Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersAny health problem related to the digestive system is complex to handle as the complications could be much more severe. The same is the case with diverticulitis, a digestive disorder with symptoms ranging from mild to severe. Read through this HealthSpectra post to thoroughly understand the Diverticulitis diet and treatment.
What Is Diverticulitis?
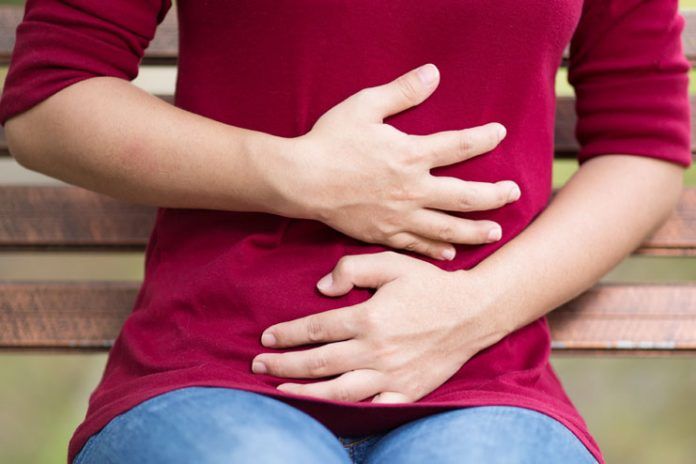
Diverticulitis is a medical condition in which pouches, called diverticula, are formed on the walls of the colon and become swollen, inflamed, or infected. It is a painful condition commonly observed in elderly people.
Causes of Diverticulitis
No specific cause for diverticulitis has been identified. It is the most common condition observed in people over 60. Doctors assume that the condition may result from low fiber content in the diet. In a diet low in fiber content, the colon has to work harder to push the stools forward.
The resulting pressure is assumed to be one reason for the formation of pouches on the colon’s walls. When bacteria grow in the diverticula, inflammation or infection can occur.
Who Is At Increased Risk of Diverticulitis?
The major risk factor for diverticulitis is age, which means the older you get, the higher the risk. Several other risk factors supported by recent research include:
- Lack of Fiber: One of the most suspected risk factors is the lack of dietary fiber (12).
- Genes: A genetic link may be associated with diverticulitis. According to a study on siblings and twins, around 50% have the potential risk of diverticular disease through genetics (13).
- Obesity: In most cases, obesity is the apparent risk factor for diverticulitis. Several studies reveal that obesity increases the risk of diverticulitis and bleeding (14).
- Lifestyle Factors: A sedentary lifestyle is also a risk factor for diverticulitis. Exercise reduces the risk of developing diverticular disease.
- Smoking: Several studies indicate that smoking raises the risk of symptomatic and complicated diverticular disease (16).
- Medication: Regular use of drugs like aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) increases the diverticulitis risk.
- Low Vitamin D: A study found that people with complicated diverticulitis show lower vitamin D levels than people with uncomplicated diverticulosis.
- Gender: The disease is more common in men than women among people below 50 years. In people over 50 years old, the condition is seen as more common in women (19).
Diverticulosis vs Diverticulitis
Diverticulosis is a common digestive disorder manifested in the form of symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease (SUDD) that causes abdominal pain, irritable bowel syndrome, bloating, etc. Diverticulosis is the precursor to diverticulitis.
Diverticulitis occurs when the diverticula becomes inflamed. Of people over 70, 60% have diverticulosis, whereas 75% of people over 80 have diverticulitis.
According to a study, even younger people diagnosed with diverticulosis are at high risk for the condition to progress to diverticulitis.
Symptoms of Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis typically causes symptoms and can lead to serious health complications. Below are the most significant symptoms of Diverticulitis, which usually range from mild to severe. Moreover, the symptoms can appear suddenly or gradually over a few days (20).
The most common symptoms of diverticulitis:
- Pain on the left side of the lower abdomen
- Fever
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Increased urge to urinate
- Burning sensation while urinating
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Blood in the stool
- Bleeding from the rectum
More severe complications of diverticulitis include:
- Collection of pus (abscess) in the pelvis region where the diverticulum has ruptured
- Extensive inflammation causing colonic obstruction
- Generalized infection of the abdominal cavity
- Bleeding into the colon
- Spread of the bacteria within the colon into the surrounding tissues
- Constipation or diarrhea, along with inflammation
- The rupture of the diverticulum into the abdominal cavity causes a life-threatening infection called bacterial peritonitis.
- Erosion of the inflamed diverticulum into the urinary bladder leads to the bladder infection.
When to See Your Doctor?
Patients with mild pain episodes can be treated at home with enough rest. However, a doctor should be visited immediately at the first sign of diverticulitis as he may suggest antibiotics after a thorough examination.
