Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersFor diabetic patients, it’s essential to prioritize whole foods over processed options. Whole fruits and vegetables meet the body’s nutritional requirements and reduce the risk of complications. Below, we will explore a variety of superfoods that are particularly effective in managing diabetes and promoting overall health.
What Makes a Food a “Superfood” for Diabetics?
Superfoods are nutrient-dense and well-known for their remarkable health advantages, especially in treating long-term illnesses like diabetes. Superfoods for people with diabetes have a unique nutritional composition that helps regulate blood sugar and maintain general health. Due to their generally low glycemic index, these foods raise blood sugar levels gradually and with more control.
Additionally, they are a great source of fiber, vitamins, antioxidants, and healthy fats—nutrients that can lower inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity.
Superfoods provide vital nutrients that will enhance general health, reduce the risk of problems, and help stabilize the blood glucose level in people with diabetes. Leafy greens, berries, and nuts are a few examples. Keep reading for our complete list!
19 Diabetes-Friendly Superfoods
A healthy diet consisting of lean proteins, whole grains, fresh fruits, and veggies would go a long way toward leading a healthy life. Incorporating these powerful nutrients into your diet will give you optimal health results.
1. Green Apples
 Green apples are rich in antioxidants and effectively control the body’s cholesterol levels.
Green apples are rich in antioxidants and effectively control the body’s cholesterol levels.
Not only do you significantly lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes, but the carbohydrates in your diet also keep your body functioning correctly.
2. Asparagus
 Asparagus’s nonstarchy yet high caloric content makes it a favorite among many. The veggie boosts our systems’ insulin-producing capacity. Glutathione, an antioxidant, prevents and treats diabetes and cancer, acts as an anti-aging agent, and ensures the heart functions normally.
Asparagus’s nonstarchy yet high caloric content makes it a favorite among many. The veggie boosts our systems’ insulin-producing capacity. Glutathione, an antioxidant, prevents and treats diabetes and cancer, acts as an anti-aging agent, and ensures the heart functions normally.
3. Avocados
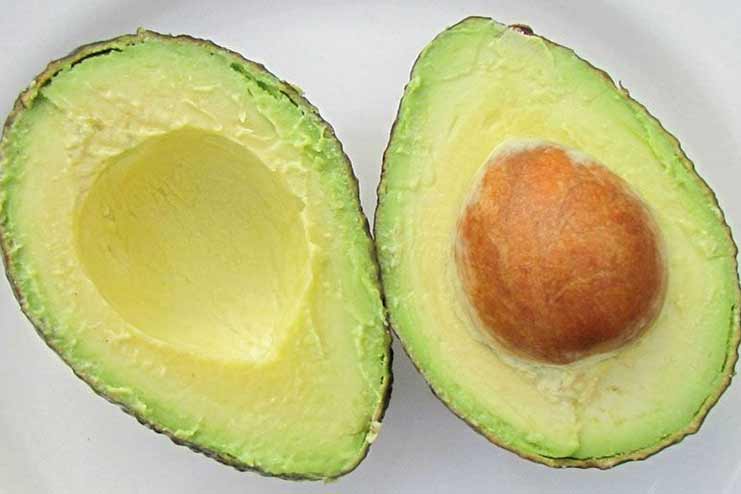 Monounsaturated fats in avocados play a crucial role in supporting heart health. A well-functioning heart is better equipped to circulate oxygen-rich blood throughout the body, helping to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
Monounsaturated fats in avocados play a crucial role in supporting heart health. A well-functioning heart is better equipped to circulate oxygen-rich blood throughout the body, helping to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
4. Beans
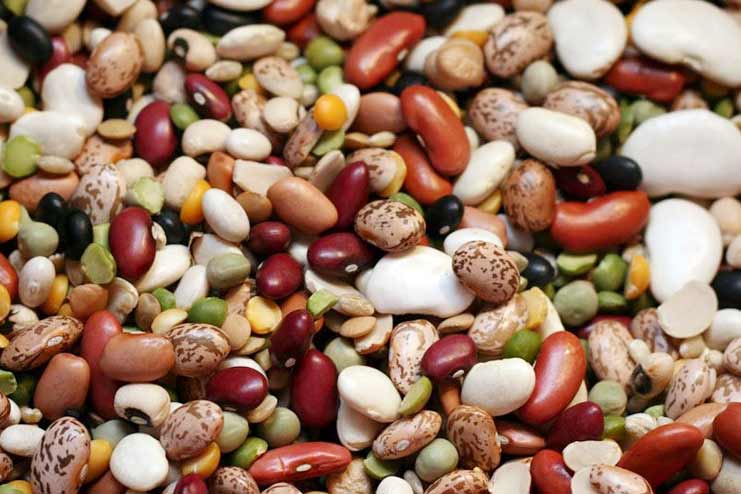 Beans are legumes high in B vitamins, fiber, and healthy minerals like magnesium, potassium, and calcium. Additionally, they have a low glycemic index (GI), which is crucial for controlling diabetes.
