Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersDiet plays an essential role in managing gout, a type of inflammatory arthritis resulting in sudden flare-ups of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the joints. Gout is caused by an excess of uric acid in the blood, which, over time, may crystallize in joints and tissues. This stimulates an inflammatory response, causing pain. Managing gout effectively requires a comprehensive approach that involves medication, lifestyle changes, and dietary modifications.
Certain foods influence the level of uric acid in the body. High-purine foods, such as red meat, shellfish, and alcohol consumption, spur more uric acid production and thus elevate gout symptoms. Low-purine foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein, may reduce uric acid levels in the body and prevent gout attacks.
Understanding what to eat and what to avoid can help gout patients manage their condition and live a comfortable life.
Understanding Gout and Diet
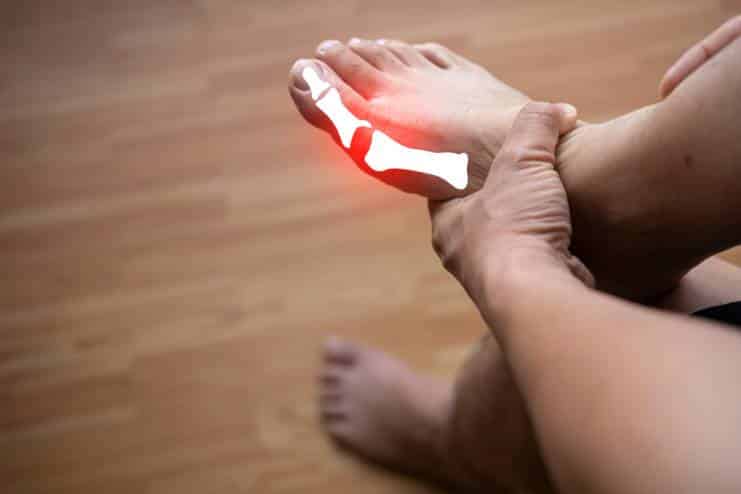
Gout is a painful form of arthritis caused by excessive uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is a by-product created from the breakdown of purines found in certain foods and in the body. Uric acid may crystallize and collect in joints, causing inflammation and intense pain. Gout typically affects the big toe, although it may affect other joints as well.
Diet is the most critical aspect in managing gout, as it directly impacts uric acid levels.
High-purine foods like red meats, organ meats, and some seafood, especially anchovies and sardines, might increase uric acid production in the body. Consumption of sweet beverages and alcohol, particularly beer, elevates uric acid by inhibiting the body’s ability to excrete uric acid.
In contrast, low-purine foods help manage and avoid gout flare-ups. A diet consisting of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products can contribute to decreased blood uric acid levels. Adequate hydration and healthy body mass index are also principal components in gout management. Incorporate foods like cherries, which decrease flare-ups of gout, and foods rich in Vitamin C.
By making mindful dietary choices, one can keep gout at bay and enjoy a better quality of life.
Foods To Eat to Reduce Gout Symptoms
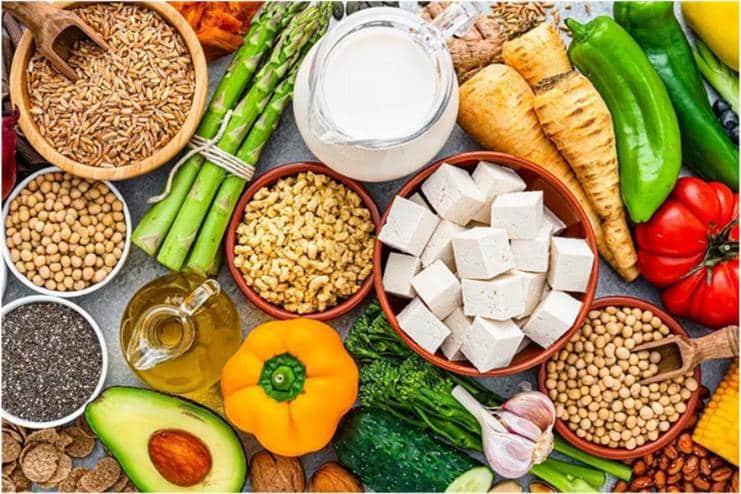

