic reactions. Contact dermatitis, caused by exposure to allergens or irritants, can produce this reaction. For instance, coming into contact with poison ivy or using some cosmetics on sensitive skin can cause a reaction in which the skin that is affected becomes pale when it is subsequently touched.
Systemic Diseases: Diseases that affect the entire body, such as anemia, characterized by a lack of red blood cells, can cause generalized blanching because of a decrease in the amount of oxygen delivered to the tissues. Furthermore, severe infections or septic shock can induce widespread blanching because the body shifts blood flow to critical organs, leaving peripheral skin pale.
It is important to understand these factors to diagnose and treat the underlying diseases.
Symptoms Associated with Blanching Skin
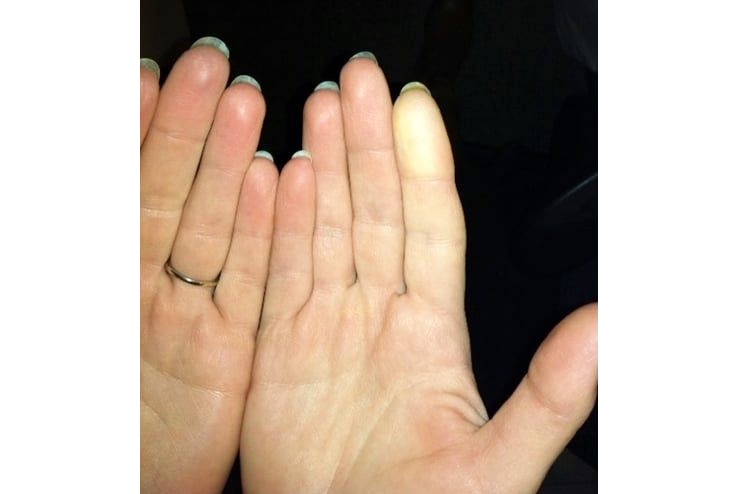
Various symptoms frequently accompany the appearance of blanching skin, which might help determine the underlying problem. Typical symptoms include:
A Pale Appearance: The most obvious symptom is a pale or white appearance of the skin when pressure is applied to the affected area. This is one of the most important indicators of decreased blood flow to the area.
Skin Sensitivity: Affected parts of the skin may become more sensitive to pressure, temperature changes, or touch sensations.
Coldness: The skin may feel colder than the surrounding parts due to diminished blood flow. This sensation almost always occurs in conjunction with blanching.
Numbness or Tingling: It is typical for illnesses such as Raynaud’s Disease to cause a tingling or numbing feeling in the afflicted area. Reduced blood flow can cause the affected area to feel numb or tingly.
Delayed Color Return: Once released, the skin may take longer to regain its usual color, indicating potential vascular difficulties.
To effectively identify these symptoms, it is necessary to observe the appearance of the skin in response to the application of pressure, taking note of any changes in color, temperature, and sensitivity. Recognizing these indications is essential for making an early diagnosis and effectively managing the condition’s underlying cause.
Diagnosis of Blanching Skin
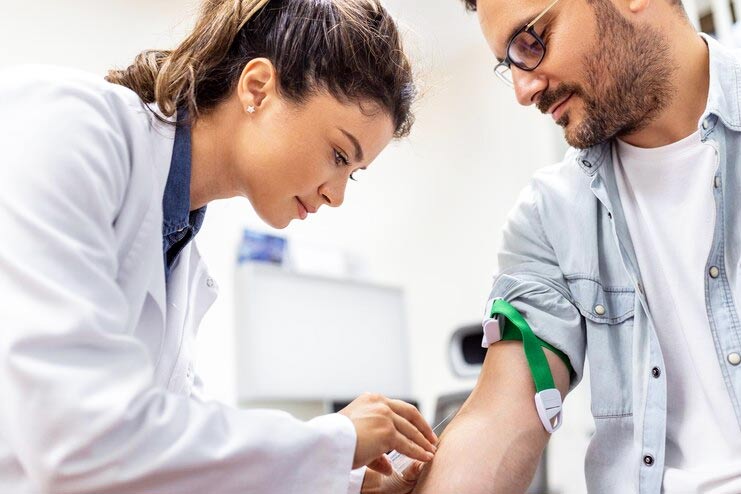
The diagnosis may include several medical procedures to effectively identify the underlying reason for blanching skin.
Medical History and Physical Examination: Doctors first conduct a comprehensive medical history and a physical examination of their patients. During this process, they will evaluate the skin’s response to pressure and note any accompanying symptoms, such as a change in sensitivity, numbness, or extreme coldness.
Blood Tests: Several systemic disorders, including anemia and infections, can cause blanching, which healthcare providers can identify through blood tests.
Imaging Tests: Doppler ultrasound and angiography are two imaging tests that can evaluate blood flow and identify vascular problems, such as Peripheral Artery Disease.
Allergy Testing: If an allergic reaction is detected, skin prick tests or patch tests can help determine the precise allergens responsible for the symptoms.
Biopsy: A skin biopsy is a procedure that may be carried out in certain circumstances to evaluate the tissue for any indications of disease or infection.
Subsequent professional evaluation and diagnostic testing are essential to determine the precise reason behind skin blanching. An accurate diagnosis ensures the provision of appropriate therapy, which in turn helps to avoid problems and promotes improved health outcomes.
Treatment Options for Blanching Skin