Beans are legumes high in B vitamins, fiber, and healthy minerals like magnesium, potassium, and calcium. Additionally, they have a low glycemic index (GI), which is crucial for controlling diabetes.
A study with over 3,000 high-risk cardiovascular disease participants found that individuals who consumed more legumes had a lower risk of type 2 diabetes.
5. Strawberries
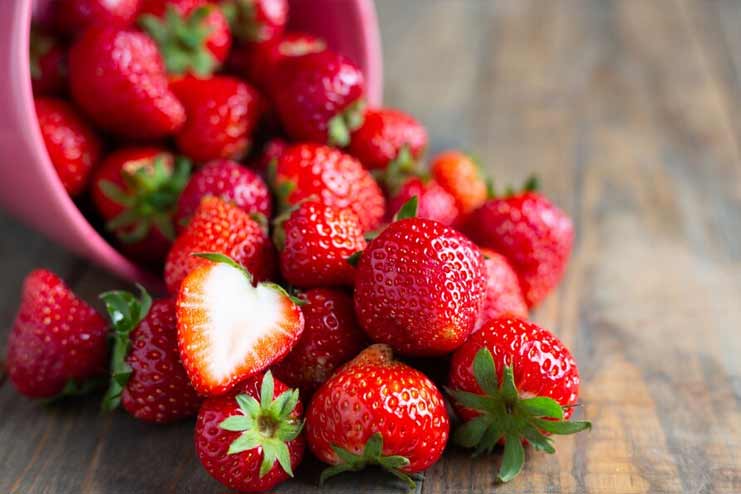 Strawberries’ red hue comes from an abundance of antioxidants called anthocyanins. Additionally, they contain plant components called polyphenols, which have antioxidant qualities.
Strawberries’ red hue comes from an abundance of antioxidants called anthocyanins. Additionally, they contain plant components called polyphenols, which have antioxidant qualities.
According to a 2017 study, persons who were overweight or obese but did not have diabetes showed enhanced insulin sensitivity after consuming polyphenols from strawberries and cranberries for six weeks.
6. Broccoli
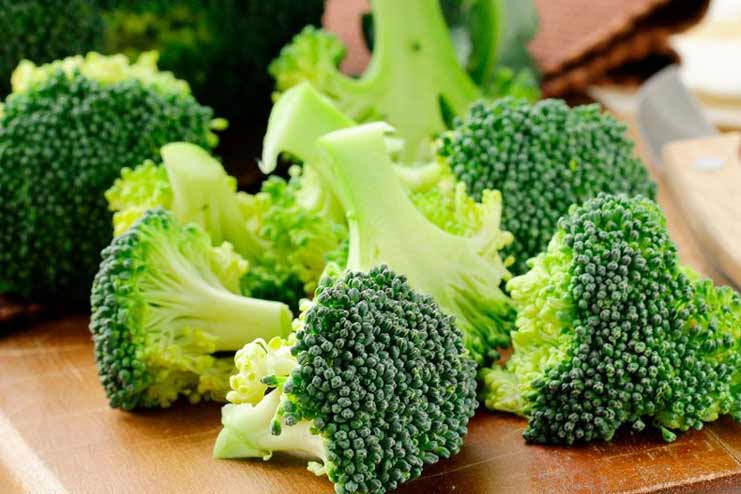 Half a cup of cooked broccoli contains 27 calories and 3 grams of easily digested carbohydrates, and essential nutrients such as magnesium and vitamin C.
Half a cup of cooked broccoli contains 27 calories and 3 grams of easily digested carbohydrates, and essential nutrients such as magnesium and vitamin C.
