Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersDiabetic eye disease refers to a group of diseases that comprise diabetic retinopathy, macular edema, cataracts, and glaucoma. All these complications, if left untreated, lead to vision loss. Fortunately, there are treatment options available depending on the type and severity of the disease. From laser therapy to advanced injections, surgeries, and other interventions, these are aimed at preventing the loss of vision or at managing the progression of the complications affecting the diabetic patient’s eyes.

In this article we discuss treatment and prevention strategies. If you are interested in learning more about the causes, risk factors, and types of diabetic eye disease, we recommend reading another article, “Understanding Diabetic Eye Disease.”
Also, read: Diabetes and Eye Health: The Critical Need for Regular Eye Exams
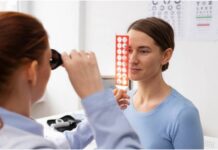
Treatment Options for Diabetic Eye Disease
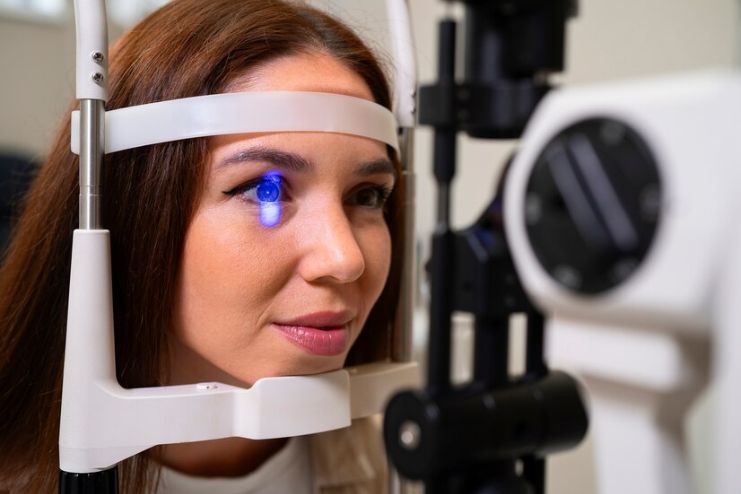
Various treatment options are available, depending on the specific type and severity of the condition. Below are the primary treatment methods for the main forms of diabetic eye disease:
1. Diabetic Retinopathy
- Laser Therapy (Photocoagulation): Laser treatment is often used to seal leaking blood vessels or to shrink abnormal blood vessels in the retina. This treatment can significantly reduce the risk of vision loss in individuals with proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
- Anti-VEGF Injections: Medications that block vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) are injected into the eye to reduce swelling and prevent the growth of new, abnormal blood vessels. These injections can help improve vision in patients with diabetic macular edema and proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
- Vitrectomy: In more advanced cases, a surgical procedure called vitrectomy may be performed. This involves removing the gel-like substance (vitreous) from the eye and may be necessary when there is severe bleeding or retinal detachment.
2. Diabetic Macular Edema
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injections of corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and swelling in the retina, improving vision.
- Intravitreal Implants: Sustained-release implants containing corticosteroids can be placed in the eye to provide long-term treatment for diabetic macular edema.
- Anti-VEGF Therapy: Similar to the treatment for diabetic retinopathy, anti-VEGF injections are commonly used to manage diabetic macular edema by reducing swelling and improving vision.
3. Cataracts
- Cataract Surgery: When cataracts develop, surgical removal of the clouded lens is typically recommended. The lens is replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL), which can restore clear vision. This surgery is safe and effective, with a high success rate.
4. Glaucoma
- Medication: Prescription eye drops are often the first preference for glaucoma. These medications help lower intraocular pressure by reducing the production of fluid or improving its drainage.
- Laser Surgery: If medications are not sufficient, laser surgery may be performed. Procedures such as trabeculoplasty or iridotomy can help improve drainage and lower intraocular pressure.
- Conventional Surgery: In some cases, a surgical procedure may be necessary to create a new drainage pathway for fluid in the eye, thereby reducing pressure.
