Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersWe have all heard of the prominence of diabetes worldwide. Type 2 diabetes is the most prevalent one, which is not only incurable but goes unnoticed for many years. Despite a healthy lifestyle and proper fitness routine, you can get diabetes, and eating healthy is the most crucial preventive mechanism that can avert most of the complications of diabetes, which otherwise may even get fatal.
Let’s review the complications of diabetes and how we can prevent them with some specialist diabetes weight loss and exercise routines.
Critical Diabetes Complications You Shouldn’t Ignore:
If you do not take proper care of your diet and fitness when you have diabetes, it can result in some severe diabetes complications. We must understand these complications of diabetes and prevent them:
1. Kidney Disease
Elevated blood glucose levels force the kidneys to work harder by filtering excess blood, leading to overexertion and eventual kidney damage. Over time, this strain can cause waste to accumulate, potentially leading to kidney failure. At this advanced stage, the only option is dialysis, as restoring normal kidney function is impossible. That’s the reason diabetes is checked with abnormally high levels of protein in urine, which is an early sign of kidney damage.
2. Eye Problems

Elevated blood sugar levels can weaken the blood vessels in the eye, causing injury. Over time, the abundance of glucose may cause these arteries to narrow and get blocked, decreasing blood supply to the retina and causing abnormal development of new vessels. It can worsen eyesight and result in consequences such as diabetic retinopathy. Excess glucose in blood vessels in the back of the eye or the site of the retina can damage vision. People with diabetes are thus advised to go for eye checkups once every year to prevent retina damage. Also, drugs and surgeries may be prescribed to avoid or treat this complication of diabetes.
3. High Blood Pressure

Complications from diabetes may cause hypertension, which significantly increases the risk of severe health issues. When blood sugar levels are consistently high, it may cause the arteries to stiffen and narrow, making it harder for the heart to pump blood. This extra strain on the cardiovascular system raises the likelihood of heart attacks and strokes.
4. Heart Disease

If left unchecked, diabetes can severely damage heart function. Most people with diabetes eventually develop arteriosclerosis, a condition where the arteries in the heart harden. Elevated blood glucose levels contribute to this damage and are often associated with hypertension and high cholesterol, further straining the heart. Effective management of diabetes is crucial to prevent these serious cardiovascular issues.
5. Low Testosterone Levels

One significant complication of diabetes is reduced testosterone levels, a critical hormone for reproductive health. Low testosterone may lead to various health problems, including decreased libido, fatigue, and muscle weakness. In individuals with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels often takes precedence over other aspects of health, which can result in lower testosterone production. The body’s focus on addressing immediate metabolic issues related to diabetes can overshadow hormone regulation, leading to a decline in testosterone.
6. Foot Complications
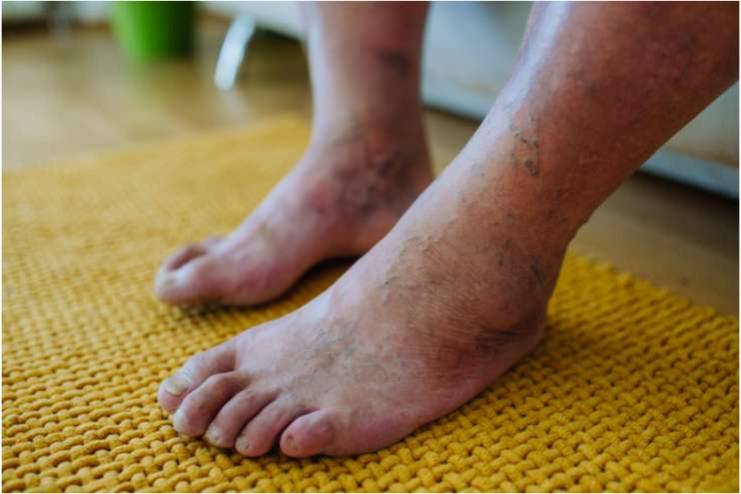
Numbness in the feet and poor balance are common symptoms experienced by individuals with diabetes, often resulting from nerve damage known as diabetic neuropathy. This condition can cause a constant tingling or “pins and needles” sensation in the feet and occasional shivering. The elevated blood sugar level associated with diabetes can damage the nerves over time, reducing sensation and coordination. As a result, people may struggle with balance and feel less aware of their foot position, increasing the risk of falls and injuries.
7. DKA or Ketoacidosis and Ketones