Broccoli consumption has been reported to lower blood glucose in 2024 research. The probable cause of this drop in blood glucose levels is sulforaphane. Broccoli contains glucosinolates, which the body transforms into sulforaphane for use in metabolic functions.
7. Carrots
 Although carrots, when cooked, have the rich look and feel of a starchy vegetable, they are classified as nonstarchy because they contain few carbohydrates. Raw carrots have about 5% carbohydrates per 100 grams, dramatically halved once cooked.
Although carrots, when cooked, have the rich look and feel of a starchy vegetable, they are classified as nonstarchy because they contain few carbohydrates. Raw carrots have about 5% carbohydrates per 100 grams, dramatically halved once cooked.
They are also rich in the antioxidant beta carotene, which promotes the production of Vitamin A in our bodies.
8. Fatty Fish
 Salmon, sardines, herring, anchovies, and mackerel are rich sources of heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids, DHA and EPA.
Salmon, sardines, herring, anchovies, and mackerel are rich sources of heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids, DHA and EPA.
Individuals with diabetes should regularly consume adequate amounts of these fats because they are more susceptible to heart disease and stroke. Fish oil is a practical component in aiding insulin production in the body, keeping diabetes under control.
9. Flaxseeds
 Flaxseeds contain alpha-linolenic acid, which the body converts to Omega-3 fatty acids. They are also a rich source of the antioxidant Lignan, which is good for the heart and prevents cancer.
Flaxseeds contain alpha-linolenic acid, which the body converts to Omega-3 fatty acids. They are also a rich source of the antioxidant Lignan, which is good for the heart and prevents cancer.
Although they are rich in calories, they are low in carbs and high in dietary fiber. Hence, we can easily classify them as superfoods necessary for people with diabetes.
10. Garlic
 Garlic is a member of lily family, and people have used this edible bulb as a medicinal and flavoring agent since ancient times. Garlic has been used to treat high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and heart diseases.
Garlic is a member of lily family, and people have used this edible bulb as a medicinal and flavoring agent since ancient times. Garlic has been used to treat high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and heart diseases.
Although its anti-diabetic effects may not be particularly strong, it is safe for people with diabetes to consume. The real advantage comes from its ability to suppress appetite, which in turn helps manage calorie intake.
11. Kale
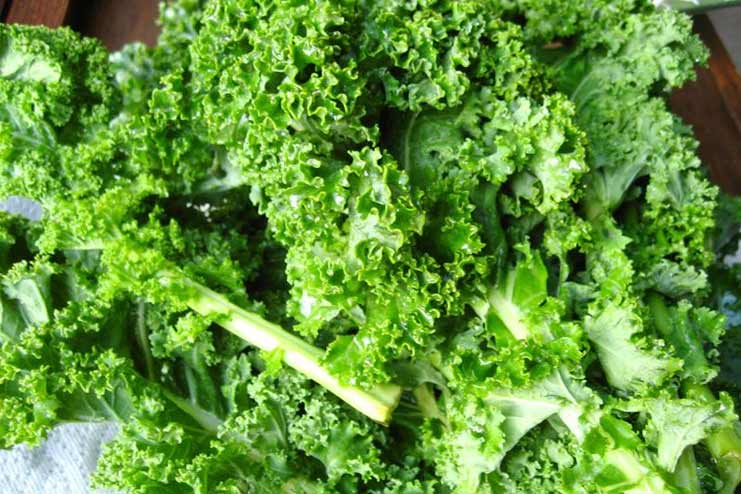 Kale stands out with its unique flavor, packs a wealth of nutrients, and serves as a versatile ingredient in the kitchen. Like spinach, it is nonstarchy and helps treat type 2 diabetes.
Kale stands out with its unique flavor, packs a wealth of nutrients, and serves as a versatile ingredient in the kitchen. Like spinach, it is nonstarchy and helps treat type 2 diabetes.
Kale is low in calories and carbohydrates. Like most green and leafy vegetables, it is abundant in vitamin A and zinc.
Moreover, kale also contains lutein and zeaxanthin, two pigments that are beneficial for healthy eyes. A secondary benefit against diabetes is that high sugar levels in the blood can affect eyesight sooner or later.
