Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersRingworm, or tinea, is a common fungal infection that affects the skin, hair, or nails. Despite its name, ringworm is not related to worms.
The fungus that causes the infection is known as dermatophytosis, and they like warm, humid conditions. The scalp, feet (athlete’s foot), and groin (jock itch) are among the body parts that these fungi can infect. The typical presentation of ringworm is a red, round rash with elevated margins that is frequently itchy.
It spreads readily in close contact. Additionally, touching contaminated objects or surfaces can spread the infection. Public places, like locker rooms, swimming pools, and common areas, increase the risk of exposure.
Read More: Acne Around the Mouth? Here’s What Your Skin Is Trying to Tell You
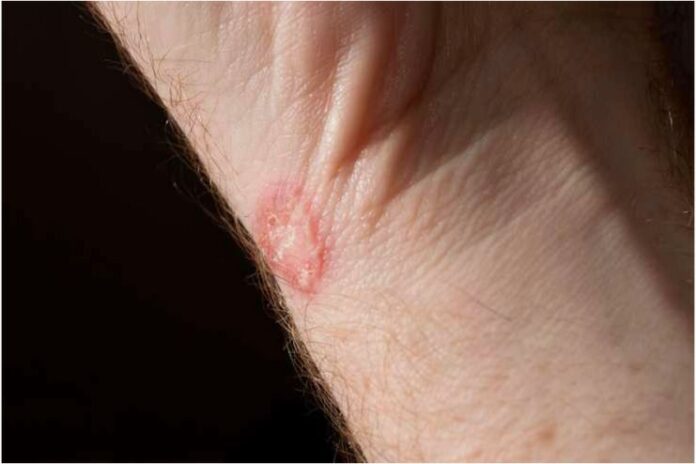
Is Ringworm Contagious?
Approximately 10–20% of people will eventually experience a fungal skin infection. Ringworm affects people of any age, but it is more common in youngsters and older people.
Indirect contact with contaminated surfaces or direct touch with individuals can easily transmit ringworm, which is highly contagious. It is among the rare fungus that may infect humans and animals similarly. Therefore, you might get ringworms from your dog or cat and other individuals. Additionally, you and other animals can give it to your pets.
Ringworm is transmitted primarily through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person or animal. Sharing personal objects like clothing, combs, or towels can also spread it.
People with compromised immune systems are more susceptible to the infection, so it’s necessary to avoid exposure.
Read More: Skincare Mistakes That Make Acne Worse (And How to Avoid Them)
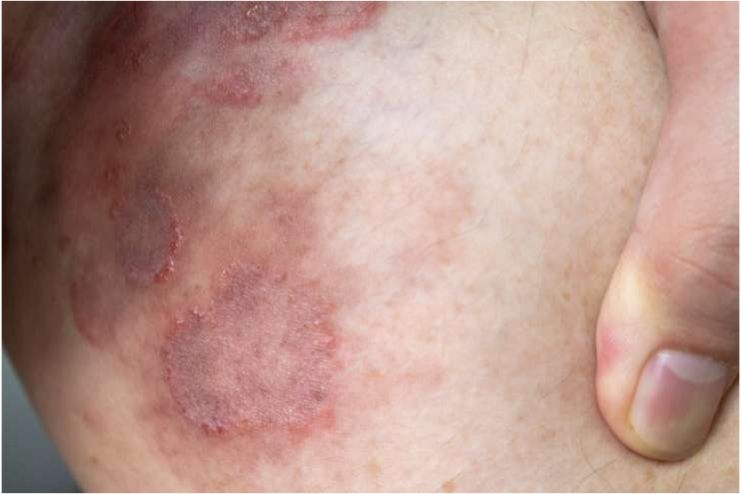
Symptoms and Stages of Ringworm
As the infection spreads and recovers, the symptoms of ringworm change over various phases. Early-stage identification can facilitate timely treatment.
First stage: During this phase, you can have a dry, scaly, and discolored skin patch.
Stage two: The lesion enlarges during this phase. A circular, scaly patch around the rash’s core may mimic healthy skin.
Symptoms of Ringworm:
The following symptoms usually show up four to fourteen days after the fungi that cause ringworm come into contact with your skin:
- The damaged area inside the ring may have tiny, color-changing pimples and seem clear or scaly. These pimples can be red on white skin and range from reddish and purple to brown or gray on black and dark skin.
