Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersSevere head injuries necessitate immediate actions, medical treatment, and emergency response to minimize risks and complications. Prompt and adequate action is vital in a brain injury. Because the brain is the body’s control center, damage to it can have serious repercussions, including concussions, fractured skulls, and traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Carelessly or slowly handling a head injury might worsen it, resulting in permanent neurological problems, cognitive deficits, or even potentially fatal situations. Knowing what to do immediately after a head injury will make a big difference in recovery.
1. Assess the Situation

When a head injury occurs, the first and most important step is to conduct an initial evaluation to assess the severity of the injury.
- Initiate the process by determining the individual’s level of consciousness.
- Before proceeding to subsequent tests, it is essential to ensure that the individual is breathing and that they have a pulse if they are unconscious.
- For conscious people, assess their awareness by asking them straightforward questions to determine their direction and coherence.
The early symptoms of head trauma include confusion, dizziness, and obvious bleeding from the face or scalp. It is essential to look for these symptoms.
It is important to look for further indications of trauma, such as bruising, swelling, or fluid pouring from the nose or ears. A detailed assessment of the injury’s severity is necessary to provide the best potential outcome for the injured party.
2. Call for Emergency Help

If you or someone around you have sustained a significant head injury, it is imperative to contact emergency services as soon as possible to guarantee that you receive fast medical assistance.
- Make a prompt call to 911 or the number for your local emergency services. When communicating with those who are responding to an emergency, it is essential to convey information that is both clear and concise.
- Mention that the individual has suffered a head injury, describe the individual’s current state of consciousness, and note any symptoms noted during the initial evaluation, such as bleeding, confusion, or dizziness.
- In addition, make sure they are aware of any obvious consequences of the trauma, such as swelling or bruises.
- Make it abundantly clear where the incident took place and offer any pertinent information regarding the manner in which the injury was sustained.
Calling for expert medical aid as soon as possible assures the injured individual that they will receive the appropriate care and raises the possibility of a positive outcome.
Next read: 7 Best Antiseptics for Open Wounds: A Comprehensive Guide
3. Stabilize the Head and Neck
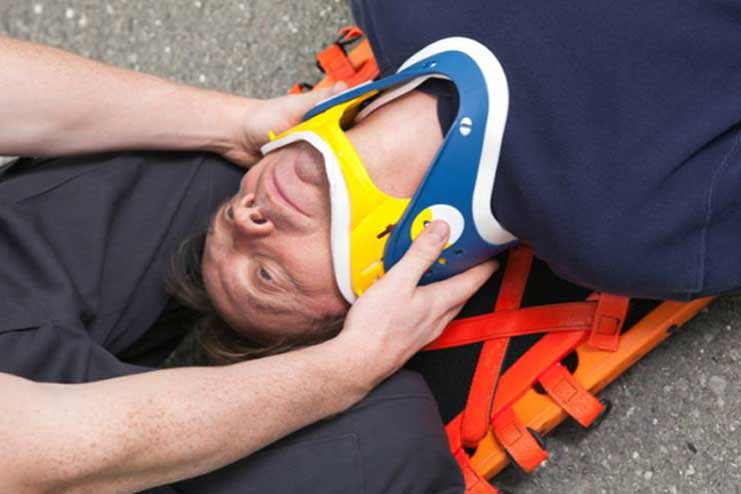