12. Bitter Melons
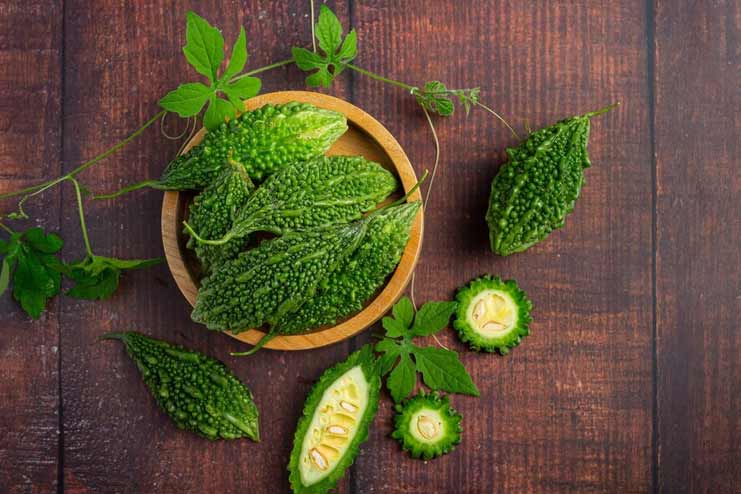 As you might expect, it’s not the tastiest cuisine available. Therefore, it might not be as accessible as the other items mentioned. However, the health benefits of bitter melon connected to diabetes more than offset its taste. It has been demonstrated that individual with type 2 diabetes can reduce their blood sugar by consuming 2,000 mg of this plant daily.
As you might expect, it’s not the tastiest cuisine available. Therefore, it might not be as accessible as the other items mentioned. However, the health benefits of bitter melon connected to diabetes more than offset its taste. It has been demonstrated that individual with type 2 diabetes can reduce their blood sugar by consuming 2,000 mg of this plant daily.
13. Nuts
 Since the time of the nomads, nuts have remained one of the healthiest food options available to mankind. They are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, unsaturated fats, and vitamin E, among other nutrients.
Since the time of the nomads, nuts have remained one of the healthiest food options available to mankind. They are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, unsaturated fats, and vitamin E, among other nutrients.
Studies have shown that nuts keep the artery walls flexible and prevent blood from clotting. Scientific studies have shown that nuts are a great addition to a diabetes diet and help reduce high cholesterol levels.
They are your most definitive super snacks, with a long shelf life and requiring no refrigeration. They are notorious for their calorie content, and eating them in small portions is better.
14. Oatmeal
 Few breakfast options are quite as healthy as oatmeal. Its high fiber content keeps your energy levels high longer than other low-fiber options.
Few breakfast options are quite as healthy as oatmeal. Its high fiber content keeps your energy levels high longer than other low-fiber options.
It is rich in soluble fibers, which help control cholesterol levels. Moreover, it is a wholesome and delicious option that helps to control glucose levels in your bloodstream.
15. Quinoa
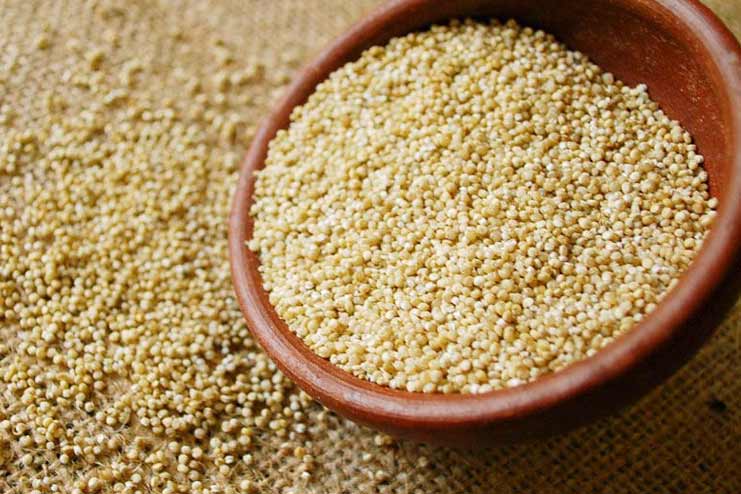 Quinoa should be a definite addition to your diet if you are looking to expand your vegetarian options. The Incas first consumed this whole grain, which then remained obscure for a long time until people rediscovered it in the late 1960s.
Quinoa should be a definite addition to your diet if you are looking to expand your vegetarian options. The Incas first consumed this whole grain, which then remained obscure for a long time until people rediscovered it in the late 1960s.
