Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersManaging high blood pressure is crucial in maintaining overall health and preventing severe cardiovascular complications. Lifestyle factors greatly contribute to hypertension; therefore, you need to understand how diet, exercise, and other habits affect blood pressure regulation.
Making informed decisions will help you regulate your blood pressure effectively, prevent heart disease risks, and improve your quality of life. In this article, we will explore what blood pressure is, key dietary recommendations, lifestyle modifications, and some simple natural remedies that help control blood pressure levels without medication.
What is Blood Pressure?
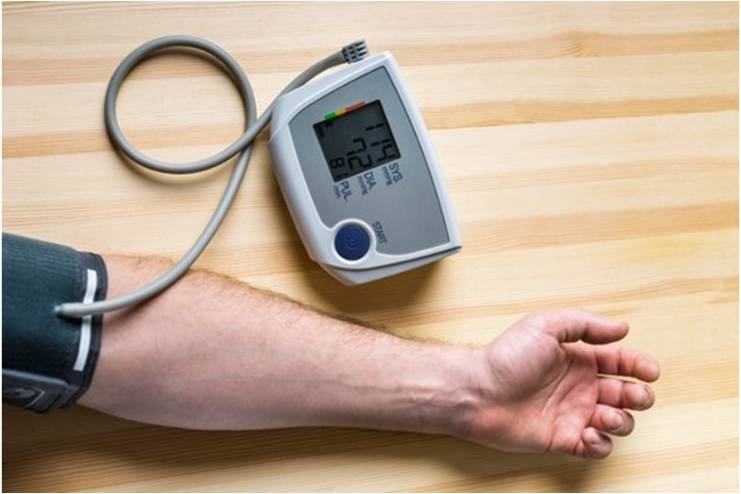
Blood pressure measures the force of blood against the walls of your arteries and is expressed in two numbers: systolic pressure (the higher number) and diastolic pressure (the lower number). Healthy blood pressure is generally around 120/80 mm Hg.
High blood pressure puts extra strain on your arteries and heart, which can lead to several health issues. When blood pressure is consistently high, it can damage the inner lining of your arteries, leading to a condition called atherosclerosis. This means your arteries become narrowed and hardened due to the buildup of plaque, which can restrict blood flow. This damage increases the risk of heart attack and stroke because the heart has to work harder to pump blood, and clots can form more easily.
High blood pressure can also lead to heart failure, where the heart struggles to pump blood effectively. Additionally, high blood pressure can affect other organs. It’s a major risk factor for kidney disease and can contribute to vision problems due to damage to the blood vessels in the eyes. According to the American Heart Association, long-term high blood pressure can also increase your risk of developing dementia, as it can lead to damage to blood vessels in the brain.
Why Natural Methods Are Ideal
While medication can help lower blood pressure, it’s not always the best first step. Natural methods and lifestyle modifications such as diet, exercise, and stress management address the root causes of high blood pressure and offer broader health benefits rather than just masking the symptoms.
Moreover, many hypertension medications can cause unwanted side effects, whereas lifestyle changes generally enhance the quality of life.
So, let’s dive into how you can lower your blood pressure without medication.
Dietary Recommendations

A heart-healthy diet is key for controlling blood pressure. The right foods can significantly impact hypertension, while poor dietary choices can worsen the condition.
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension also called the DASH diet, recommends consuming more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while reducing sodium intake. To promote optimal heart health, incorporate the following foods into your diet:
1. Vegetables and Fruits
A diet rich in fruits and vegetables provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which help lower blood pressure. Foods like berries, leafy greens, beets, and bananas are particularly beneficial due to their high potassium content. Potassium helps balance sodium levels in the body, which can lower blood pressure by easing tension in blood vessel walls.
2. Whole Grains
Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole-wheat bread are high in fiber, which is essential for a healthy heart. Fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels and can support weight loss. Studies show that high-fiber diets are associated with lower blood pressure and reduced risk of heart disease.
3. Include Low-Fat Dairy Products
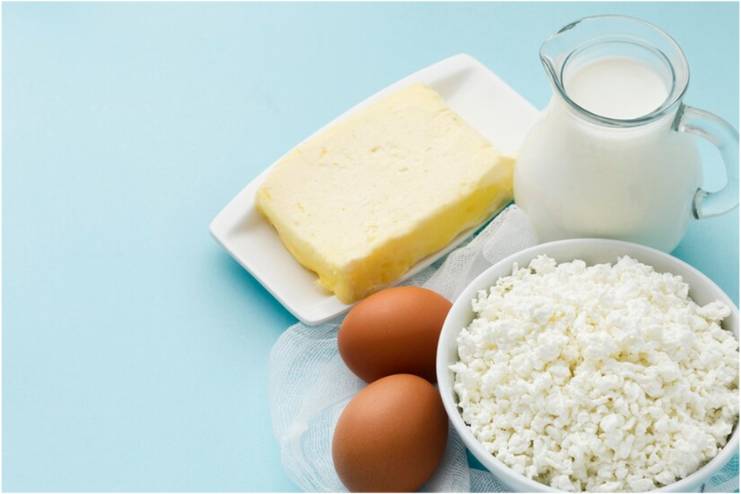

