Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersMaintaining general health and avoiding severe consequences from diabetes need effective management. If you don’t control diabetes, it can cause significant, frequently fatal problems like kidney damage, nerve damage, and cardiovascular disease. Over time, elevated blood sugar levels can worsen these risks. Therefore, early detection and action are crucial. The possible risks associated with uncontrolled diabetes emphasize the necessity of proactive management techniques, such as routine monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and medical assistance. Remaining informed and acting promptly can enhance long-term well-being and significantly decrease the risk of severe health consequences.
Immediate Implications of Untreated Diabetes
Due to high blood sugar levels, diabetes can cause several immediate symptoms if left untreated. Frequent urination, intense thirst, and inexplicable weariness are typical symptoms. The body experiences these sensations to get rid of extra glucose. Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a dangerous, short-term consequence of Type 1 diabetes.
Excessive production of ketones by the body can result in diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a potentially lethal condition that requires emergency medical attention. The condition known as hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS), which is characterized by severe dehydration and raised blood sugar levels, can result from untreated high blood sugar in people with Type 2 diabetes.
Prompt treatment is necessary for both illnesses to avoid serious health problems and complications. It is essential to identify these symptoms as soon as possible and seek medical attention to control diabetes and prevent these harmful side effects effectively.
Long-Term Complications of Untreated Diabetes
Untreated diabetes symptoms may not be apparent initially, but in due course, you will eventually see some of these signs, which you must pay attention to. If the diabetes gets untreated for long, it may give rise to complications from diabetes, which can even be fatal. Some of the effects of untreated diabetes are:
1. Rise in Cholesterol Levels:

Maintaining high blood sugar levels harms cholesterol balance. In particular, they lower “good” cholesterol and HDL. HDL cholesterol transports excess cholesterol to the liver for processing and elimination. When HDL levels drop, this protection is impaired. At the same time, blood triglycerides rise. As triglycerides rise, arteries stiffen and harden, causing arteriosclerosis. Atherosclerosis narrows arteries, reducing blood flow and causing heart attacks and strokes. These complications significantly increase diabetes and heart disease deaths.
2. Rise in Blood Pressure:
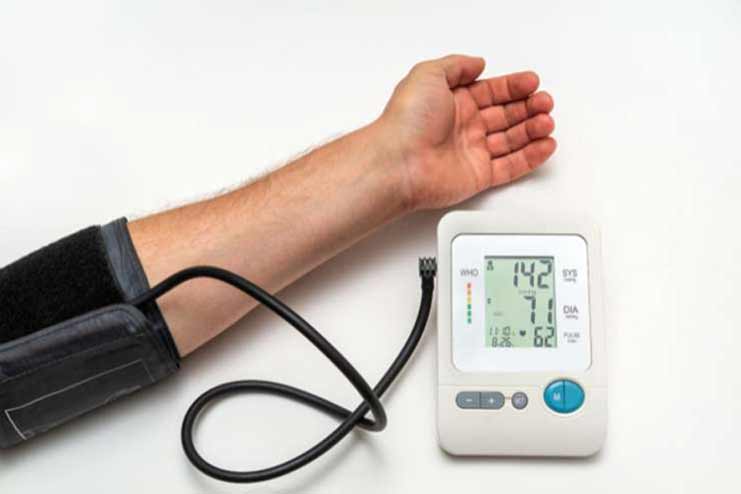
Insulin resistance occurs when the blood sugar levels are high, and the body struggles to respond to insulin. This disorder causes arteriosclerosis, which stiffens and narrows the arteries. As arteries stiffen and constrict, the heart must pump blood harder, raising blood pressure. About 70% of people with diabetes have hypertension. Hypertension, insulin resistance, and excessive blood sugar put the cardiovascular system at risk of life-threatening events like cardiac arrest and stroke. To prevent severe cardiovascular consequences, people with diabetes must manage their blood sugar levels and blood pressure.
