Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersExcess sugar in the bloodstream is known as hyperglycemia, a major health concern. It has a negative effect on a person’s overall health condition. Whenever the blood sugar balance is disrupted, and it rises beyond normal, health problems begin to arise.
Understanding the effects of having excess sugar in the blood can help in the management and prevention of serious conditions like diabetes mellitus. If left high for a long period, the consequences of high blood sugar can become very serious, affecting multiple organs and systems.
In this article, we will understand the mechanisms behind excess blood sugar, the causes and symptoms of hyperglycemia, and possible short-term and long-term effects on health. Once you know these, you’ll be able to recognize signs of elevated blood sugar and take proactive steps toward managing and mitigating the effects.
Also Read: Understand the basics of glucose
Causes of Excess Blood Sugar
There are several causes of hyperglycemia:
- Insulin: Insufficient insulin production or ineffective use of insulin is a primary cause. This happens because type 1 diabetes patients produce minimal or zero insulin, while type 2 diabetes patients produce insulin, but it’s not utilized effectively.
- Diet: Overconsumption of foods rich in carbohydrates and sweetened beverages increases sugar levels in the blood. The excessive intake of refined sugars and processed foods strains the body’s ability to control blood sugar.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle reduces the body’s efficiency in using glucose, leading to higher blood sugar levels.
- Stress: Stressful events cause the production of certain hormones, like cortisol, which elevate blood sugar for a short period.
- Medications: Certain drugs like corticosteroids and certain antipsychotic drugs affect insulin sensitivity or production, resulting in hyperglycemia.
- Infections and Illnesses: The body’s reaction to infection or illness elevates glucose levels as part of the immune response.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes from Polycystic ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) or pregnancy can cause insulin resistance, making blood sugars elevate.
Short-Term Effects of Excess Blood Sugar

If not addressed on time, excess glucose in the blood may cause various discomforting symptoms and acute health risks. Regular monitoring of blood glucose and following a diabetic management plan keep these short-term complications at bay.
- Hyperglycemia Symptoms:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Fatigue and blurred vision
- Headaches and difficulty concentrating
- Impact on Mood and Energy Levels:
- Mood swings and irritability
- Feeling lethargic or unusually tired
- Difficulty focusing on tasks
- Digestive Issues:
- Nausea or stomach discomfort
- Increased appetite despite eating
- Potential for vomiting in severe cases
- Immediate Health Risks:
- Risk of dehydration due to increased urination
- Potential for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in uncontrolled diabetes
- Higher risk of infections due to a weak immune system
Long-Term Consequences of Chronic Hyperglycemia
Prolonged hyperglycemia can further lead to serious complications, affecting nearly every organ and organ system. Understanding the consequences of diabetes emphasizes the need to manage the condition effectively. Key long-term effects include:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Nerve damage
- Eye degeneration
- Kidney disease
- Diabetic foot complications
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Increased infection risk
Diagnosis and Monitoring
Accurate diagnosis and effective monitoring are essential for diabetes management and long-term health maintenance. How do these processes go? Well, here they are:
Diagnosis:
Diabetes is commonly diagnosed by using blood tests including fasting blood glucose, oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), and HbA1c levels. These evaluate blood sugar levels to determine if they are within the diabetic range.
Health professionals examine symptoms such as frequent urination and excessive thirst, as well as unexplained weight loss, in addition to blood tests, in the diagnosis of diabetes.
Family history, age, and obesity are the other contributing factors in evaluating the risk for diabetes.
Monitoring:
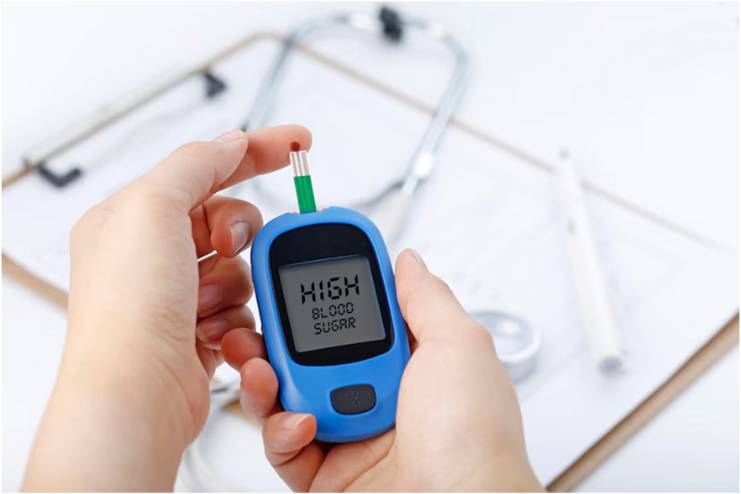
Testing your blood glucose level daily is very important in a self-monitored approach to managing diabetes, which involves changing treatment plans where necessary.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is ideal for more detailed real-time glucose readings and daily trends.
Visits to your doctor for overall check-ups, including blood tests and complication screenings, are important in diabetes management to avoid adverse outcomes.
Management and Treatment

Several health conditions are managed effectively by control and treatment. A structured approach will significantly enhance the quality of life and improve overall well-being. Some of the strategies are:
- Medical Interventions: Regular consultations with your doctor, medications, therapies, or surgery are used based on the condition.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Improvement in management can be achieved with the help of certain healthy lifestyle changes.
- Balanced Diet: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical exercise will improve your physical fitness and mental health.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure having adequate sleep for general health and healing.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular monitoring of symptoms and improvement is essential. Follow-up visits will help determine the results of treatment and make any necessary changes accordingly.
- Support Systems: Support groups, in addition to family and friends, may encourage you to maintain a positive attitude when dealing with this condition.
- Education and Awareness: Understanding the disease and its available treatments will help you make informed decisions and adhere strictly to the management plan.
- Vaccinations: Keeping up with vaccinations saves against preventable diseases, such as flu, pneumonia, and other infections.
- Safe Practices: To prevent injuries and illnesses, follow safety guidelines such as using seat belts, practicing good hygienic practices, avoiding harmful drugs, etc.
Conclusion
Normal blood glucose levels in the body ensure health and prevent complications. Some known causes of hyperglycemia include diet, lack of exercise, stress, medications, or hormonal changes. Familiarity with the causes and symptoms of high blood sugar ensures early detection and management.
Excess glucose levels impact your lifestyle and health by causing thirst and polyuria, followed by fatigue and disturbances in the digestive system. Chronic hyperglycemia, if left untreated, has numerous severe long-term effects, including cardiovascular diseases, neuropathy, retinopathy, nephropathy, and increased susceptibility to infections.
All these risks can be mitigated with regular follow-up and proper management. Blood tests ensure proper diagnosis, regular self-monitoring, and check-ups with your doctor. A healthy lifestyle, with a healthy diet, exercise, and stress management, can work wonders for your overall well-being.
In this Article