Stabilizing the victim’s head and neck is essential to preventing additional injuries after requesting emergency medical help, especially if a spinal injury is suspected. It is crucial to keep the injured person still to avoid aggravating any possible brain or spinal damage.
- First, tell the person to avoid making needless movements and stay as still as possible.
- If the person is in a lying posture, place your hands lightly on either side of their head to keep it in a neutral position and line with their spine.
- Use temporary supports to immobilize the head and neck further safely. Roll-up clothes or towels on either side can keep the head in place.
- Refrain from relocating the person unless it is really necessary, like in an emergency situation.
- To avoid twisting or bending, ensure the head and neck are supported and moved together when necessary.
Preventing movement of the head and neck is essential to managing head trauma and probable spinal injury, as well as lowering the likelihood of any consequences until professional medical assistance comes.
Read more: 7 Best Products to Make Life with MS a Little Easier
4. Control Bleeding
One of the most important parts of brain injury first aid is controlling bleeding. Initial treatment measures such as wound care and bleeding control are vital since they can significantly impact the wounded person’s recovery and prevent further problems.
- Using a clean towel or bandage, apply light pressure to the wound to start managing bleeding.
- If a clean cloth isn’t available, use any clean, absorbent material to cover the wound and apply pressure.
- To assist in controlling bleeding, apply steady pressure without applying too much effort, as this could worsen the wound.
- If blood seeps through the bandage or fabric, apply another layer without removing the previous one to keep the pressure in place.
- Continue to monitor the injuries and be ready to apply more pressure as needed until emergency medical assistance arrives.
Managing bleeding and reducing the chance of infection is critical. Make sure your hands are clean before touching the wound, and if feasible, use gloves or a makeshift barrier to keep your hands away from the blood.
Your main objective at this point should be to control the bleeding. Do not try to clean the incision excessively, and avoid any unsterilized items that can contaminate the wound with bacteria.
Next read: Sweat It Out: 12 Compelling Reasons Why Physical Activity Is Your Best Medicine
5. Monitor Vital Signs
While waiting for medical aid, it is essential to monitor vital signs to manage a brain injury effectively.
- It is crucial to ensure the injured person is stable by regularly checking breathing, pulse, and level of awareness.
- Observe the rise and fall of the chest and listen for any breathing anomalies to track them. You can check the wrist or neck for a consistent and regular beat to check the pulse.
- Assess the individual’s responsiveness by asking them questions in a kind manner or by giving them straightforward directions.
- Please note any shifts in their level of consciousness, such as an increase in perplexity or a lack of energy.
Continuous observation is essential; any rapid changes in vital signs could indicate a worsening condition and should be reported to emergency services as soon as they arrive.
Regularly monitoring vital signs allows you to supply critical information to medical personnel, enabling them to provide more effective care to patients. When dealing with a head injury, one of the most important aspects of first aid is ensuring the patient’s respiration, pulse, and responsiveness stay steady.

6. Avoid Giving Food or Drink
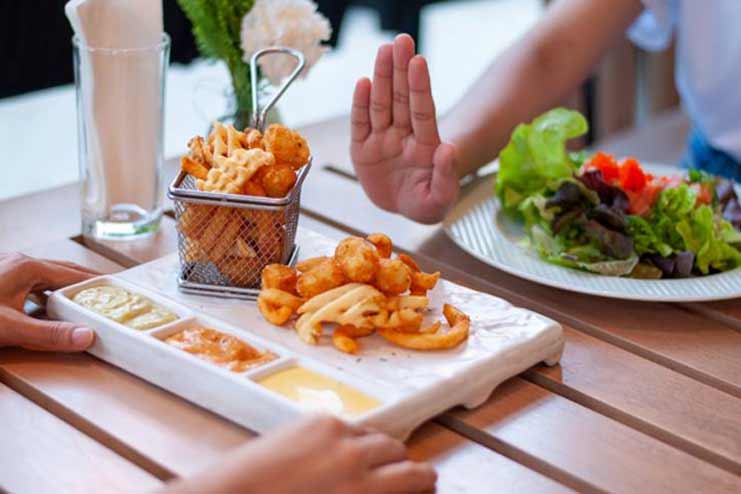

Immediately following a head injury, it is essential to refrain from providing the injured individual with food or drink. If the client is experiencing nausea or vomiting, which are frequent symptoms following a head trauma, offering food or drink might increase the aspiration risk of choking. This is especially true if the individual is experiencing these symptoms.
If the injured person is unconscious or has a diminished level of consciousness, there is a considerable chance of aspiration. Aspiration is when food or liquid enters the lungs rather than the stomach. It can result in serious problems such as pneumonia or airway obstruction.
In addition, if the individual needs surgery or other medical treatments, having food or drink in their system can make these processes more difficult to complete. As a result, it is of the utmost importance to refrain from consuming any food or drink until medical specialists can assess the situation and provide the necessary care.
Ensuring the injured individual does not consume food or drink reduces the risk of aspiration and other complications, contributing to a safer and more successful rehabilitation process.
7. Provide Comfort and Reassurance
After a brain injury, it is critical to offer the afflicted individual comfort and reassurance to help them recover. Staying calm and maintaining your own composure is of the utmost importance since it assists in calming and stabilizing the injured person, lowering their anxiety and panic.
- Communicate with them in a soft and soothing manner, assuring them that assistance is on its way and that they are not alone in this situation.
- While the individual is waiting for emergency services, it is essential to ensure they remain motionless and in a secure posture to retain as much comfort as possible.
- If lying down, they should maintain a slight elevation of their heads, provided that doing so does not cause discomfort.
- You should keep them warm by covering them with a blanket and providing them with vocal comfort to keep them quiet.
- Refrain from sudden movements or loud noises for fear of startling them.
The injured person is comforted by maintaining a cool demeanor and providing reassurance, which not only helps control the situation more successfully until professional medical assistance arrives but also comforts the situation.
8. Recognize Signs of Serious Injury

