Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersAnother name for Baker’s cysts is popliteal cysts. These are swellings behind the knee. It frequently results from diseases like arthritis or cartilage tears that inflame the knee joint. Swelling behind the knee, stiffness, and occasionally pain—especially when the knee is stretched or flexed—are typical symptoms. The investigation of natural remedies as adjunctive therapies for Baker’s cyst has garnered increased attention in recent years. These substitutes seek to promote healing and lessen symptoms without the possible adverse effects of drugs or invasive procedures. Examining these natural methods can give people more choices for efficiently treating their illness.
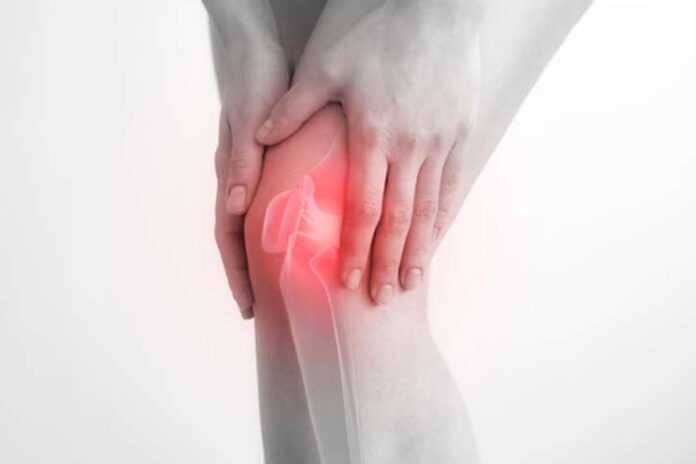
What Is Baker’s Cyst?

In most cases, it manifests as a cystic swelling caused by the accumulation of excess synovial fluid responsible for lubricating the knee joint. This disorder is frequently the result of underlying knee joint problems, such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, in which inflammation causes an increase in the production of synovial fluid. Additional factors that contribute to the development of Baker’s cyst include traumas such as cartilage rips.
Causes: Inflammation of the knee joint, which increases the production of synovial fluid, is the critical factor leading to the development of Baker’s cyst. The fluid then becomes gathered in a pouch-like structure behind the knee, where the cyst is formed.
Symptoms: The most common symptoms include swelling behind the knee, which can be seen as a lump or protrusion, stiffness, and soreness. The pain becomes more intense when the knee is extended or flexed. In extreme circumstances, the cyst can rupture, resulting in fluid flowing down the calf.
The identification and management of Baker’s cyst can be improved by better understanding these aspects. It’s important to note that while natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments can be beneficial, they should not replace medical advice or treatment. A healthcare professional can provide proper diagnosis, recommend appropriate treatments, and monitor your condition to ensure the best outcomes.
List of Natural Remedies:

