Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersMany beneficial bacteria live both on and inside the human body, known as resident bacteria. They play a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions. One of these bacteria is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which is commonly found in the intestines of humans and some animals.
However, certain strains of E. coli can lead to severe health problems in humans. This may come as a surprise. Continue reading to learn more about E. coli infections, the symptoms associated with them, and the available treatments for these infections.
What is E. Coli?
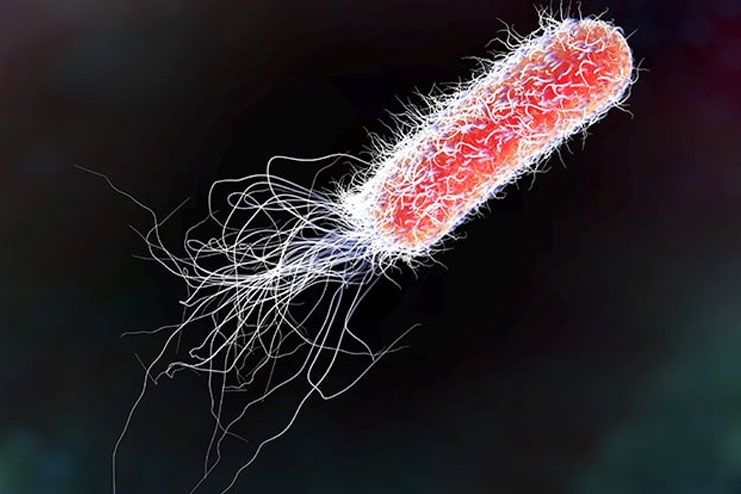
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is the resident bacteria in the intestines of animals and humans. Several E. coli strains are harmless and part of gut flora. In fact, a few E. coli strains keep the digestive tract healthy.
However, some strains, like E. coli O157: H7, can cause severe problems like diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps. Such strains usually enter the body when contaminated food is consumed. Around 75% to 95% of urinary tract infections are caused by E. coli strains.
Some strains of E. coli produce toxins called Shiga. These strains are called Shiga toxin-producing E. coli or STEC. These toxins damage the intestine lining and may also cause acute kidney failure in children and other life-threatening symptoms even in adults, like liver failure, confusion, bleeding, seizures, or fever.
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms.
Causes of E. Coli Infection
Harmful E. coli strains enter the body by ingesting contaminated food, such as untreated milk, ground meat, beverages, fruits, or vegetables.
- If the meat is not cooked well and contains coli, the chances of the strains entering the body are high.
- Similarly, unpasteurized or untreated milk or cheese, if not boiled or heated enough, can make its way from the cow’s udder to the human body.
- Manure of nearby animals may contaminate fruits and vegetables.
- Water, especially in pools, ponds, or lakes, may contain coli, and when such contamination is swallowed, the body gets infected.
- Improper hygiene may contaminate food items in the kitchen, and an infection develops when such foods are consumed.
Hence, hygiene and healthy food habits are major contributors to preventing E. coli contamination. If proper care is not taken, the infection may also pass to other family members.
Symptoms of E. Coli Infection
What are the symptoms associated with an E. coli infection? Symptoms may start building slowly and show up after 2 to 5 days of contaminated food ingestion.
The common symptoms of an E. coli infection are:
- Bloody diarrhea
- Nausea
- Abdominal cramps
- Constant fatigue
- Fever
These are the early symptoms, and if the infection is milder, it may take a week or more for full recovery. At times, infection may go away on its own. However, some may experience complications like hemolytic uremic syndrome, which affects kidneys, especially in older people or children whose immune systems are weak.
Other complications fall under three categories including:
1. Hemorrhagic Diarrhea
Hemorrhagic diarrhea is characterized by blood in the diarrheal stools and severe abdominal pain. In some cases, this may lead to dehydration and anemia.
2. Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
The symptoms of HUS include fever, nosebleeds, bruising, shortness of breath, fatigue, body swelling, or jaundice. These are late E. coli symptoms that develop a week after the beginning of diarrhea. This syndrome is common among kids under 10 years of age.
3. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
TTP is nothing but platelet loss, and symptoms differ from person to person. Common symptoms include fever, bruising, weakness, mental impairment, and kidney failure. Plasma exchange and infusion techniques have rapidly reduced the death rate in TTP patients since the 1980s.