Call the doctor right away if :
- Abdominal pain doesn’t go away
- Bleeding or more severe symptoms show up
Also Read: Diverticulitis Complications: Signs to Watch For
Diagnosis for Diverticulitis
The doctor will suggest several tests to diagnose the condition. He will also ask for health history, symptoms, and ongoing medications.
A physical examination will help check the abdomen for tenderness—a digital rectal exam checks for pain, bleeding, masses, or other problems.
Your doctor may also prescribe other tests like:
- Blood tests – check for anemia, inflammation, liver or kidney problems
- Imaging tests – abdominal CT scan, abdominal ultrasound for gastrointestinal tract pictures
- Urine tests – check for infections
- Stool tests – GI infections
- Pelvic examination for women
- Pregnancy tests for women to rule out pregnancy
Treatment for Diverticulitis
The treatment depends on the severity of the condition. In case of uncomplicated diverticulitis, home treatment or remedies may be suggested. Home treatment for diverticulitis usually includes rest and fluids with required follow-ups. The doctor may also prescribe some medications along with a low-fiber diet, a liquid diet, etc.
Medications to Treat Diverticulitis
Along with the normal fiber-rich diet that helps prevent constipation and further formation of diverticula, anti-spasmodic drugs can be part of the treatment for diverticulitis. Drugs commonly prescribed for diverticulitis include:
- Chlordiazepoxide (Librax)
- Atropine, Scopolamine, Phenobarbital (Donnatal)
- Dicyclomine (Bentyl)
- Hyoscyamine (Levsin)
Oral antibiotics prescribed for mild symptoms include:
- Ciprofloxacin (Cipro)
- Metronidazole (Flagyl)
- Cephalexin (Keflex)
- Doxycycline (Vibramycin)
Over-the-counter medications like Acetaminophen (Tylenol) ease the discomfort.
Also Read: Home Treatment And Diet To Soothe Diverticulitis
Surgical Treatment for Diverticulitis
If medical treatment fails, surgical intervention is required. Surgery involves draining pus cells and removing the colon segment containing diverticula. In people with persistent bleeding, the bleeding diverticulum is removed. Hence, it is essential to accurately diagnose where the bleeding happens.
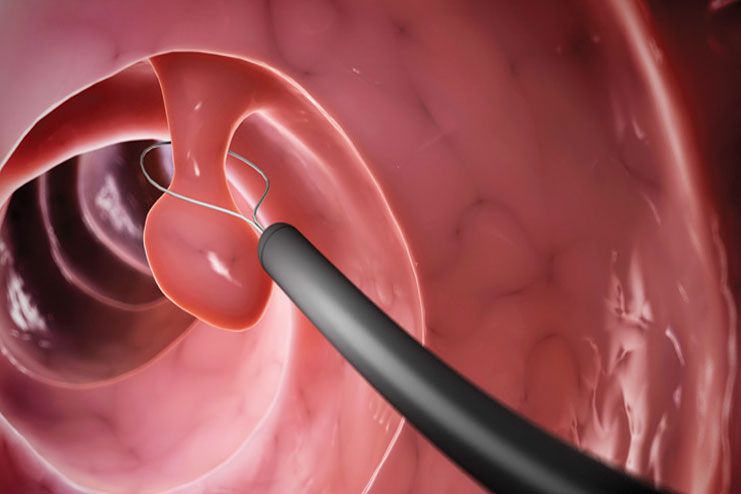
Also, surgery is required in cases where:
- Diverticula erode into the adjacent urinary bladder
- Recurrent urine infection
- Passage of gas during urination
- Frequent, recurrent diverticulitis attacks
- Health conditions leading to multiple courses of antibiotics, hospitalizations
The surgery can mostly be done laparoscopically, which limits post-operative pain and recovery time.
As part of the treatment, your doctor may also suggest a colonoscopy six to eight weeks after your first episode of diverticulitis. This test would confirm whether the episode was not related to other problems.
Meanwhile, the doctor may also suggest:
Home Treatment with Diet for Diverticulitis
The doctor will suggest a liquid diet until diverticulitis symptoms subside. It is called a short-term clear liquid diet that offers rest to the digestive system during the recovery. Liquids to include in the diet are:
- Broth
- Ice chips
- Fruit juices without pulp, such as apple juice
- Ice pops without bits of fruit or fruit pulp
- Water
- Gelatin
- Tea or coffee without cream
A low-fiber diet for diverticulitis:
The doctor may then recommend a low-fiber diet while your digestive system is recovering (24). Low-fiber foods include:
- White bread
- White rice
- Foods made with refined white flour
- Low-fiber hot and cold cereal
- White pasta
- Eggs
- Potatoes without the skin
- Well-cooked canned or fresh vegetables
- Fats like olive oil, mayonnaise, gravy, and butter
- Dairy products (if tolerable)
- Tender protein sources like eggs, chicken, tofu, and fish
- Creamy peanut butter
Low-fiber fruits:
- Fruit juices without pulp
- Bananas
- Cantaloupe
- Canned fruit
- Honeydew melon
- Nectarines
- Watermelon
- Papayas
- Plums
- Peaches
Also Read: The Diverticulitis Diet: What to Eat and Avoid
What Foods Can You Eat with Diverticulitis?
