AI Contribution
At HealthSpectra, we may use AI to refine grammar and structure, but every piece is shaped, checked, and approved by real people, our expert writers and editors, to ensure clarity, credibility, and care. Learn more..Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersAcid reflux from the stomach frequently runs back into the esophagus, causing gastroesophageal reflux diseases. It’s commonly known as GERD. This is a widespread ailment that impacts millions of individuals globally. Anybody can have occasional acid reflux, which is frequently brought on by particular meals, stress, or lifestyle choices.
However, if it persists for an extended period and goes untreated, acid reflux can worsen into significant health issues. Prolonged symptoms can raise the risk of esophageal cancer, cause swallowing difficulties, and cause esophageal inflammation. For efficient treatment and avoiding these possible long-term effects, it is essential to understand the symptoms and causes of acid reflux. Understanding the importance of early intervention can empower people to make an educated decision about their health and seek the proper care before problems worsen.
1. Progression to GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)

Chronic acid reflux is more than just a minor annoyance; it can develop into a severe condition known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Repeated episodes of acid reflux, defined as those that occur more than twice per week, may be an indication of a more serious underlying problem that requires medical care. The chronic backflow of stomach acid can, over time, lead to ongoing discomfort, including heartburn, regurgitation, and a persistent cough.
Acid reflux can cause inflammation and damage lining of the esophagus, leading to severe repercussions if left untreated. Prolonged exposure to acid can trigger acid reflux. Damage of this kind not only causes discomfort and anguish but also raises the likelihood of developing esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus, and even esophageal cancer. For individuals interested in maintaining their digestive health and avoiding long-term issues, it is essential to be aware of the symptoms of chronic acid reflux and comprehend the process that leads to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Treatment and intervention at an early stage can significantly assist in efficiently managing symptoms and protecting the esophagus from further damage.
2. Development of Barrett’s Esophagus
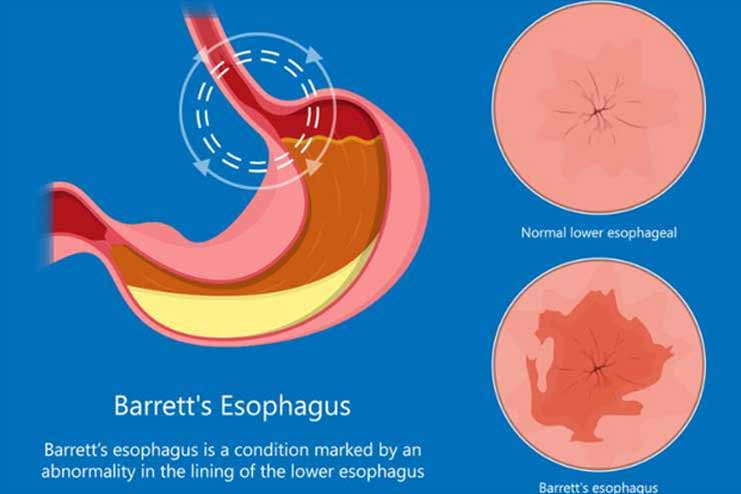
Barrett’s esophagus is a dangerous disorder that can develop from prolonged exposure to stomach acid brought on by persistent acid reflux. The cellular makeup of the lining of your esophagus changes when you have Barrett’s esophagus. Food travels down your esophagus, the swallowing tube, from your mouth to your stomach. Like the rest of your gastrointestinal (GI) tract, the mucus lining inside your esophagus protects it. However, if something irritates this lining for an extended period, it may harm the tissues. There are situations when this harm truly reprogrammes the cells. These modifications alter your esophageal lining’s structure and appearance.
People who have Barrett’s esophagus are more likely to acquire esophageal cancer, specifically esophageal adenocarcinoma. Studies reveal that between 5 and 10% of individuals suffering from persistent acid reflux would eventually develop Barrett’s esophagus, underscoring the significance of prompt identification and observation. In addition to increasing risk of cancer, the alteration in the esophageal cellular structure can cause limitations and trouble swallowing, among other more severe symptoms.
Conduct routine screenings and surveillance for people with Barrett’s esophagus or persistent acid reflux to detect precancerous alterations early. By being aware of the connection between extended acid exposure and Barrett’s esophagus, people can manage their acid reflux more efficiently and lower their risk of acid reflux cancer. It will also improve long-term health results.
3. Esophagitis and Ulcers