- Expanding, slightly raised rings that keep growing over time are frequently the result of the illness.
- When it affects the scalp or body hair, ringworm can result in bald patches or considerable hair loss in the affected area.
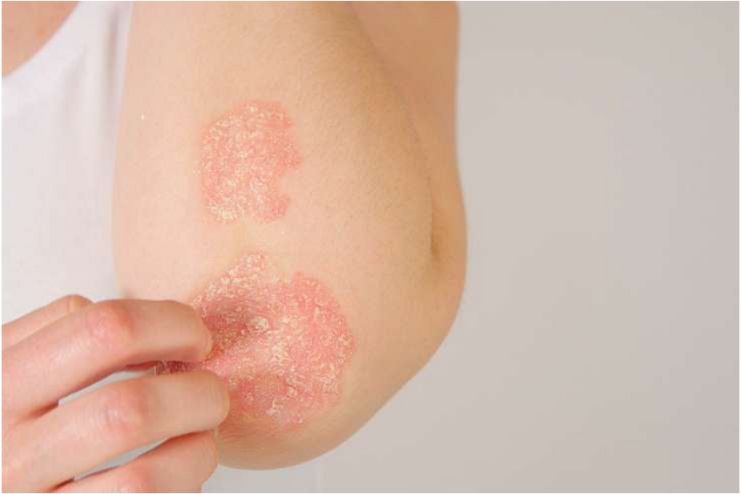
Ringworm vs Psoriasis vs Eczema
Common skin disorders, including psoriasis, ringworm, and eczema, can be complex and difficult to distinguish. They can all affect identical body areas, resulting in a flaky, itchy rash with fine scales. Each, however, differs in its cause and distinguishing traits.
Ringworm:
Ringworm causes a red, round, and frequently scaly rash. Several different fungi can cause ringworm infection. Though there are varieties that affect the scalp, feet, groin, and nails, the term primarily refers to ringworms of the body (tinea corporis).
Ringworm grows best in damp conditions and is highly contagious. Both direct touch with wet floors and interpersonal contact can spread the fungus.
Although ringworm can affect anyone, children are more prone to developing ringworms on the scalp and body. Some are more prevalent among teenagers and adults, such as jock itch and athlete’s foot.
Read Next: Home Remedies to Treat Ringworm
Eczema:
Eczema, sometimes referred to as atopic dermatitis or atopic eczema, is an allergy-related disorder linked to asthma, food allergy, and allergic rhinitis (hay fever). Having eczema as a newborn puts you at risk of developing all of these other illnesses in the future. The condition often presents symptoms such as dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, which can become red, cracked, and even ooze in severe cases.
Eczema is caused by an overreactive immune system. Stress, hormone fluctuations, allergies, irritants, weather changes, and infections can all cause the symptoms to flare up and go away in short bursts or exacerbations. Although it can impact persons of any age, eczema typically first appears before age five.
Psoriasis:
In psoriasis, an autoimmune disease, the immune system targets the lowest layer of skin cells with inflammation. This results in red, scaly plaques that may peel or have a gray tint. Because the skin sheds so quickly during a psoriasis flare, a person experiences scaly, red, and itchy patches of skin.
Psoriasis is not contagious. Although the exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, it usually runs in families. Specific things, including stress or alcohol, might bring on a flare. Similar to eczema, infections, cold temperatures, sunburn, wounds and scrapes, insect bites, and excessive alcohol use are risk factors that might cause exacerbations.
Although it can begin at any age, psoriasis often peaks between the ages of 20 and 30 and then again between the ages of 50 and 60.
Read More: 6 Dermatologists Recommended Skin Care Routine – Decoding The Best From Professionals!
Ringworm Prevention Tips
It’s crucial to adhere to a few essential prevention guidelines to promote healing and stop the infection from spreading. The following are critical actions to take:
Keep the infected area dry and Clean: Wet conditions are ideal for fungus growth. Using a fresh towel, pat the skin dry to prevent moisture buildup that can encourage the formation of fungi. This procedure should be repeated regularly to lower the chance of recurrence.
Avoid Scratching: Scratching ringworm can exacerbate the infection by rupturing the skin, causing open sores, and introducing bacteria. In addition to extending the illness, this raises the possibility that it will spread to other areas of the body or other individuals.