Diabetes can lead to ketones in the urine, which signals an increased risk of ketoacidosis. When blood sugar levels are too high, and insulin is insufficient, the body starts by breaking down fat for energy, producing ketones as a byproduct. These ketones can accumulate in the blood and spill over into the urine. High levels of ketones can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a severe condition characterized by symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and confusion. If left untreated, DKA can result in severe complications, including coma or even death. Regular monitoring and proper diabetes management are essential to prevent ketoacidosis.
8. Gastroparesis
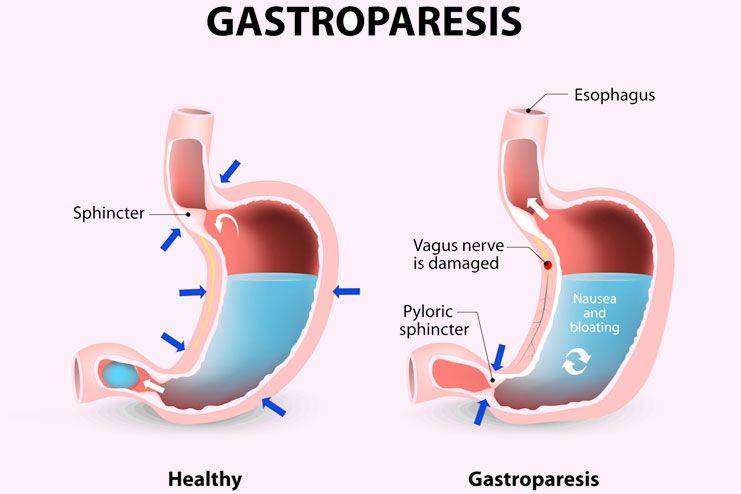
Gastroparesis is a common complication of diabetes where the stomach’s ability to move food to the small intestine slows down or halts entirely. This digestive disorder results from nerve damage caused by prolonged high blood sugar levels, which disrupts the normal functioning of the stomach muscles. Symptoms of gastroparesis include persistent nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, and a reduced appetite. As a result, individuals with diabetes may struggle with maintaining proper nutrition and blood sugar control.
9. Sleep Apnea

Sleep apnea is prevalent in people with type 2 diabetes. The majority of overweight individuals already have sleep apnea, and this condition is made worse by diabetes. Blood sugar levels can be regulated, and an individual’s energy levels can be enhanced by sleep apnea treatment.
Why Do Diabetes Complications Occur?
Prolonged periods of high blood sugar levels are the leading cause of diabetes complications because they can harm blood vessels and nerves all over the body. Chronically high blood sugar causes oxidative stress and inflammation, two detrimental consequences that compromise the health of essential organs. Ineffective diabetes care increases the risk of complications by allowing blood sugar to stay uncontrolled.
Long-term diabetes, inactivity, poor diet, and noncompliance with treatment regimens are risk factors for complications from diabetes. High blood sugar’s cumulative effects over time can lead to significant problems. Patients with diabetes can lower their risk and maintain better overall health by learning the causes of the disease and appropriately managing blood sugar levels.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Diabetes Complications
Making significant lifestyle adjustments is crucial to avoiding complications from diabetes. A diabetes-friendly diet high in whole grains, lean proteins, veggies, and healthy fats can achieve stable blood sugar levels. Lowering the likelihood of complications requires consuming fewer processed foods and refined sugars.
Another critical element is regular exercise; sports like cycling, swimming, or walking increase insulin sensitivity and help control blood sugar.
Stress management is also crucial. Long-term stress can increase blood sugar levels and complicate the management of diabetes. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can improve overall well-being and dramatically reduce stress.
Implementing lifestyle modifications can help people with diabetes live happier lives and reduce their chance of developing serious problems.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes proactively can avoid future complications from the disease. Diabetes demands constant attention and care, but it is possible to live a healthy and active life by making wise lifestyle decisions and being careful about routine checkups with the doctor. Remember that the best way to prevent diabetic complications and ensure long-term health is through early intervention and constant care.
-
Nov 2017Written by Minu Manisha
-
Sep 2024Edited by Ankita
In this Article