Acid exposure regularly due to long-term acid reflux can lead to esophagitis, an esophageal inflammation. One kind of peptic ulcer that arises in the lining of the esophagus—the tube that joins the throat to the stomach—is called an esophageal ulcer. When the mucous layer that coats and shields the gastrointestinal tract erodes, esophageal ulcers can result. It makes it possible for gastric fluids and acid from the stomach to irritate the gastrointestinal wall and cause ulcers. These ulcers cause severe discomfort and difficulties when the esophageal tissue deteriorates due to the constant attack of acidic fluids.
People who have acid reflux ulcers and esophagitis frequently have dysphagia or trouble swallowing. It may result in a dread of food, which can cause malnourishment and weight loss. Swallowing pain can prevent people from following their regular diets, negatively affecting their general health and quality of life.
Acid reflux must be well managed to prevent esophagitis and ulcers from developing. Medication that lowers the production of stomach acid, dietary modifications, and weight control are examples of lifestyle treatments.
4. Stricture Formation
One serious consequence of long-term acid reflux is esophageal stricture, characterized by constricting the esophagus. An unusual constriction of the esophagus is known as an esophageal stricture. The swallowing tube that passes through your chest and connects your mouth to your stomach is called your esophagus. Any duct or route in your body that narrows or becomes restricted is called a stricture. Things may find it difficult to flow through a stricture. A stricture in your esophagus may make it difficult for you to swallow.
This impairment can significantly affect day-to-day living, making eating uncomfortable and occasionally causing people to avoid particular foods. In extreme circumstances, the stricture may result in total esophageal blockage, requiring medical attention. Physicians usually treat esophageal strictures by performing dilatation procedures, using specialized devices to widen the restricted area. In some instances, they may also recommend medication to treat acid reflux and prevent further damage.
5. Risk of Aspiration and Respiratory Problems

Persistent acid reflux causes digestive difficulties and seriously risks lung health. Aspiration, or when something you swallow “goes down the wrong way” and enters your lungs or airway (trachea or windpipe), is one of the most worrisome problems. It may also occur if something escapes from your stomach and re-enters your throat. Unlike choking, aspiration does not result in an obstructed airway.
Individuals who have difficulty swallowing are at a higher risk of aspirating. Up to 15 million Americans suffer from dysphagia, a disorder that impairs swallowing. It can be temporary or a symptom of something more serious. Aspiration pneumonia, an infection that develops when foreign objects enter the lungs and cause inflammation, is one of the significant outcomes of acid reflux aspiration. Aspiration pneumonia can cause symptoms ranging from fever and trouble breathing to a chronic cough and wheeze that calls immediate medical attention. Chronic aspiration can also make pre-existing lung diseases worse, exacerbating symptoms of asthma and raising the risk of respiratory infections.
Recurrent acid reflux sufferers should be aware of their symptoms to avoid lung complications from aspiration. Refraining from lying down right after eating, sleeping with the head raised, and making dietary changes are a few lifestyle changes that can help lower the risk of reflux and aspiration.
6. Preventive Measures and Treatments

Preventing long-term acid reflux issues and managing GERD require preventive measures.
- Lifestyle adjustments are essential for symptom management and harm reduction. Avoiding trigger foods like hot, fatty, and acidic foods, eating fewer quantities, and maintaining a healthy weight will significantly prevent acid reflux episodes. Preventive measures include elevating the head when sleeping and not lying down after meals.
- Many people can alleviate symptoms with lifestyle modifications. Others may need acid reflux and heartburn medications. Antacids and PPIs neutralize stomach acid, and proton pump inhibitors are one of the most effective treatment for chronic acid reflux. Their safety is generally high. They lower gastric acid production. Unlike other drugs, you simply need to take them once a day to avoid symptoms, reduce acid production, and heal the esophagus.
- Only uncommon cases of acid reflux and heartburn require surgery. The most common acid reflux surgery is Nissen fundoplication. In this treatment, a surgeon elevates and tightens a section of your stomach around your esophagus, increasing lower esophageal sphincter pressure. Laparoscopy is used in this procedure. One to three days in the hospital are required after the procedure.
Conclusion
You must diagnose and treat acid reflux as soon as possible to avoid significant side effects like GERD, esophagitis, and breathing problems. Identifying the symptoms and obtaining prompt medical attention can decrease the chance of long-term harm to the esophagus and general health. Proactive management allows people to take charge of their health and maintain a higher quality of life through dietary adjustments, medication, or surgical choices.
References
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17019-acid-reflux-gerd
- https://www.nm.org/healthbeat/healthy-tips/gerd-symptoms-you-shouldnt-ignore
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gerd/symptoms-causes/syc-20361940
- https://www.healthline.com/health/can-acid-reflux-kill-you
- https://www.webmd.com/heartburn-gerd/untreated-heartburn
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441938/
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/advanced-stages-of-gerd
- https://www.cooperhealth.org/services/gastroesophageal-reflux-disease-gerd/stages-of-gerd
- https://www.kansashealthsystem.com/care/conditions/gastroesophageal-reflux-disease
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/barretts-esophagus/symptoms-causes/syc-20352841
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14432-barretts-esophagus
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/barretts-esophagus
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470400
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318786
- https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/esophagitis
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/esophagus-ulcer
- https://www.goodrx.com/conditions/peptic-ulcer-disease/esophageal-ulcer
- https://myhealth.ucsd.edu/3,40532
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21456-esophageal-strictures
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/stricture
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542209
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470169
- https://www.healthline.com/health/gerd/preventing-heartburn#Medication
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/gerd-diet-foods-that-help-with-acid-reflux-heartburn
- https://www.orlandohealth.com/content-hub/you-can-prevent-acid-reflux-here-s-how
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/4200-nissen-fundoplication
- https://www.samitivejhospitals.com/article/detail/acid-reflux-disease
- https://www.health.com/condition/gerd/feeling-stressed-why-you-may-feel-it-in-your-gut
In this Article