Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersSkin conditions such as hives and rashes are common and difficult to distinguish. Both can cause discomfort and concern, yet their causes and treatments can differ significantly. Understanding whether you are experiencing hives or a rash is crucial for effective treatment and relief. In this guide, we identify the differences between hives and rashes, understand their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment, and discuss when it’s essential to seek medical advice.
Understanding Hives
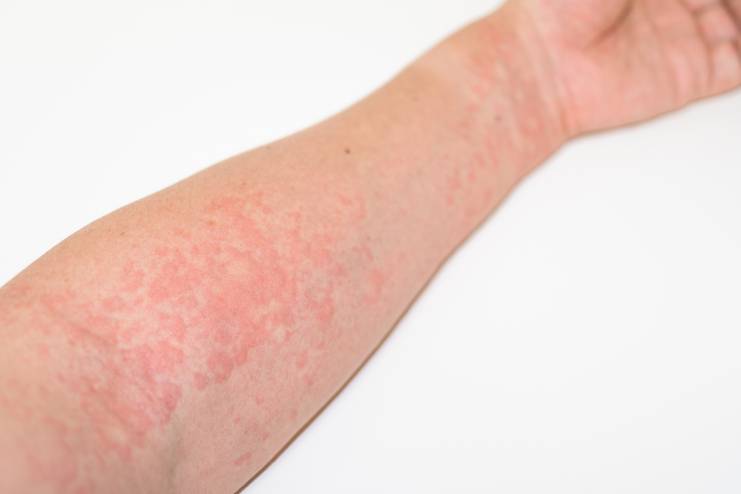
Urticaria, or hives, is a common form of a rash consisting of itchy, swollen, pale red, or even skin-colored bumps that come up suddenly and resolve quickly. The bumps vary in size and shape and run from small pinpoint dots to large map-like patches.
Causes of Hives
Many cases of urticaria occur for non-allergic reasons. These include:
- Allergies: Foods (nuts, chocolate, fish, tomatoes, eggs, fresh berries, and milk), medications (aspirin, NSAIDs, ACE inhibitors), insect bites, and latex.
- Physical Stimuli: Pressure, cold, heat, exercise, or sun exposure.
- Infections: Colds, infectious mononucleosis, hepatitis, urinary tract infections, and strep throat.
- Other Factors: Blood transfusions, chemical additives in foods, and underlying diseases such as thyroid disease, cancer, or hepatitis.
Symptoms of Hives
The primary symptoms of hives include:
- Itching
- Swelling
- Formation of red welts
Welts vary in their size and shape and often merge to form larger plaques. Hives are either acute, lasting less than six weeks, or chronic, lasting more than six weeks.
Angioedema is similar to hives, but it is the swelling that occurs deeper in the skin. It can occur around the eyes, lips, genitals, hands, or feet. If it causes swelling around the throat or lungs, it can be fatal by restricting the airway.
The most recommended treatment for urticaria is antihistamines. Histamine is the chemical responsible for causing inflammation, swelling, and itching. Cold compresses or anti-itch salves applied to the affected area reduce symptoms. Understanding the characteristics and causes of urticaria permits one to cope with this and provide relief.
Understanding Rashes
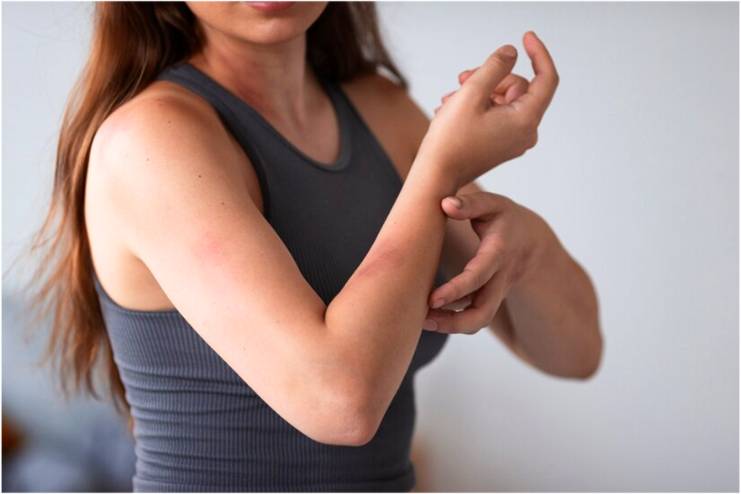
Skin rashes are irritated areas of skin. These are characterized by small, itchy, red bumps. Sometimes the skin breaks from scratching. Blisters form in certain types of rashes.
Causes of Rashes
The causes of rashes are diverse and include:
- Allergies: Reaction to foods, medications (e.g., amoxicillin, sulfa drugs), or plants (e.g., poison ivy).
- Chafing: Skin irritation from friction.
- Chemical Exposure: Contact with irritating substances.
- Infections: Caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi.
- Insects and Animals: Bites or stings from insects, spiders, or jellyfish.
- Autoimmune Conditions: Such as psoriasis.
- Environmental Factors: Sunlight exposure.
Skin rashes can be different in appearance and severity. Some rashes manifest suddenly, while others take time and may appear over several days.