Low-Purine Foods
A low-purine diet is a critical component in managing gout. A diet low in purines and rich in anti-inflammatory agents, along with proper hydration, will help manage gout symptoms.
Here are some very low-purine foods that are recommended for those who suffer from gout:
- Dairy Products: Low-fat dairy products like yogurt, skimmed milk, and cheese are excellent for gout patients. Dairy foods can help lower uric acid levels.
- Vegetables: Most vegetables are low in purines and thus are gout-friendly. These include green leafy vegetables, bell peppers, tomatoes, and broccoli. All vegetables previously thought to be aggravating, such as spinach and asparagus, have been found not to increase the risk of gout attacks.
- Whole Grains: People with high blood glucose levels usually produce high uric acid levels. Whole grains such as oats, brown rice, barley, and whole wheat bread provide complex carbohydrates for stable blood sugar levels.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
The addition of anti-inflammatory foods to the diet reduces inflammation in the body, which eases the pain and swelling associated with a gout attack.
- Cherries: Cherries and their juice are associated with a decreased frequency of gout attacks. They contain anthocyanins, which are a potent anti-inflammatory endogenous compound.
- Berries: Berries like blueberries and strawberries are rich in antioxidants, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
Hydration
Hydration and gout are also interlinked. Sufficient water intake is associated with gout prevention because water clears the kidneys and helps eliminate uric acid, which lowers the risk of crystal formation in the joints.
- Water: Consume 8-12 cups of fluid per day. At least half should come from water to help dilute uric acid and promote its excretion.
- Other Hydrating Beverages: Other than water, herbal teas and decaf coffee are good options.
HS Recommendations
- 13 Health Benefits Of Cucumber Water – Know Why Detox Is Important
- 12 Health Benefits of Sparkling Water – Sizzling Benefits
Foods to Avoid For Gout
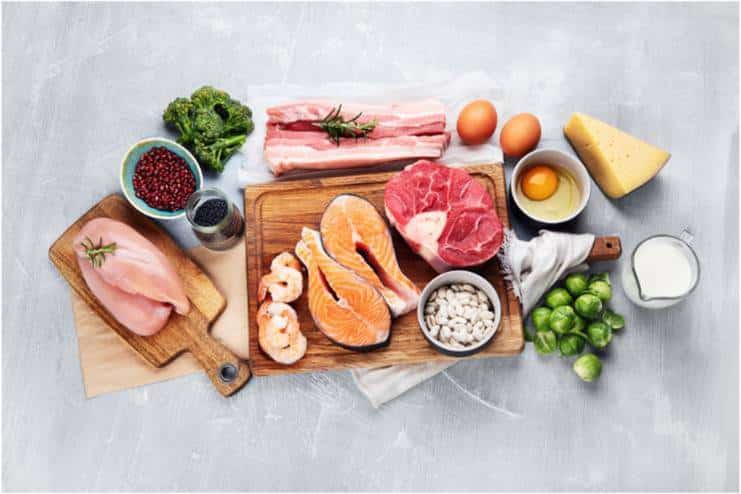

High-Purine Foods
High-purine foods increase uric acid in the blood and form crystals in joints, leading to painful gout attacks. Avoiding the following high-purine foods is important:
- Red Meat: Foods rich in purine content are beef, lamb, and pork. These trigger severe gout attacks by elevating uric acid levels in the blood. It is best to limit or avoid red meat and have leaner protein sources instead. Try skinless white poultry meat instead.
- Organ Meats: Liver, kidneys, and other glandular meats such as sweetbreads have an extremely high content of purines. All these food items should be avoided entirely.
- Seafood: Some seafood, like anchovies, sardines, mussels, scallops, and tuna, are high in purines, which can trigger gout. Although the omega-3 fatty acids in some fish are nutritious, it is still highly recommended to consume them in moderate quantities and avoid those extremely rich in purines. Salmon, tuna, and tilapia are lower in purine but should be consumed no more than 2-3 times per week.
Sugary Drinks and Alcohol
Sugary beverages and alcohol can also increase uric acid levels and trigger gout attacks:
- Sugary Drinks: Drinks with high fructose corn syrup, such as sodas and some fruit juices, can elevate uric acid levels. The high intake of fructose causes an increase in purine metabolism, thereby enhancing gout. Limiting or avoiding sugary drinks may improve the management of the condition.
- Alcohol: Alcohol, especially beer and distilled liquors, triggers gout. It interferes with the body’s capacity to excrete uric acid and elevate its level in the blood. Taking alcohol in moderation may be acceptable, but overall alcohol intake should be low, especially during gout attacks.
Also, read: What Are The Effects Of Alcohol On Your Skin? 7 Alarming Side Effects
Processed Foods
Processed foods contain unhealthy fats and sugars, which can have a negative impact on gout management.
- Fast Food: Fast foods are high in purines and unhealthy fats. These can raise uric acid levels in the body and increase weight, which could exacerbate attacks. Foods such as burgers, fried foods, and other junk foods should be consumed in moderation or totally avoided.
- Processed Snacks: Chips, crackers, and pre-packaged baked goods are a few common snack foods usually loaded with unhealthy fats, added sugars, and artificial ingredients. These foods not only contribute to higher uric acid levels in the blood but can result in bad overall health, making it challenging to manage gout.
Related Article: Baking Soda For Gout Pain – Is It Effective?
3-Day Sample Gout Meal Plan

Additional Tips
Importance of Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excess body weight leads to the production of excess uric acid and reduces the ability to excrete it. This results in higher uric acid levels in the blood and a greater risk of a gout attack.
By losing weight, the uric acid level decreases, and the frequency and severity of gout symptoms reduce. Prioritize maintaining a healthy weight through a well-balanced diet and regular physical activity.
Read more: 20 Effective Ways To Stick To A Healthy Diet For Weight Loss
Regular Exercise and Its Benefits
Exercise enhances the general health of a person by minimizing stress and helping in weight loss. Exercise also increases joint movement and limits the risk of joint damage. Thirty minutes of moderate exercise a few days a week is recommended.
Try brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. Strength training helps build muscles, support joints, and improve overall body function.
Read more: 15 Enjoyable Exercises For People Who Hate Working Out
Conclusion
Effective gout management includes mindful dietary choices to control uric acid in the body and reduce gout flare-ups.
A diet low in purine content, rich in anti-inflammatory properties, and proper hydration will help relieve the symptoms. High-purine foods, sugar-laden beverages, alcoholic beverages, and processed foods should be avoided to prevent gout attacks.
Diet alone can’t prevent gout, but it plays an important role by reducing attack frequency and severity, supporting general health, and complementing medical treatments.
Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment plans based on your individual health needs. Following gout dietary recommendations with regular medical check-ups and healthy living tips, managing gout would become easier..
References
In this Article





















