Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersInsulin sensitivity plays a crucial role in regulating blood glucose levels and maintaining metabolic health. It refers to how efficiently our body responds to insulin, the hormone that helps glucose enter cells for energy use. If our body is insulin resistant, our cells are less responsive to insulin, thus leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Understanding how glucose is absorbed from what you eat and the role insulin plays impacts not only the management and prevention of Type 2 diabetes but also other metabolic disorders.
Today we’ll explore how the process works, factors that influence its efficiency, and how lifestyle choices can improve or impair that process.
How Insulin Sensitivity Affects Glucose Absorption
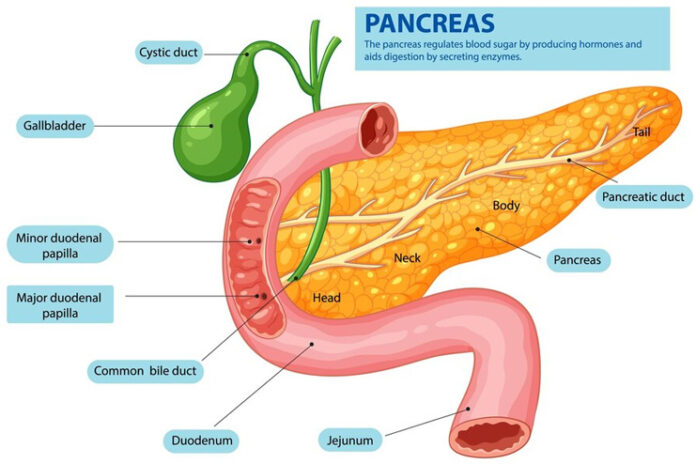
Insulin sensitivity measures how sensitively your body responds to the hormone insulin. Once you eat, your digestive system breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which enters your bloodstream and raises your blood glucose levels. This leads the pancreas to release insulin, which acts like a key to unlock the cells’ ability to absorb glucose. This absorbed glucose is used for immediate energy or stored for future use.
When cells, especially those in muscles, fat, and the liver, are highly sensitive to insulin, they use it efficiently to absorb glucose, helping to maintain balanced blood sugar levels.
However, if you are insulin resistant, the cells do not respond well to insulin. Glucose does not leave the blood as quickly as it would have in a healthy individual, and blood sugar levels rise in case of hyperglycemia. Longstanding hyperglycemia is a key factor leading to metabolic issues and type 2 diabetes.
Basically, if you are sensitive to insulin, your body’s cells absorb glucose more efficiently, leading to stable blood glucose levels and reducing your risk of diabetes and other metabolic conditions.
For a more detailed understanding, read glucose absorption.
Consequences of Impaired Insulin Sensitivity

Insulin resistance causes a broad range of serious health conditions. Decreased cellular sensitivity to insulin impairs mechanisms of regulating blood glucose levels and causes side effects. The most serious ones are the following:
- Increased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
- Higher Blood Sugar Levels
- Elevated Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
- Increased Risk of Obesity
- Development of Metabolic Syndrome
- Potential for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
- Compromised Mental Health
- Hormonal Imbalances
- Increased Risk of Certain Cancers
Factors Affecting Insulin Sensitivity

Several factors influence insulin sensitivity, including:
- Diet: Consuming processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can decrease insulin sensitivity. A diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity by promoting glucose absorption and utilization and improving overall metabolic health. You may practice both aerobic exercise and strength training.
- Body Weight: Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, is associated with reduced insulin sensitivity. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity.
- Sleep Patterns: Poor sleep quality and sleep disorders can adversely affect insulin sensitivity. Taking adequate sleep supports metabolic health.
- Stress Levels: Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that affect insulin sensitivity. Managing stress through techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or counseling can be beneficial.
- Genetics: Genetic predisposition can influence how sensitive your body is to insulin. Though you can’t change your genetics, understanding your risk factors can help in managing insulin sensitivity through lifestyle choices.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids or some antipsychotics, can affect insulin sensitivity. Consult with your doctor if you have concerns about your medications and insulin sensitivity.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity Naturally

Here are some easy strategies for improving insulin sensitivity:
- Get More Sleep: Studies show that insufficient sleep decreases insulin sensitivity. Adequate rest can help reverse these effects.
- Exercise More: Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity. Exercise helps transport glucose into muscles for storage, reducing blood sugar levels. Plan for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise 3–5 times a week. Resistance training can also boost insulin sensitivity over time.
- Reduce Stress: Chronic stress activates the “fight-or-flight” response, increasing stress hormone levels in the body and leading to increased blood sugar levels. Manage your stress through relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and adequate rest.
- Lose a Few Pounds: Excess weight can reduce insulin sensitivity and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. Lose weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Eat Health-Promoting Foods
- Increase soluble fiber foods like oats, beans, and apples in your diet.
- Add a variety of fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants. However, be mindful of fruit portion size.
- Cut down on carbs, especially refined carbs. Opt for low glycemic index carbs to provide a steady release of sugar into the bloodstream.
- Reduce added sugars, such as high fructose corn syrup. Minimize or avoid processed foods and sugary beverages.
- Incorporate Herbs and Spices: Include certain herbs and spices, such as fenugreek, turmeric, cinnamon, and ginger, in your meals to support your metabolic health.
- Drink Green Tea: Consider drinking a cup of green tea daily as it contains antioxidants like epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which reduces blood sugar levels.
- Try Apple Cider Vinegar: Add a small amount of apple cider vinegar to your diet. It slows carbohydrate digestion and promotes a gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream, thereby improving insulin sensitivity.
- Avoid Trans Fats: Often found in processed foods, trans fats have been linked to various health issues, including insulin resistance. Avoid these fats to maintain better insulin sensitivity and overall health.
- Consider Supplements: Supplements, such as vitamin C, probiotics, and magnesium, may help improve insulin sensitivity.
Conclusion
Understanding the science of insulin sensitivity and glucose absorption can help you manage various health problems. Insulin sensitivity measures how well the cells respond to insulin, maintaining normal blood glucose levels and good metabolic health.
Insulin resistance disrupts the glucose absorption process, leading to excess glucose in the bloodstream. This, in turn, causes a variety of major complications, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and obesity.
Lifestyle modifications that inhibit insulin resistance reduce the risk of chronic diseases. These healthy habits include proper exercise, well-balanced diets, and sound sleep. Poor diet, inactivity, and obesity have been known to reduce insulin sensitivity and lead to metabolic disorders.
Through health-promoting practices, an individual can improve insulin sensitivity, control blood sugar effectively, and prevent chronic diseases.
References
- https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/insulin-resistance-syndrome
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/improve-insulin-sensitivity
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22206-insulin-resistance
- https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/36/5/1132/29442/The-Effects-of-Carbohydrate-Unsaturated-Fat-and
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-023-01400-z
- https://e-cmsj.org/DOIx.php?id=10.51789/cmsj.2021.1.e9
In this Article