Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersThe pineapple, a tropical fruit, is renowned for its delicious sweetness and multiple positive health effects. Loaded with high concentrations of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, it helps digestion, strengthens the immune system, and improves overall health. It is a well-liked option for enhancing nutrition and assisting in the healing process after illness because of the high levels of vitamin C and the enzyme bromelain it contains. To assist you in enjoying this delectable fruit responsibly, we will discuss the potential adverse impacts that pineapple may have in this article.
Nutritional Profile of Pineapple
Pineapple is a fruit abundant in nutrients, providing a very wide variety of vitamins, minerals, and other valuable components to the body. One cup (165 grams) of pineapple chunks contains around 82 calories, 0.9 grams of protein, 0.2 grams of fat, and around 21.6 grams of carbohydrates, including 2.3 grams of dietary fiber. Additionally, pineapple chunks include 0.2 grams of healthy fat. Extremely high in vitamin C, it provides more than one hundred percent of the daily required intake, essential for the proper functioning of the immune system and the skin’s health. In addition, pineapple is a very rich source of vital minerals, including manganese, copper, and potassium, as well as considerable quantities of vitamin A, B6, thiamine, and folate.
Bromelain is a digestive enzyme with potent anti-inflammatory and proteolytic capabilities. Pineapple explicitly contains it as a unique component. In addition to assisting in the digestion of proteins and lowering inflammation, bromelain has been investigated for its potential benefits in healing wounds, maintaining healthy joints, and reducing the severity of infections. However, even though bromelain has many positive effects on health, it is also possible that it is responsible for some of the adverse effects of eating pineapple.
Common Side Effects of Pineapple
1. Throat Infections

When consumed, pineapple can sometimes cause throat pain or infections, characterized by symptoms such as soreness, swelling, itching, and a burning sensation. This is because of the firm acidity of the fruit and the presence of bromelain, an enzyme that can potentially irritate the fragile tissues found in the throat. In extreme circumstances, this irritation can act as a contributing factor in the development of minor infections, particularly in cases when the immune system is diminished.
Individuals who have a history of allergies to tropical fruits, recurrent acid reflux, or pre-existing throat disorders are at a higher risk than those who do not presently have any of these conditions. Individuals who have compromised immune systems may also be more prone to developing throat infections due to consuming pineapple.
There are preventative methods such as:
Moderation: Pineapple should be consumed in relatively small amounts to reduce the risk of irritation.
Ripe Pineapple: Choose fully ripe pineapples because they have a lower acidity level.
Eat Pineapple with Other meals: To reduce pineapple’s acidity, it is best to consume it with other meals.
Hydration: Drinking a lot of water after eating pineapple is essential to help wash away the acids and enzymes present in it.
Implementing the aforementioned precautions can reduce the chance of developing a throat infection after eating pineapple.
2. Oral Irritation and Burning Sensation
Eating pineapple could cause irritation to the mouth and tongue, as well as a burning sensation in the mouth. The discomfort is frequently related to two primary factors: acidity and bromelain.
Causes of irritation in the mouth and tongue include:
Acidity: Pineapple is naturally acidic, and when it comes in touch with the delicate tissues of mouth and tongue, the acidity of pineapple can irritate. Pineapple is a naturally acidic fruit.
Bromelain: Pineapple contains an enzyme called bromelain, which is beneficial to digestion and may be found in pineapple. On the other hand, it has the potential to irritate the mucous membranes of the mouth, which can result in a sensation that is either burning or tingling.
Role of Bromelain: Although bromelain is helpful for digestion, it can also cause discomfort in the mouth when ingested in high concentrations. Bromelain plays a role in this unpleasant sensation. This enzyme is responsible for the breakdown of the proteins, particularly those present in the lining of the mouth and tongue, which results in irritation and sensitivity.
A Few Suggestions to Alleviate Discomfort:
Combining Pineapple with Other Foods: Consuming pineapple with other foods, such as yogurt or cheese, can help reduce the effects of bromelain and acidity in the body.
Choose Ripe Pineapples: When they are fully ripe, they have lower levels of bromelain, which means they are less likely to cause oral discomfort.
Rinse Mouth: After dining on pineapple, it is recommended that you rinse your mouth with water to balance the acidity of the pineapple and remove any remnant of bromelain.
Consumption under Moderation: Consuming a smaller quantity of pineapple in a single sitting can lessen the severity of any potential pain.
If you follow these suggestions, you may reduce the amount of oral irritation you experience and still enjoy pineapple without experiencing substantial discomfort.
3. Digestive Issues
Sometimes, eating pineapple can cause digestive problems, such as an upset stomach or diarrhea, especially if it’s ingested in large amounts or by someone with a sensitive stomach.
Possibility of Inducing Diarrhea or Stomach Discomfiture: Pineapples are high in fiber, especially when eaten whole in pieces or slices. Even though fiber aids digestion, overeating can cause diarrhea or loose stools, particularly in people not used to eating a lot of fiber.
Pineapple’s Impact on Digestion: Apart from its high fiber content, pineapple also has an enzyme called bromelain that facilitates the breakdown of proteins. However, occasionally, bromelain can irritate the lining of the intestines and stomach, causing discomfort or upset in the stomach.