Symptoms of Rashes
Common signs and symptoms associated with rashes include:
- Redness
- Inflammation
- Different textures on the skin areas
Treatments for rashes depend on the cause and may include:
- Moisturizers and lotions to soothe and hydrate the skin
- Corticosteroid creams to relieve redness and swelling.
- Antihistamines to alleviate itching and redness.
Monitor rashes. If they persist for more than a few days, are severe, or are accompanied by other concerning symptoms, seek medical advice. Diagnosis of underlying causes of rash is very important for treatment and management.
Key Differences Between Hives and Rashes
Hives are usually allergic reactions characterized by rapidly appearing itchy bumps, while rashes encompass a broader range of skin changes caused by various factors.
| Characteristics | Hives | Rashes |
| Appearance | Red or flesh-toned bumps, change size/shape, blanch when pressed | Red, bumpy, scaly, rough, may have blisters or welts |
| Duration | Hours to days; chronic can last longer | Days to weeks |
| Causes | Allergies, stress, infections, environmental factors | Allergies, infections, autoimmune conditions, irritants |
| Symptoms | Intense itching, clusters of bumps, red/swollen skin | Itching, pain, irritated/raw skin, blisters |
Progression and Treatment
Hives commonly appear shortly after exposure to a trigger. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is key to the management of hives. Oral antihistamines, corticosteroid creams, and cool compresses are the common drugs used to treat this. Various prescription drugs, such as omalizumab, help manage chronic urticaria.
Rashes take time to develop and can be localized or generalized. Treatment depends on the cause and involves application of moisturizers, topical steroids, oral antihistamines, and avoiding irritants. Severe rashes require prescription medications.
When to See a Doctor
It is important to know when to see a doctor for hives or rashes. Some symptoms require immediate attention:
- Severe Symptoms: See a doctor if itching, pain, or discomfort is severe, disrupting daily activities or sleep, especially when over-the-counter treatments don’t provide relief.
- Prolonged Duration: See doctor when hives and rashes persist for many days or keep recurring despite treatment. Chronic or long-lasting symptoms might indicate underlying health issues.
- Spreading: See the doctor if the rash or hives begin to spread rapidly or cover a large area of your body. This could signal a more serious condition as well.
- Signs of Infection: Watch for symptoms such as increased redness, swelling, pain, or fluid discharge from the rash area. These signs suggest a possible infection.
While most rashes are not considered a medical emergency, hives can sometimes be a sign of anaphylaxis, a severe or life-threatening allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention. Call for emergency medical care if you experience:
- Difficulty breathing
- Lightheadedness
- Swelling of your face or tongue
- Feel that your throat is closing
A physician can diagnose and treat rashes and hives. Professional diagnosis and treatment are important for symptom management and the prevention of potential health issues.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Accurate diagnosis and effective treatment are important for managing hives and rashes. Here’s an overview of common diagnostic methods and treatment options.
Diagnosis of Hives and Rashes
- Physical Examination: Doctors begin by examining the affected skin and asking about symptoms, medical history, and possible exposure to allergens or irritants.
- Allergy Testing: For hives, allergy testing may be suggested to identify specific triggers. This may involve skin prick tests or blood tests.
- Skin Biopsy: A small sample of skin may be taken for laboratory analysis.
Treatment for Hives
- Antihistamines: These medications, such as cetirizine (Zyrtec) or diphenhydramine (Benadryl), help relieve itching and reduce hives.
- Corticosteroids: For severe cases, oral corticosteroids like prednisone may be prescribed to reduce inflammation.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding allergens or irritants that cause hives is crucial. This can include changes in diet, environment, or medications.
- Omalizumab: For chronic hives unresponsive to other treatments, an injectable medication called omalizumab (Xolair) may be recommended.
Treatment for Rashes
- Topical Treatments: Depending on the type of rash, topical creams or ointments such as corticosteroids or antifungal agents can reduce symptoms.
- Medications: Oral medications, including antihistamines and antibiotics, might be prescribed for severe or infected rashes.
- Addressing Underlying Conditions: Effective management often involves treating the underlying condition causing the rash, such as eczema or psoriasis.
Specific Treatments for Different Types of Rashes
- Atopic Dermatitis: Management includes over-the-counter anti-itch medications, gentle moisturizers, and avoiding known triggers.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Special shampoos or antifungal treatments can reduce flaking and scaling.
- Contact Dermatitis: Avoiding the triggering substances and using medications to relieve discomfort during flare-ups are essential.
Conclusion
Understanding hives and rashes is essential for managing them. These skin conditions range from mildly frustrating to very disturbing and require correct identification and proper treatment. Recognizing symptoms like severe, long-lasting, and spreading rashes, and those that signal infection will help in timely treatment. Diagnostic measures include physical examinations, allergy testing, and skin biopsies to determine the cause. Treatment options range from antihistamines and corticosteroids to topical ones and treatment of underlying health problems. It’s important to seek medical advice when necessary to ensure proper care and avoid complications.
References
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/hives-vs-rash
- https://www.drugs.com/medical-answers/difference-between-hives-rash-3505373/
- https://www.healthline.com/health/hives-vs-rash
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8630-hives
- https://www.health.com/hives-vs-rash-8659152
- https://www.medicinenet.com/are_hives_and_rash_the_same_thing/article.htm
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/hives-vs-rash-7111822
In this Article



