Wear Breathable, Loose Clothes: Clothing that is too tight or doesn’t breathe might retain sweat and moisture, making it perfect for the fungus to flourish. To help keep the diseased region dry, choose loose-fitting clothes made of natural materials like cotton, which promotes air circulation.
You can effectively control ringworms and reduce the danger of spreading them by combining these prevention tips with the right treatments.
Dietary Guidelines for Ringworm
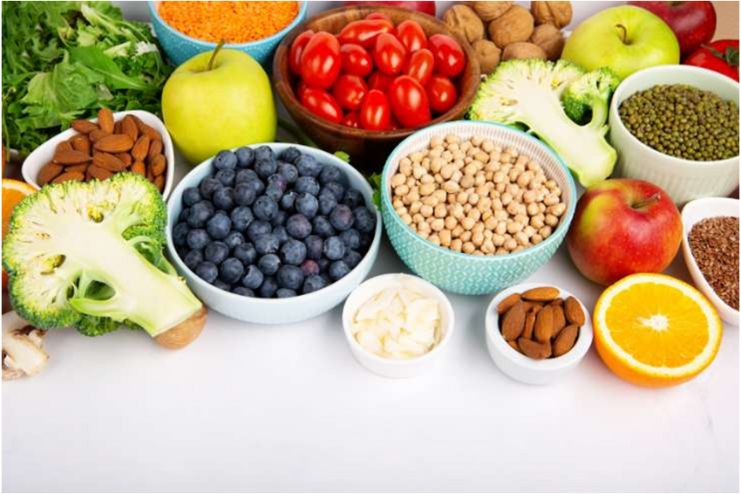

Although topical treatments are crucial for ringworm management, a well-balanced diet can also help boost the immune system and fast-track the healing process. In addition to providing vital nutrients to fight the fungal infection, a well-balanced diet can help lower inflammation.
Foods to Incorporate:
- Proteins, including lean meat, eggs, and beans
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids from fatty fish, nuts, and seeds.
- Whole grains such as quinoa, brown rice, and oats.
- Vegetables
- Yogurt
- Water
Foods to Avoid:
- Caffeine, reduce intake to prevent dehydration.
- Sugary food, such as pineapples, bananas, and grapes.
- Processed grains and foods like bread, pasta, and some cereals that contain gluten.
- Foods such as packaged snacks, sauces, and fast food include many cornstarch and sugar compounds.
Read More: 15 Effective Natural Remedies to Get Rid of Skin Rashes Easily
FAQs
Can you die from ringworm?
Ringworm does not pose a threat to life. This topical fungal infection impacts the skin, hair, and nails. It does not result in death, but if treatment is not received, it may cause discomfort and problems, such as bacterial infections. The infection usually goes away with prompt treatment.
What happens if you lick ringworm?
The fungus that causes ringworm can spread to your lips and other body parts when you lick it. Avoiding touching or licking infected areas is crucial since doing so raises the possibility that the fungus will spread to other areas of your skin or even other people.
Can ringworm cause hair loss?
Ringworm can lead to hair loss, especially if it affects the scalp. Bald spots could result from the illness, causing patches of hair to fall out. The fungus weakens the hair follicles, which is why this happens. After the infection disappears with the right care, hair frequently regrows.
Conclusion
Ringworm is a common fungal infection that can affect many parts of the body. It is entirely treatable and can be managed and stopped by following a treatment plan, avoiding contact with infected individuals, and maintaining proper hygiene.
Early detection and regular care help prevent complications like hair loss or chronic itching. Changes in your diet can also help your body fight off the infection faster. You can efficiently cure ringworm using the proper treatment method and ensure it heals without lasting consequences.
References
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ringworm-body/symptoms-causes/syc-20353780
- https://www.cdc.gov/ringworm/about/index.html
- https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-ringworm.aspx
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4560-ringworm
- https://www.healthline.com/health/ringworm
- https://www.goodrx.com/conditions/ringworm/when-is-ringworm-contagious-for
- https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/ringworm-myths-facts
- https://www.healthline.com/health/ringworm#causes
- https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/ringworm-symptoms
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22757-nummular-eczema
- https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/psoriasis/what/causes
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323242#psoriasis-vs-ringworm
- https://www.goodrx.com/conditions/eczema/ringworm-vs-eczema
- https://www.homeocareclinic.in/diet-chart-for-fungal-infection/
- https://www.livestrong.com/article/459159-diet-for-ringworm/
In this Article