Diagnosis And Treatment For E. Coli
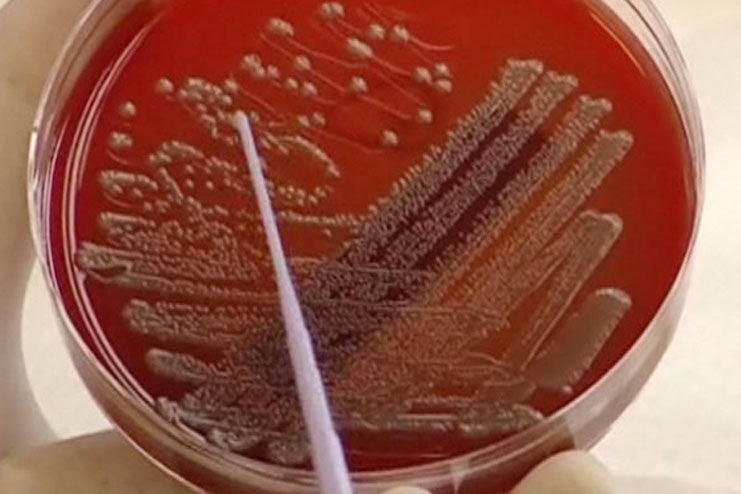
If any symptoms are observed, the doctor may ask for a diagnosis through your stool sample examination. To detect the E. coli 0157:H7 strains, the stool sample is cultured on special culturing plates and tested with antiserum or antibodies that react with only those strains. The test may take a few days to give results.
Other tests, such as blood tests (complete blood count or CBC) and platelets, blood levels of electrolytes, creatinine, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN), are periodically performed to look for TTP or HUS development.
Antibiotics are prescribed if an E. coli infection is diagnosed and associated with watery diarrhea. If a Shiga toxin-producing E. coli is suspected, antibiotics are not suggested as they raise the levels of toxin production and worsen the condition. Instead, plenty of fluids are advised to maintain the body’s hydration levels.
However, treatment for infection and complications may include treatment in an Intensive care unit (ICU), red blood cell transfusion, intravenous fluids and electrolytes, plasma exchange, platelet transfusion, kidney dialysis, hypertension medications, and kidney transplantation.
How to Prevent E. Coli
Preventing E. coli infection means reducing the risk factors for it. Follow simple hygiene conditions to avoid a wide range of infections.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap before preparing food, eating, and feeding.
- Be careful while preparing food for infants and toddlers. Use sterilized utensils to reduce the risk.
- Wash your hands each time you change your child’s diaper or clean the house.
- Wash your hands after getting into contact with your pets.
- Make sure to consume food that is thoroughly cooked and properly prepared before eating.
- Avoid raw or unpasteurized dairy products and unpasteurized juices.
- Avoid swallowing water while swimming in ponds, streams, lakes, public pools, and backyard pools.
- Prevent cross-contamination during food preparation by washing cutting boards, counters, and utensils.
- Use separate chopping boards for raw foods like meat, fruits, and vegetables.
Certain E. Coli strains acquired through the consumption of contaminated food cause infections. In milder cases, the infection subsides on its own within a week. But in severe cases, medical treatment is needed.
FAQs
1. Is E. coli contagious?
- E. coli may be passed from one person to another due to poor hygiene. For instance, the infection may spread if an adult cleans up a child infected with E. coli and does not wash their hands well before touching the mouth.
2. Which foods should be eaten in case of E. coli infection?
- Low-fiber foods are advised when infected with E. coli. These include eggs, rice, crackers, and toast. Avoid dairy products like cheese, milk, and butter, which can worsen the symptoms. Also, avoid any high-fat or high-fiber foods.
3. What are the risk factors for E. coli infection?
- Risk factors for the development of E. coli infection include age, time of year, immune system, and consumption of certain foods.
- Children and older adults with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of developing coli infection. People with chronic illnesses like AIDS or cancer are susceptible to infection.
- Certain foods, such as improperly cooked bakery products, apple juice, and unpasteurized or raw milk, can easily transfer the strains.
- Moreover, decreased stomach acid levels are also the culprits. The condition also arises due to the ingestion of some medications like pantoprazole (Protonix), omeprazole (Prilosec), esomeprazole (Nexium), and lansoprazole (Prevacid) (R).
-
Feb 2018Written by Sumana Maheswari
-
Dec 2024Edited by Lakshmi Gayatri
In this Article