Advice for Those with Sensitive Stomachs:
Moderation: Eat pineapple in moderation, mainly if you are prone to digestive problems or have a sensitive stomach.
Keep an eye on the portion sizes: Be mindful of serving quantities and refrain from ingesting excessive pineapple at once.
Select Properly Ripped Pineapples: Choose completely ripe pineapples over unripe ones because the former are usually more accessible on the stomach.
Examine Alternative Formats: If eating a whole pineapple gives you stomach problems, you can handle pineapple juice or smoothies, which are also good options.
If they adhere to these guidelines, people with sensitive stomachs can still reap the advantages of pineapple while lowering their chance of experiencing any discomfort in their digestive system.
4. Bleeding Gums
After eating pineapple, bleeding gums can occasionally happen, especially in people with sensitive gums or pre-existing dental issues. Though pineapple’s acidic nature and high bromelain concentration don’t directly cause bleeding gums, they can aggravate pre-existing gum conditions or sensitive gum tissue.
Reasons:
Acidity: Pineapple’s acidic nature may impact the gums, which may irritate the gums if they are already sensitive or inflamed.
Bromelain: When pineapple enzymes come into touch with gum tissue, they can potentially irritate the gums.
Preventive Measures:
Rinse Mouth: After consuming pineapple, rinse your mouth with water to help offset the acidity and remove any lingering bromelain residue.
Aim to Reduce Direct Contact: Try to keep the pineapple and gums from coming into direct contact. Irritation is when chewing lowly and in a little piece; miniature pieces can minimize irritation. Hygiene: Brush and floss frequently to keep your gums healthy and lower your chance of bleeding. To prevent future irritation, consider using a toothbrush with soft bristles.
If bleeding gums continue or worsen after eating pineapple, you should see a dentist to rule out any underlying tooth problems.
5. Interaction with Medications

Certain drugs and pineapple may interact, possibly decreasing the effectiveness of the treatment or producing adverse side effects. The following are a few drugs that are known to interact with pineapple:
Blood Thinners: Bromelain, found in pineapples, may make bleeding more likely when used with aspirin or warfarin, two drugs that thin the blood.
Antibiotics: Bromelain may improve an antibiotic’s absorption, which could increase an antibiotic’s efficacy or adverse effects.
Hazards and Adverse Reactions of These Combinations:
Increased Risk of Bleeding: Bleeding, such as bruising, nosebleeds, or gastrointestinal bleeding, can occur when pineapple is used with blood thinners.
Modified Antibiotic Effects: The way bromelain interacts with antibiotics might impact how well they are absorbed and metabolized, which could change their effectiveness or raise the possibility of negative side effects.
Patients’ Medication Advice:
See Your Healthcare Provider: Patients who are on medication should always speak with a healthcare provider before ingesting pineapple or pineapple supplements.
Watch for any side effects: When taking medication with pineapple, watch out for symptoms or adverse reactions.
Modify Medication Dosage: Healthcare may need to modify medication dosages or regimens.
To guarantee safe and efficient treatment for any possible interactions with pineapple, patients should be transparent with their healthcare professionals about their eating habits and any worries about potential drug interactions.
6. Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
Consuming pineapple can impact blood sugar levels, so it’s crucial for people to watch how much they eat—especially those with diabetes. When taken, the natural sugars in pineapple, such as fructose and glucose, can quickly raise blood sugar levels.
The Impact of Pineapple Consumption on Blood Sugar:
Pineapple sugars are rapidly absorbed into the system, causing blood glucose levels to rise.
In addition, compared to other foods, pineapple has a high glycemic index, which means it can quickly raise blood sugar levels.
Diabetes Patients’ Consequences:
- Controlling blood sugar levels is very critical for people with diabetes. Significant blood sugar rises can occur when consuming pineapple alone or in large quantities.
- To help balance blood sugar levels, diabetics should watch portion sizes and consider eating pineapple with foods high in fiber or protein.
- After eating pineapple, people with diabetes can monitor the blood glucose levels to understand better how their bodies react and change their diet and medication schedule as needed.
- Diabetics should speak with a qualified dietitian or healthcare professional before including pineapple in their diet to effectively manage their blood sugar levels.
7. Tooth Decay
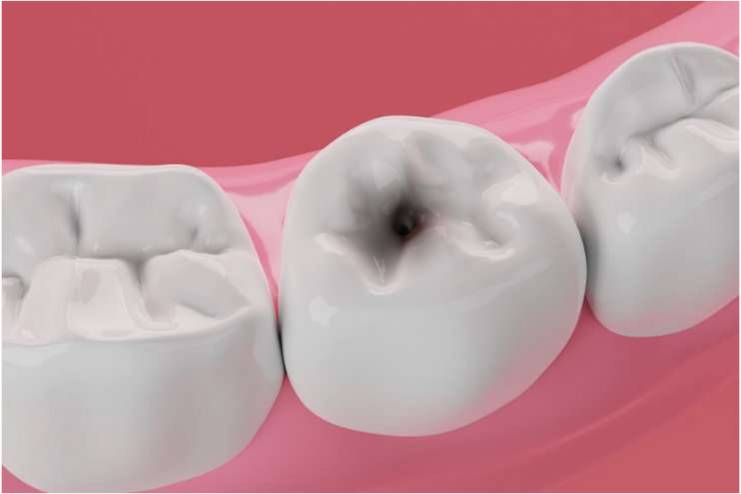
Pineapple consumption can exacerbate tooth decay, especially when consumed in very large quantities or concentrated forms like juice. Because pineapples are naturally sweet, their acidity can contribute to an environment favorable to tooth disease and enamel degradation. Over time, the acids in pineapple can erode tooth enamel, increasing the risk of the cavities and rotting in teeth. Consume pineapple in moderation and practice healthy oral hygiene, such as routine brushing and flossing and rinsing the mouth with water after eating acidic foods, to reduce the risk of tooth decay.