Epsom Salt Compress: Epsom salt, with its high concentration of magnesium sulfate, is a comforting remedy for the discomfort and swelling associated with Baker’s cyst. When dissolved in warm water and used as a compress, it helps draw out excess fluid from the cyst, providing soothing relief and relaxation to the affected area.
Turmeric: Turmeric contains curcumin, a potent anti-inflammatory compound that can significantly reduce inflammation and swelling. Including turmeric in one’s diet or taking supplements containing turmeric can support the body’s natural healing processes and alleviate symptoms of Baker’s cyst.
Ginger: Ginger possesses anti-inflammatory characteristics, which can assist in alleviating the discomfort and swelling linked with Baker’s cyst. Drinking ginger tea or applying ginger compresses can provide calming comfort and enhance movement. Ginger tea can also be consumed.
Ice Pack Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected knee can dramatically reduce swelling and mute pain by restricting blood vessels surrounding the knee. To prevent damaging your skin, you should apply this straightforward yet powerful cure on a sporadic basis for brief periods.
Compression Bandages: Bandages that apply compression reduce the amount of fluid that accumulates around the knee joint, which helps reduce swelling and provide stability. You can wear them during activities or sleeping to promote healing and alleviate discomfort.
Apple Cider Vinegar:The acidic nature of apple cider vinegar, when diluted and applied topically, can help reduce swelling and inflammation. For soothing relief, it can be used as a compress or added to bath water.
Cayenne Pepper: The compound capsaicin, found in the cayenne pepper, is well-known for its ability to alleviate pain. It is possible that applying this substance topically can help decrease the discomfort associated with Baker’s cyst by temporarily desensitizing the nerves in the affected location.
Magnesium Supplements: Taking magnesium supplements can help alleviate the symptoms of Baker’s cyst by relaxing muscles and controlling discomfort. Taking them orally can support both the overall health of joints and the reduction of inflammation.
Flaxseed Oil: People who suffer from Baker’s cyst may find that flaxseed oil, which is abundant in omega-3 fatty acid, has anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit them. When used daily, flaxseed oil has the potential to reduce edema and increase joint mobility.
Arnica: Arnica, frequently found in topical ointments or gels, is utilized for its analgesic and anti-inflammatory qualities throughout treatment. When applied to the problematic area, arnica can provide localized pain relief and promote the healing process.
Willow Bark: One of the compounds found in willow bark is salicin, a chemical comparable to aspirin and recognized for its ability to alleviate pain. Additionally, it can be used locally or taken orally to ease the discomfort associated with Baker’s cyst.
Rest and Elevation: Resting the afflicted knee and keeping it raised above the level of the heart’s surface can minimize swelling and encourage fluid evacuation from the cyst. This straightforward medicine, which works in conjunction with other treatments, supports the body’s natural healing process.
These natural therapies offer a holistic approach to managing the symptoms of Baker’s cyst. They not only provide relief but also empower individuals to take control of their health and recovery, without the potential adverse effects of medications or invasive procedures. Incorporating these treatments into a comprehensive care plan can help individuals regain their mobility and satisfaction with their lives.
Lifestyle Tips to Manage Baker’s Cyst

Effective management of Baker’s cyst requires not only treating the symptoms but also making lifestyle adjustments. By taking proactive steps to facilitate healing and prevent recurrence, individuals can play an active role in their own health and well-being.
Exercise regularly: Participate in low-impact workouts such as swimming or cycling to keep the joints flexible and develop the muscles around your knee without worsening the cyst.
Weight Management: Maintain healthy weight to alleviate symptoms and prevent cyst enlargement. You can do this by reducing the pressure on the knee joint.
Proper Posture: Maintaining correct posture is essential for minimizing stress on the knees and ensuring that the joints are entirely aligned.
Avoid Prolonged Standing or Sitting: To avoid stiffness and swelling, avoid standing or sitting for extended periods. Instead, alternate between sitting and standing and take intervals to stretch and move around.
Hydration and Nutrition: To support joint health, it is very important to maintain proper hydration and consume a very well-balanced diet that is abundant in anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Stress Management: Stress management involves engaging in relaxation activities such as yoga or meditation to alleviate stress, which can increase inflammation and pain.
Implementing these lifestyle adjustments into their daily routines can help individuals effectively manage the symptoms of Baker’s cyst, improve their joint health, and limit the likelihood of a recurrence of the condition.
When to See a Doctor

While many cases of Baker’s cyst can be managed with home remedies and lifestyle adjustments, certain circumstances necessitate medical care to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Severe Pain or Swelling: If the pain becomes severe or the swelling grows rapidly, it may indicate complications such as a ruptured cyst or deep vein thrombosis (DVT), both of which require prompt evaluation.
Difficulty Walking or Moving: If you have persistent difficulty walking, bending your knee, or bearing weight on the afflicted leg, you should consult a healthcare specialist to evaluate the function of your joints and rule out the possibility of underlying joint damage.
Redness or Warmth: If the skin covering the cyst becomes red or warm to the touch or displays any other signs of infection, you must get medical assistance to prevent further difficulties.
Fever or chills: The presence of the fever or chills in conjunction with other symptoms indicates a systemic infection requiring rapid medical examination and treatment.
No Improvement with Home Remedies: If the symptoms do not improve with self-care measures or worsen over time, it is recommended that you speak with a physician to investigate alternative therapies or interventions.
When experiencing these symptoms or concerns, it is essential to seek the guidance of a medical professional to ensure that Baker’s cyst is managed appropriately and limit the risk of complications during treatment.
Conclusion
Exploring natural treatments for Baker’s Cyst will significantly help with symptom management and recovery. These methods, ranging from Epsom salt compresses to turmeric and therapeutic lifestyle modifications, offer comprehensive and long lasting advantages. By integrating various homeopathic treatments under medical supervision, people can significantly reduce pain and improve their overall quality of life.
In this Article