3. Deterioration in Vision:
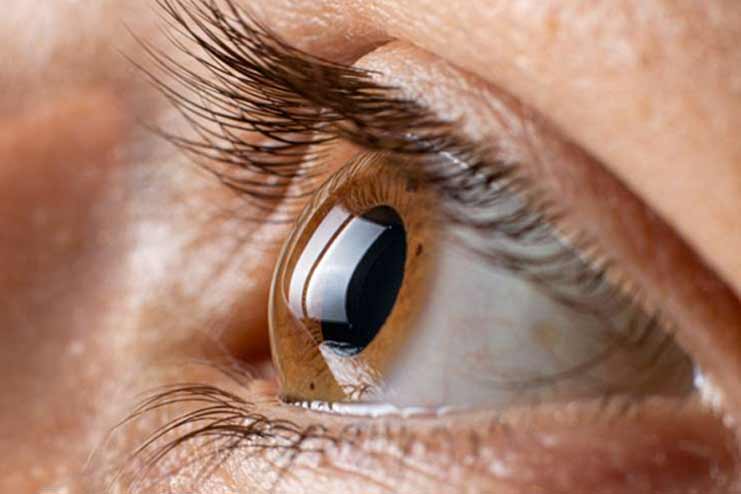
Retinopathy is common in people with diabetes. It is a condition in which damage occurs to light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. High blood glucose levels cause damage to delicate blood vessels in the eyes. However, these symptoms may not occur initially. After a few years of having diabetes, blurred vision, and other eye problems start appearing.
4. Nerves Failure:
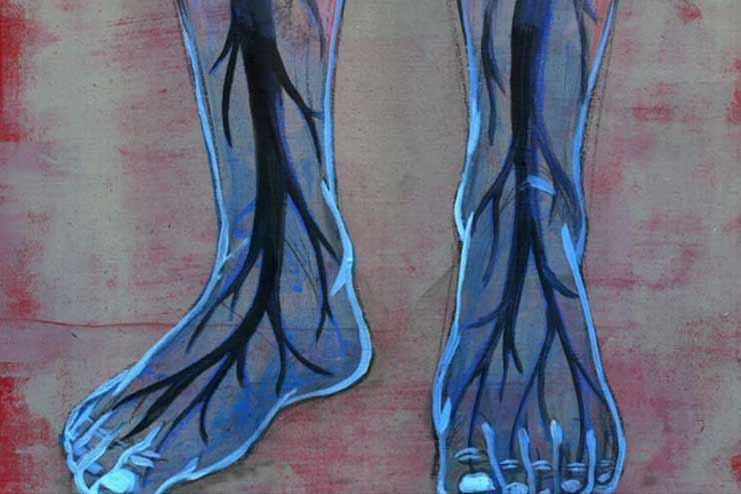
High blood glucose causes nerve damage, and around 50% of people with type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes can develop it. At first, there may not be any symptoms, but eventually, there will be tingling and numbness, which can cause digestive system issues and weakness.
5. Failure of Kidneys:
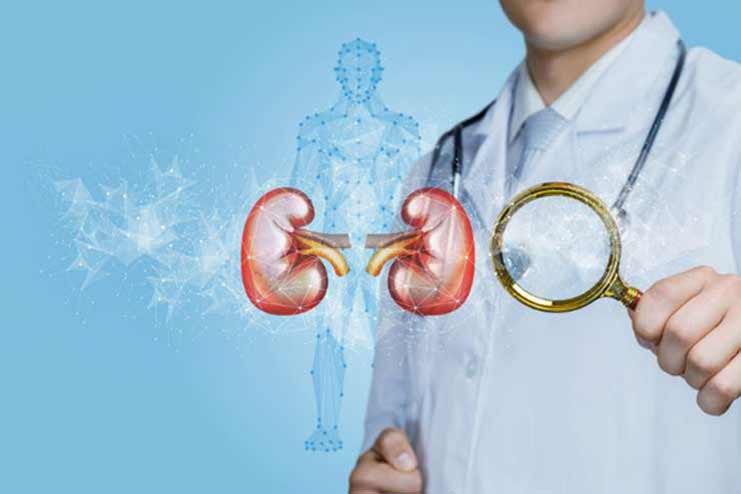
A high blood glucose level thickens and scars the nephrons in a kidney. These nephrons filter the impure blood, and protein leaks into the urine when they get scarred. Over 50% of people whose diabetes is untreated will get kidney failure over ten years. And around 40% may require dialysis or even a kidney implant.