Both non-medical and medical treatments can treat blanching skin, depending on the underlying reason.
Non-Medical Treatments: Alterations to one’s way of life and home cures are examples of non-medical treatments that can significantly alleviate symptoms.
For vascular conditions such as Raynaud’s disease, it is essential to maintain a warm body temperature and avoid stress. Elevating the affected limb and engaging in light to moderate workouts can increase circulation.
Using products that are gentle and hypoallergenic, as well as hydrating to the skin, can help alleviate the symptoms produced by contact dermatitis.
Medical Treatments: When lifestyle modifications are not adequate, it may be necessary to seek medical assistance.
Some disorders, like Peripheral Artery Disease, can be treated with medications like vasodilators, which enhance blood flow.
Antihistamines and corticosteroids are two medications that can help minimize allergic responses and inflammation.
When the condition is severe, it may be necessary to undergo surgical procedures such as angioplasty or bypass surgery to restore blood flow.
Potential Outcomes and Prognosis: In terms of potential outcomes and prognosis, the prognosis varies depending on the underlying cause as well as the efficiency of the therapy treatment.
For mild cases, non-medical treatments may provide relief, whereas medical treatments can control more severe diseases.
Diagnoses and treatments that are administered at an earlier stage often result in better outcomes, reducing the likelihood of problems and improving the quality of life. It is crucial to maintain regular follow-up appointments with healthcare experts to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments to treatment.
Prevention Strategies

Taking preventative steps and adjusting one’s lifestyle to reduce risk factors can prevent skin blanching.
Tips to Prevent Blanching Skin: The most important thing is to keep your skin in good health overall. When you moisturize your skin regularly, it stays hydrated and is less likely to become irritated. When exposed to cold weather, avoiding illnesses such as Raynaud’s disease is possible by wearing protective gear. It is possible to limit the risk of contact dermatitis, which can result in blanching, by avoiding contact with recognized allergens and irritants.
Modifications to one’s lifestyle: Adopting healthy routines can considerably reduce the likelihood of developing conditions that cause skin to become pale.
Exercising regularly promotes circulation, which is beneficial to vascular health.
A well-balanced diet that is abundant in iron, vitamins, and antioxidants benefits the overall health of the skin and blood vessels.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation can help prevent vascular disorders caused by stress. Read More: Spirituality For Stress Relief ! What’s The Tie-In? Awaken Your Mind!
Smoking interferes with blood flow and makes vascular diseases worse, quitting smoking is a critical priority.
Practices to Reduce Risk Factors: Routine skin check ups can assist in detecting early indicators of underlying disorders, which is one of the practices that can help reduce risk factors.
The maintenance of a healthy weight and the management of chronic illnesses such as diabetes and hypertension are also essential.
Implementing these preventive techniques can help individuals reduce the likelihood of blanching skin and its associated difficulties, resulting in improved skin and vascular health over the long run.
When to Seek Medical Advice

With blanching skin, it is essential to be aware of when to seek medical guidance to facilitate early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Indications that professional medical consultation is required include the following: It is necessary to see a physician if skin blanching continues and does not improve with the application of simple treatments. If blanching is followed by acute pain, numbness, or tingling, a primary vascular disease may occur. Evaluation by a medical professional is also necessary for changes in the skin, such as ulcers, sores, or discoloration. In addition, seek a healthcare practitioner if systemic symptoms such as weariness, dizziness, or fever accompany blanching.
Seek immediate treatment based on experiencing these symptoms: Abrupt and severe blanching requires immediate medical attention, particularly if it affects significant regions of the body or is linked with signs of shock, such as a rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, or confusion. Blanching that is the result of a combination of these factors is highly dangerous. The presence of these symptoms may be an indication of serious illnesses, such as acute infections or vascular obstructions, which call for immediate medical attention.
Conclusion
Blanching skin, characterized by a brief whitening or lightening when pressure is applied, can indicate a variety of underlying disorders, such as vascular abnormalities, allergic reactions, and systemic diseases.
For early diagnosis, it is essential to be aware of the symptoms, including a persistently pale look and skin sensitivity. Depending on the underlying cause, the treatment may involve anything from alterations to one’s way of life to medical procedures. To mitigate this risk, take preventative measures such as ensuring adequate circulation and avoiding allergens.
If blanching persists or is accompanied by severe symptoms, seek medical assistance immediately. The timely identification and treatment of a condition are crucial components in ensuring efficient management and improved health outcomes.
-
Sep 2018Written by Somapika D
-
July 2024Edited by Ankita