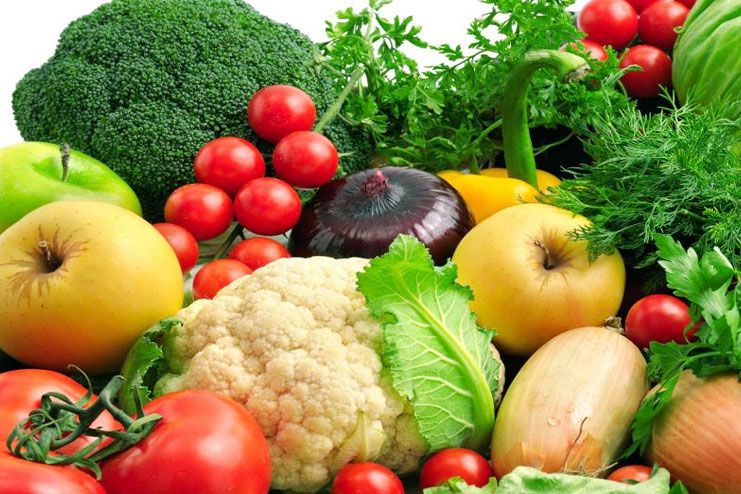

After considering a few factors, pick suitable foods for Diverticulitis. The factors to be considered include:
- Fiber: A high-fiber diet can help reduce the risk of diverticulitis in healthy individuals and its symptoms in patients (10).
- Vitamin D: A study found that among people with complicated diverticulitis who were hospitalized with low vitamin D levels, a diet rich in vitamin D can help reduce the risk of diverticular complications (12).
- Low-FODMAP Diet: Prefer foods rich in fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (FODMAPs ) (34). Some include fruits, dairy foods, fermented foods, garlic, and onions. A low-FODMAP diet is believed to benefit people with diverticulitis.
- Probiotics: Probiotics are believed to help reduce diverticulitis symptoms and encourage remission. However, consult with your doctor before adding them to your diet.

Foods to Avoid with Diverticulitis
Foods rich in insoluble fibers may be avoided when suffering from Diverticulitis. They include:
- Whole wheat bread and baked goods
- Vegetables and fruits, especially with the skins
- Whole grain breads
- Brazil nuts
- Peanuts
- Popcorn
- Brown rice
A Diverticulitis diet may temporarily rest the digestive system. Doctors usually recommend resting oral intake until bleeding and diarrhea subside.
However, there are some risks linked to the diverticulitis diet. For example, continuing a clear liquid diet for too long may lead to weakness and other complications. This is because the body cannot supply enough nutrients after a certain period.
Hence, it is important to get back to a normal diet as soon as the patient can tolerate it. Before taking any call on the diverticulitis diet, check with your doctor.
Conclusion
Managing diverticulitis is a delicate balance of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and dietary modifications. A fiber-rich diet, probiotics, and adequate hydration may reduce symptoms and prevent recurrences.
However, it is always important to follow a doctor’s recommendations, especially during acute episodes, to avoid complications. Regular monitoring and gradual dietary changes can maintain a healthy digestive system, thus providing long-term relief and an improved quality of life.
Always consult a healthcare professional before making significant dietary or treatment changes to ensure they align with your health needs.
FAQs
- What is the difference between Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis?
A. Diverticula are the main cause of diverticulosis and diverticulitis. Diverticulosis is the precursor to diverticulitis. Around 10 to 20% of people with this condition progress to SUDD—symptoms exhibited by diverticulosis, while 4% get acute diverticulitis.
- How does diet affect Diverticulitis?
A. Certainly, diet plays a prominent role in maintaining the health of the digestive system. However, it is unclear if it plays an equally good role in preventing and managing diverticulitis.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), eating seeds and nuts is not a problem, unlike before. Hence, people with diverticulitis need not avoid any particular foods; fiber can indeed be a good choice if they have diverticulitis (6, 29).
-
Feb 2018Written by Sumana Maheswari
-
Feb 2025Edited by Lakshmi Gayatri