Good sources of calcium and vitamin D, essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure, include low-fat dairy products like yogurt and milk. Calcium helps blood vessels tighten and relax, which is important for blood pressure regulation. Research has shown that higher dairy intake is linked to lower blood pressure.
4. Opt for Lean Proteins
Incorporate lean protein sources like skinless poultry, fish, beans, and legumes into your diet. Fatty fish, such as salmon and mackerel, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to reduce blood pressure and improve heart health by reducing inflammation and lowering triglyceride levels.
5. Limit Sodium Intake
Reducing sodium intake is a key strategy for lowering blood pressure. High sodium levels can cause the body to retain water, increasing blood volume and pressure. The CDC recommends limiting sodium to less than 2,300 mg per day (ideally 1,500 mg for those with high blood pressure) (R).
- Read Food Labels: Check nutrition labels for sodium content and opt for low-sodium or no salt-added versions of foods when possible.
- Limit Processed Foods: Processed and packaged foods often contain high levels of sodium. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods to minimize sodium intake.
- Cook at Home: Preparing meals at home lets you control the ingredients and avoid hidden sodium found in restaurant meals and fast food.
6. Increase Potassium-Rich Foods
Potassium helps balance sodium levels in the body and can help lower blood pressure. Include potassium-rich foods such as:
- Bananas
- Sweet potatoes
- Spinach
- Beans
- Avocados
- Oranges
7. Incorporate Healthy Fats

Foods rich in healthy fats, like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, can positively impact heart health and cholesterol levels. Healthy fats can help reduce inflammation and improve blood vessel function. However, because they are calorie-dense, consume them in moderation.
8. Stay Hydrated
Good hydration is essential for overall health, including blood pressure regulation. Plan to drink plenty of water throughout the day and limit sugary beverages and excessive caffeine intake. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day supports vascular health and can help maintain normal blood pressure.
9. Foods to Include
- Unsweetened Yogurt
- Berries
- Beets
- Sweet Potatoes
- Leafy Greens
- Fatty Fish
- Whole Grains
- Pistachios
- Bananas
- Kiwifruit
10. Foods to Avoid
To effectively manage high blood pressure, limit or avoid these foods that can raise blood pressure levels. These include:
- Fatty and processed meats (e.g., hot dogs, sausages)
- Salted snacks (e.g., pretzels, potato chips)
- Canned soups and vegetables
- Fast food
- Whole-milk dairy products
- Foods high in saturated fats
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to dietary changes, several lifestyle modifications can have a strong impact on blood pressure management. The modifications can improve overall health and reduce the risk of hypertension-associated complications.
- Regular Exercise

Engage in regular physical activity. This is one of the most effective ways to lower blood pressure. At least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise each week can help keep your blood pressure level low. Heart-strengthening and circulation-improving activities like brisk walking, cycling, swimming, and jogging can help a great deal.
- Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy body weight is essential for blood pressure regulation. Excess weight puts additional strain on the heart and can elevate blood pressure. Even modest weight loss (5-10%) can lead to significant improvements in blood pressure.
- Stress Management
Chronic stress can contribute to high blood pressure. Engage in stress-reducing practices such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises to lower blood pressure. Finding time for hobbies and socializing also promotes relaxation and well-being.
- Adequate Sleep

Good-quality sleep is essential for overall health as well as blood pressure management. Healthy adults must sleep for 7-9 hours per day. Poor quality of sleep and sleep disorders such as sleep apnea can have negative effects on blood pressure. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and relaxing bedtime habits can help a lot.
- Limit Alcohol Intake
Even though moderate alcohol consumption is generally healthy, overindulgence can raise blood pressure. The American Heart Association limits alcohol for women to one drink a day and two for men (R).
- Avoid Smoking
Secondhand smoke and smoking may also raise blood pressure and damage blood vessels. Quitting smoking is likely the most important thing you can do for your heart. There are many resources and tools available that can help quit smoking.
- Monitor Blood Pressure
A home monitor is always helpful to check your health status, as it monitors one’s blood pressure. Recording your blood pressure readings is beneficial for healthcare providers to make the right therapeutic decisions and interventions for you.
Medication Adherence
Some patients need medications when lifestyle modifications don’t work. For these patients, adherence to medication becomes an essential lifeline so as not to complicate hypertension and related diseases. Dosage and timing must be strictly followed based on a healthcare provider’s suggestions, as missed doses may lead to blood pressure spikes.
Open communication is a must. Communicate with your healthcare professional when you have any side effects or concerns. Such a discussion will be useful in adjusting the treatment plans to suit your needs best, ensuring medications both work and are manageable.
Conclusion
Managing high blood pressure is one of the critical measures in the prevention of serious cardiovascular complications. Diet, including eating blood pressure-lowering foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy, combined with healthy lifestyle habits, can make a real difference in blood pressure levels.
Regular exercise, weight control, efficient methods of stress reduction, proper sleep, and fluid intake are some major changes you can make. Avoiding smoking and exceeding caffeine use would also contribute to better health in terms of cardiovascular status.
Remember, what appear to be small, consistent changes really can add up to make a difference over time. Always consult with healthcare professionals to tailor a plan that fits your unique needs. Adopting these strategies helps not just your blood pressure but also takes you to a healthier, more vibrant life.
References
- https://www.ncoa.org/article/10-foods-that-help-lower-blood-pressure-naturally/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/in-depth/high-blood-pressure/art-20046974
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318716
- https://www.healthline.com/health/high-blood-pressure-hypertension/lower-it-fast
In this Article