Quinoa is rich in proteins and contains all nine types of amino acids, making it a complete source of proteins.
Its carb content is low, and it contains folate, magnesium, manganese, iron, and vitamin B6. Like other fibrous foods, quinoa is extremely appetizing and good for blood sugar control.
16. Red Onions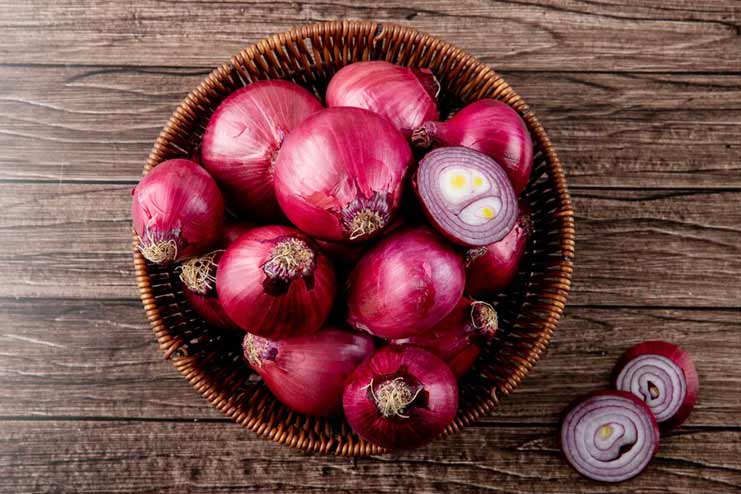 Onions, especially red ones, are rich in antioxidants and add a beautiful pop of color to salads and other dishes.
Onions, especially red ones, are rich in antioxidants and add a beautiful pop of color to salads and other dishes.
They are rich in fiber, potassium, and folates. An extra helping of onions is sure to up the delicious quotient. Moreover, their starch content is low and halves upon cooking.
17. Red Peppers
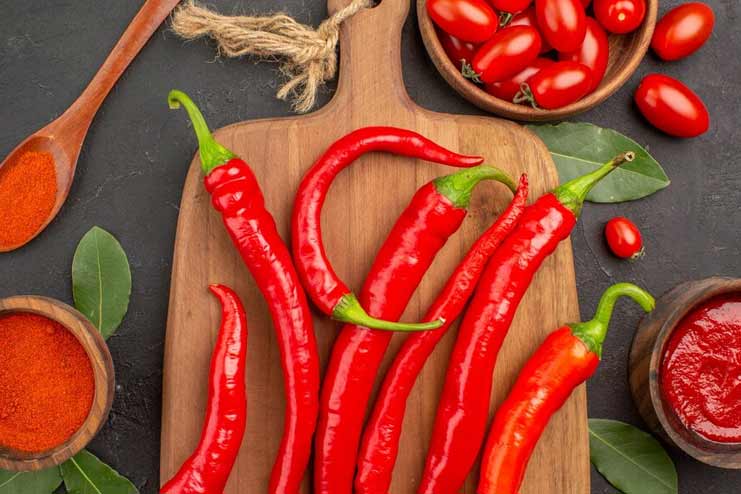 Red peppers contain various nutrients, including Vitamin C and antioxidant beta-carotene.
Red peppers contain various nutrients, including Vitamin C and antioxidant beta-carotene.
They are nothing more than the ripened version of green peppers; hence, they contain an added dose of lycopene, which, along with vitamins A and C, promotes a healthy heart and has been beneficial against diabetes.
They are non-starchy and can be added to various dishes with a host of healthy nutrients.