6. Change in Foot Shape:
The high level of blood sugar causes damage to nerves between the brain and lower limbs. The muscle tone slackens, and the shape of the foot changes. Bunions, flat feet, and other deformities can be very common, and with a slight injury and numbness, the wound may go unnoticed. Poor circulation from blood vessels eventually results in slowing the process of healing. This infection gets severe and can take the form of fatal injury which needs amputation. Around 60% of amputations are among people with diabetes.
7. Increased Risk of Heart Attack or Cardiac Arrest:

Diabetes and heart diseases are related; they can lead to higher glucose levels in the blood, which causes damage to arteries, veins, and heart muscles. It can lead to cardiac arrest and even cause death. Diabetes doubles the risk of heart attack, and there is more than four times the risk of getting a stroke. Heart attack factually is the number one fatality cause for people with diabetes. The severities of death and paralysis are alike, and you can even be disabled and paralyzed for life if diabetes is untreated on time.
8. Shortening of Life Span:

An earlier death is more likely if diabetes is untreated. The other complications which lead to severe life-threatening implications are more likely to cause fatalities sooner than later. Diabetes is 7th leading cause of death worldwide, and without diagnosing diabetes, it is more likely to cause sudden demise.
9. Metabolic Problems:

Ketoacidosis is a rapidly progressing condition resulting from high blood sugar levels. Low insulin causes sugar accumulation in the blood. The body then breaks down fat for energy and fuel, accumulating byproducts called ketones. This lowers blood pH levels and leads to vomits, nausea, confusion, dehydration, trauma, and stress.
Symptoms of untreated diabetes:
Untreated diabetes symptoms vary and usually may not be that apparent at first. You must check some of these symptoms and discuss them with your healthcare provider:
- Eye and vision problems
- Extreme thirst
- Too much urine production
- Increase in appetite and eating a lot more
- Weight loss
- Dental problems
- Numbness and tingling of limbs
- Sores and injuries take longer to heal
Prevention and Management Strategies
Effective diabetes management combines medication, dietary adjustments, and routine monitoring. Adhering to the prescribed drug regimen can help control blood sugar levels and avert problems. A balanced diet of veggies, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats is essential. Avoiding sweets and processed foods can also maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Frequent exercise improves general health and insulin sensitivity. Examples of this exercise include swimming and brisk walking. Furthermore, regular blood sugar monitoring enables prompt modifications to medication regimens and food decisions. Visiting your doctor regularly is crucial for monitoring your condition and making necessary prescription adjustments. By implementing these strategies, people can enhance their overall quality of life, lower their risk of complications, and better manage their diabetes.
Conclusion
Serious dangers are associated with untreated diabetes, including the potential for severe consequences like hyperosmolar hyperglycemia syndrome and diabetic ketoacidosis, as well as acute symptoms like high blood sugar, frequent urination, and excessive thirst. Serious health problems like renal damage and cardiovascular disease might result from long-term impacts. Effective diabetes management requires frequent exercise, a balanced diet, medication, and regular blood sugar monitoring. Avoid waiting for any symptoms to worsen before taking proactive measures to manage your health. Seek advice from medical specialists frequently to customize your treatment regimen and avoid issues. The secret to a healthier future is your proactive actions.
-
Nov 2017Written by Minu Manisha
-
Oct 2024Edited by Ankita
References
- https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/risks-complications-uncontrolled-diabetes
- https://www.unitypoint.org/news-and-articles/untreated-diabetes-what-to-know
- https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/diabetes/diabetes-complications-and-risks
- https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/diabetes-long-term-effects
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000327.htm
- https://www.unitypoint.org/news-and-articles/untreated-diabetes-what-to-know
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/untreated-diabetes-5116080
- https://www.diabetes.org.uk/about-diabetes/complications
- https://www.goodrx.com/conditions/diabetes/diabetes-complications
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560723/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetic-ketoacidosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20371551
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000320.htm
In this Article




