5. Regular Monitoring and Follow-up
- Continuous Monitoring: After treatment, ongoing monitoring is crucial to assess the effectiveness of interventions and to catch any new changes or complications early.
Also, read: The Effect of Sleep on Insulin Resistance and Diabetes
Prevention and Self-Care Strategies
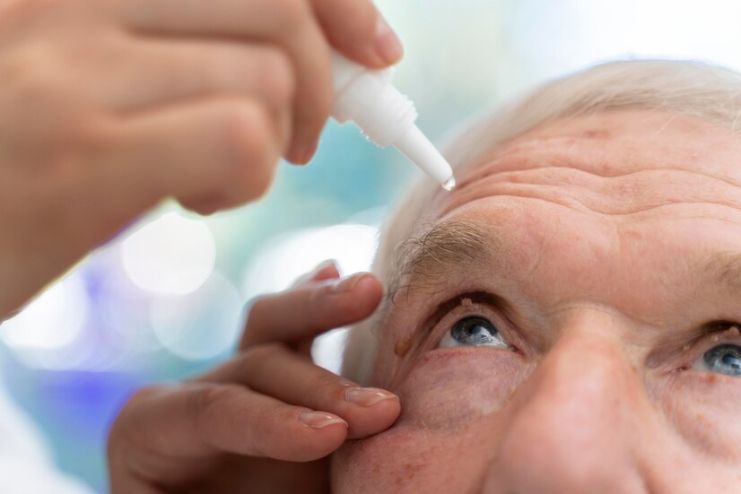
The risk factors of diabetic eye disease must be known to prevent and monitor the condition.
Effective Diabetes Management
- Regular Monitoring of Blood Sugar Levels: Keep blood sugar levels within the normal range to prevent the onset and progression of diabetic eye disease. Regularly monitor your blood glucose levels and adjust your diet, medications, and exercise as necessary.
- Adhering to Medication Regimens: Follow prescribed medication plans, including insulin and oral medications, for managing diabetes effectively. Consistent adherence can help prevent fluctuations in blood sugar that may damage blood vessels in the eyes.
Routine Eye Exams
- Annual Comprehensive Eye Exams: Opt for an annual eye exam. More positive results and better treatment are likely when the disease is detected early.
- Communicating Changes in Vision: Report any rapid changes in vision, such as blurred vision or double vision, to a professional eye specialist immediately.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Balanced Diet: A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins with healthy fats supports good blood glucose levels and minimizes complications. Foods rich in Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly fish, are supportive of eye health.
- Regular Physical Activity: Regular physical activity reduces the risk of complications, such as heart disease, by keeping the body at a healthy weight and at the best blood pressure possible.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Smoking will contribute to the development of complications relating to diabetes, such as diseases affecting the eyes. Smoking cessation will have an immediate impact as well as long-term effects on your eye health and overall health in general.
Education and Awareness

- Understanding Diabetes and Its Effects: A patient needs to know about the risks associated with diabetes and diabetic eye disease. Once the patient becomes knowledgeable, they will maintain control of themselves and further assist in taking proactive measures on how to handle them. Educational resources, support groups, and counseling can provide necessary information and encouragement.
- Involving Family and Friends: Having a support system makes people want to keep going and also inspires them to manage diabetes better. Asking friends and family members to join in with healthy lifestyle changes such as cooking healthy meals or exercising together can improve accountability and chances for success.
Conclusion
Diabetic eye disease management includes treatment, prevention, and lifestyle changes. Ranging from laser treatments to injections, the list of treatments is big and can greatly reduce the risk of vision loss if intervened early. As important as all these treatments are regular eye exams, proper diabetes management, and a healthy lifestyle for preventing complications. Patients with diabetes should stay aware, follow treatment plans, and include a support system that helps them manage their eye health to reduce the effects of diabetic eye disease on their vision.
References
- https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/diabetic-retinopathy
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/diabetic-retinopathy/treatment/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetic-retinopathy/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20371617
- https://www.aao.org/eye-health/tips-prevention/top-five-diabetes-steps
In this Article