18. Soy
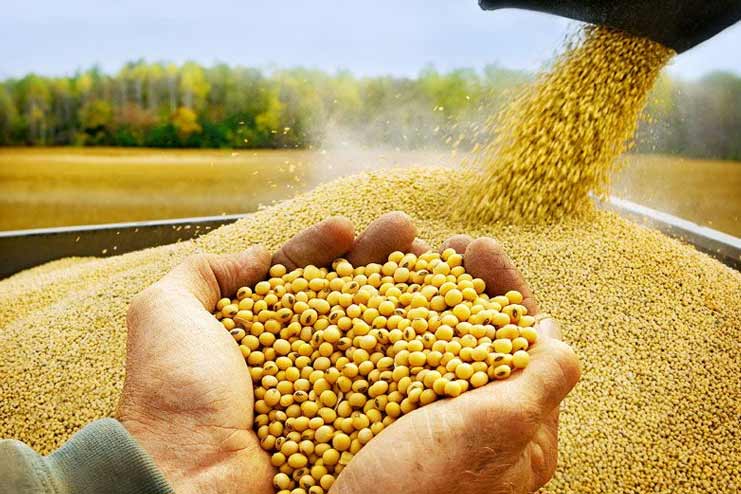 It does not matter how you consume soy as long as you are consuming it. Soy is rich in proteins and contains low saturated fats and cholesterol. Hence, it is an excellent replacement for meat with high fat content.
It does not matter how you consume soy as long as you are consuming it. Soy is rich in proteins and contains low saturated fats and cholesterol. Hence, it is an excellent replacement for meat with high fat content.
A good portion of soy in your meals will keep your hunger satiated for a long time without increasing your calorie intake.
19. Spinach
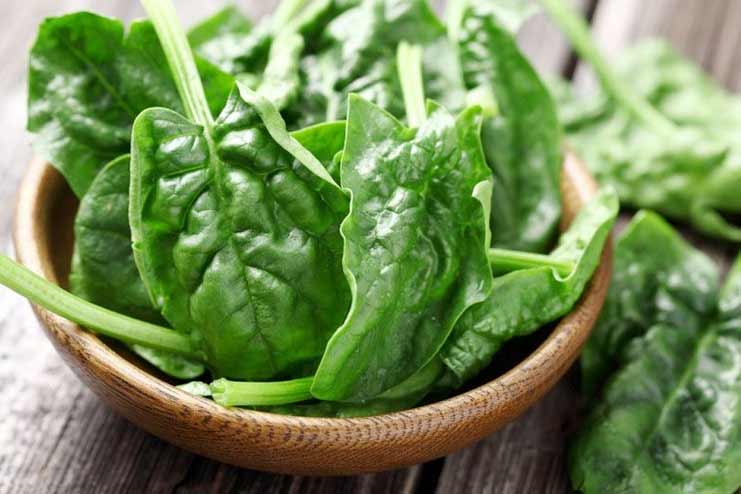 Spinach is loaded with a wide array of vitamins and minerals, including large quantities of folates and vitamin C. It is non-starchy and contains meager carbs and calories.
Spinach is loaded with a wide array of vitamins and minerals, including large quantities of folates and vitamin C. It is non-starchy and contains meager carbs and calories.
How to Incorporate These Superfoods into Your Diet
It can be fun and advantageous to include superfoods in your diet.
For a nutrient-rich breakfast, combine spinach, berries, and Greek yogurt to make a smoothie to start your day.
Add nuts and seeds, like flaxseeds or chia seeds, to increase the amount of fiber and protein in your salads or yogurt.
Quinoa or sweet potatoes are healthier options for lunch and dinner sides instead of processed grains.
Add avocado to salads or sandwiches to lend a creamy touch.
Choose a bowl of berries or a handful of almonds as your snack.
Try making quinoa-stuffed peppers, serving fish with roasted sweet potatoes on the side, or desserts like chia seed pudding.
Adding these superfoods to your meals can support healthy blood sugar regulation, boost flavor, and improve general health.
Conclusion
Superfoods offer many benefits for diabetics, including increased nutrient intake, improved blood sugar regulation, and enhanced overall health. Incorporating foods like quinoa, berries, almonds, and leafy greens into your diet can be crucial in managing diabetes.
To ensure that these dietary choices are suitable for your individual health needs, it’s essential to seek guidance from a healthcare professional or nutritionist. This step can give you a sense of security, knowing your dietary adjustments are well-informed and safe.
References
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/16-best-foods-for-diabetics#best-foods
- https://diabetes.org/food-nutrition/food-and-blood-sugar/diabetes-superstar-foods
- https://www.everydayhealth.com/type-2-diabetes/diet/superfoods-for-your-diabetes-diet
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/317112
- https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/diabetic-food-list-best-worst-foods
- https://www.eatingwell.com/article/2059770/complete-list-of-foods-to-eat-when-you-have-diabetes-and-what-to-limit
- https://www.eatthis.com/best-foods-diabetes
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/317355#foods-to-eat
In this Article