AI Contribution
At HealthSpectra, we may use AI to refine grammar and structure, but every piece is shaped, checked, and approved by real people, our expert writers and editors, to ensure clarity, credibility, and care. Learn more..Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersWhile most people understand that diabetes affects blood sugar levels, few realize the significant damage it can cause to eye health. Chronic high blood sugar levels can destroy the delicate structures of the eyes and lead to a range of serious vision complications, including diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and cataracts.
Understanding how high blood sugar affects your eyes is crucial for preventing long-term complications that might impair vision or cause vision loss.
How Diabetes Impacts Vision
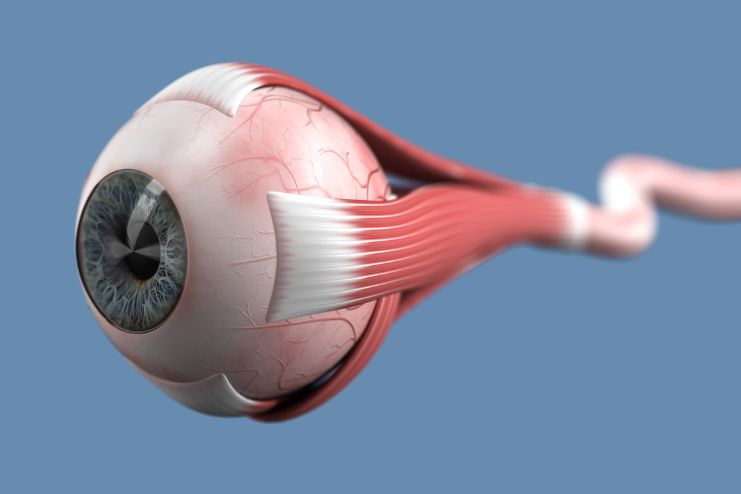
High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, impacts your eye health in both the short and long term. Short-term fluctuations in blood sugar often result in blurry vision caused by swelling in the eye’s focusing tissues. This typically resolves once blood sugar is brought under control.
However, the real danger lies in prolonged hyperglycemia, which causes long-term damage to the retina, the light-sensitive layer located at the back of the eye. This damage can occur even in the prediabetic stage, disrupts vision, and can result in permanent vision loss.
There are several ways diabetes causes progressive vision impairment:
- Retinal Blood Vessel Damage: High blood sugar weakens the small blood vessels in the retina, causing them to leak fluid or blood. This disrupts the visual pathway, leading to swelling, blurred vision, or even blindness.
- Abnormal Blood Vessel Formation: In the advanced stages of diabetic retinopathy, new, fragile blood vessels develop in damaged areas of the retina. Weak and prone to bleeding, these new vessels can cause additional harm to the retina, leading to scarring and even retinal detachment. In this latter condition, the entire retina peels away from its normal anatomical position, potentially resulting in permanent blindness.
- Fluid Accumulation in the Macula: Fluid leaks from damaged blood vessels can lead to swelling in the macula, which is responsible for sharp, central vision. It can result in blurriness or loss of central vision, significantly interfering with daily activities such as reading or driving.
- Increased Eye Pressure: A patient with diabetes becomes susceptible to glaucoma, an eye disease that results from fluid buildup in the eye, increasing internal eye pressure and damaging the optic nerve. Any damage to the optic nerve can lead to a gradual loss of peripheral vision and eventually result in complete and irreversible blindness.
- Lens Changes and Cataract Formation: High blood sugar accelerates the formation of cataracts, a clouding of the eye’s lens. Cataracts block or distort light as it enters the eye, resulting in blurred vision. People with diabetes are more likely to develop cataracts earlier and at a faster rate than those without diabetes.
Early Signs and Symptoms
Diabetic eye conditions usually progress slowly. So, knowing the early signs and symptoms indicating a developing problem is important. Early detection of these symptoms can help minimize further damage and preserve your vision. A few of the most common early signs include:
- Blurry vision
- Floaters or dark spots
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Sudden vision changes
- Eye pain or pressure
- Fading or yellowing of colors
- Double vision
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly to prevent further damage.
Major Diabetes-Related Eye Conditions
Several serious eye conditions are more common in individuals with diabetes:
- Diabetic Retinopathy: This results from damage to the tiny blood vessels in the retina. In the early stages, blood vessels may leak or swell, leading to nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. If untreated, this can lead to proliferative diabetic retinopathy, where the blood vessels become closed off, and new, fragile blood vessels may start to grow on the retina’s surface.
- Diabetic Macular Edema (DME): A complication of diabetic retinopathy, DME occurs when leaky blood vessels cause the macula to swell, impairing central vision. If untreated, DME can lead to permanent vision loss as it progresses.
- Glaucoma: People with diabetes are more likely to be affected by glaucoma, a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, the nerve responsible for carrying visual information to the brain. Increased eye pressure from fluid buildup can cause gradual loss of peripheral vision and eventually total blindness.
- Cataracts: These are a condition in which the lens of the eye becomes cloudy, obstructing vision. This process occurs more rapidly in individuals with diabetes because glucose builds up in the lens, leading to an early onset and aggressive development of cataracts compared to those without diabetes.
Importance of Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams are crucial for individuals with diabetes, as they help detect early signs of eye complications before they cause significant damage. These exams monitor any changes in your eye health and allow for appropriate interventions when necessary.
Early identification of conditions such as diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, cataracts, and other issues can help arrest or slow down vision loss.
To understand the importance of regular eye exams for diabetics, read this article.
Conclusion
Understanding how diabetes affects vision is crucial for individuals living with diabetes. From diabetic retinopathy to diabetic macular edema, glaucoma, and cataracts, uncontrolled blood sugar can lead to a wide range of eye problems that threaten vision.
By managing blood sugar levels and getting regular eye exams, you can significantly reduce the risk of vision loss and maintain good eye health throughout your life.
References
- https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/diabetic-retinopathy
- https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/diabetes-blurred-vision
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetic-retinopathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20371611
- https://www.teceyecare.com/blog/understanding-the-connection-between-high-blood-sugar-and-eye-diseases
- https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/diabetes-eye-problems
In this Article