Identifying the symptoms of a severe head injury is essential to guarantee a timely and suitable response from the emergency response.
- Be on the lookout for signs that may indicate severe trauma, such as loss of consciousness, which may indicate a concussion or a more severe brain injury.
- In some cases, an intense headache that worsens over time may indicate internal bleeding or increased pressure surrounding the brain.
- Vomiting is another sign of significant head trauma that requires prompt medical attention. This is especially true if the vomiting occurs repeatedly.
- In addition, the appearance of clear fluid draining from the nose or ears may indicate a skull fracture and a leaking of cerebrospinal fluid, both of which are severe illnesses.
If these severe injury signs are present, you must take immediate action to ensure that the wounded individual receives prompt medical attention. Contact emergency services immediately and provide specific information about the experienced symptoms.
Maintain as much stillness as possible while continuing to monitor the individual’s vital signs and check their state of consciousness. Not only should you refrain from providing them with any food or drink, but you should also refrain from moving them unless they are in imminent danger.
Recognizing and responding to any of these signs promptly can considerably impact the prognosis of the wounded individual, ensuring that they receive essential medical assistance as quickly as possible.
Conclusion
Quick action and proper emergency measures are essential to avoid further difficulties and guarantee the best possible outcome in the event of a brain injury. The most important actions are to stabilize the head and neck to prevent movement.
Check for symptoms of trauma, respiration, and consciousness, summon emergency services right away, contain any bleeding with mild pressure, and continuously monitor vital signs. In addition, wait for expert assistance and offer the injured individual comfort and reassurance while avoiding providing them food or drink.
Recognizing signs of serious injury, such as loss of consciousness, severe headache, vomiting, and fluid from the nose or ears, is also essential. Following these head injury response guidelines can significantly help the injured person’s recovery and overall prognosis.
-
Aug 2024Written by Ankita
-
Feb 2025Edited by Ankita
References
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-head-trauma/basics/art-20056626
- https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/injury/head-injury-first-aid
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000028.htm
- https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/head-and-spinal-injuries-first-aid
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322225#when-to-see-a-doctor
- https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/injuries/head-and-neck-injuries/severe-head-injury/
- https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/traumatic-brain-injury-what-know-about-symptoms-diagnosis-and-treatment
- https://www.chkd.org/our-services/emergency-care/when-to-call-911/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1250254/
- https://healthcare.utah.edu/healthfeed/2016/11/why-do-head-injuries-bleed-so-much
- https://www.nyp.org/healthlibrary/articles/how-to-stop-bleeding-from-a-head-wound
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6167472/
- http://www.tbi-impact.org/cde/mod_templates/T_12.1.%20Vital%20Signs.pdf
- https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/injuries-and-poisoning/head-injuries/overview-of-head-injuries
- https://www.uofmhealth.org/conditions-treatments/brain-neurological-conditions/concussion-treatment-and-recovery
- https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/head-injuries-and-concussion
- https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007/978-3-642-00418-6_862
- https://www.mayo.edu/research/documents/helping-with-brain-injurypdf/DOC-10027100
- https://ajcasemanagement.com/help-someone-traumatic-brain-injury/
- https://www.flintrehab.com/how-to-talk-to-a-person-with-brain-injury/
- https://neuliferehab.com/8-ways-to-support-a-loved-one-with-brain-injury/
- https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/head-injuries
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/traumatic-brain-injury/symptoms-causes/syc-20378557
- https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/injuries/head-and-neck-injuries/severe-head-injury/
- https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/traumatic-brain-injury-tbi