8. Kidney Problems
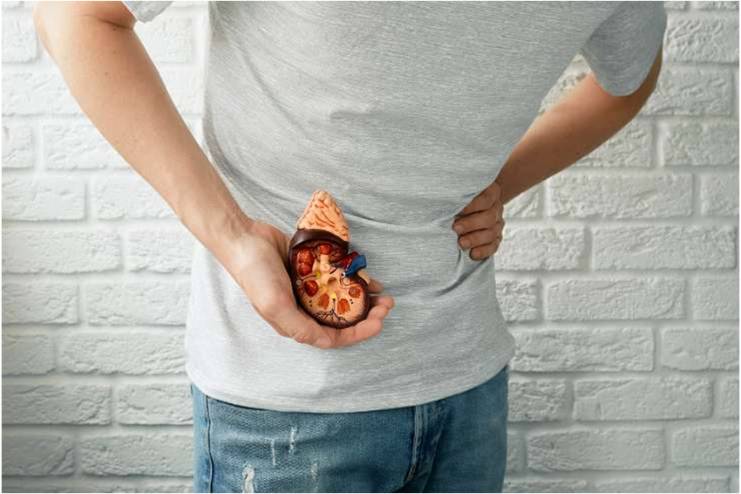
For the most part, pineapple is considered safe for ingestion; nevertheless, persons with kidney issues or kidney disease should exercise caution when consuming pineapple. On the other hand, pineapple has a considerable quantity of potassium, a mineral that might be problematic for people with severely damaged kidney function. The condition known as hyperkalemia, which occurs when there is an excessive amount of potassium in the blood, can put stress on the kidneys and make kidney function worse. Therefore, individuals with kidney issues or kidney disease should watch the amount of potassium they consume and get the advice of a healthcare practitioner before introducing pineapple into their diet. To keep kidney health in good condition while enjoying pineapple in moderation, it is vital to follow the advice and suggestions of medical professionals.
9. Effects During Pregnancy

Although pineapple is generally safe to eat while pregnant, too much of it can be dangerous because of the bromelain it contains; the use of bromelain has been linked to cervical softening and possible uterine contractions, which may cause early labor or miscarriage. Because unripe pineapple has higher quantities of bromelain, pregnant women are recommended to consume pineapple in moderation and to choose fully ripe fruit. To reduce any potential dangers during pregnancy, it is imperative to follow safe consumption recommendations and get tailored guidance from a healthcare expert.
10. Rheumatism
People with rheumatism should consult a healthcare professional for advice on dietary choices and treatment options. It’s essential to consider individual factors and medical history when deciding about pineapple consumption and its potential impact on rheumatism. Limited scientific evidence suggests that pineapple consumption directly affects rheumatism or rheumatoid arthritis. While pineapple contains bromelain, an enzyme with anti-inflammatory properties, its effects on rheumatism are not well-established. Some anecdotal evidence suggests that bromelain may help alleviate symptoms of inflammation associated with rheumatism, but more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness.
How to Safely Include Pineapple in Your Diet
When consumed in moderation, pineapple may be a tasty and nourishing addition to your diet. Here are some valuable suggestions for eating pineapple without suffering any adverse effects:
- Select Ripe Pineapples: Completely ripe pineapples are usually sweeter and less acidic, so they are less likely to cause stomach distress and oral irritation.
- Pair with Other Foods: To lessen pineapple’s acidity and bromelain content, eat it with other foods. Proteins like cottage cheese or yogurt can also help counteract its digestive effects.
- Moderate Ingestion: To avoid consuming too much sugar, acid, or enzymes, consume pineapple in moderation. Reducing portion sizes can help avert possible negative consequences.
- Balance with Other Fruits: To reduce the risk of overconsumption and balance pineapple’s nutritional advantages with other essential nutrients, include a range of fruits in your diet.
These pointers can help you take advantage of pineapple’s health benefits and enjoy its sweet and tangy flavor without worrying about unfavorable side effects.
Conclusion
Although pineapple is a tasty and healthy fruit with many health advantages, it’s essential to be aware of any possible adverse effects. Understanding how pineapple can influence your body for healthy ingestion is necessary, from allergic reactions to digestive problems. To reduce adverse effects, always select ripe pineapples, eat them in moderation, and match them with other foods.
In this Article

















