Affiliate Disclaimer
Some links in this article are affiliate links. We may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we find useful to our readersProlonged menstrual bleeding, referred to as menorrhagia, affects many women’s health across the globe. When your period doesn’t stop, it can cause discomfort, fatigue, and anemia. Understanding the underlying cause is essential to finding the proper treatment and maintaining menstrual health.
By identifying the root cause of prolonged menstrual bleeding, you can work with healthcare providers to ensure that any underlying health concerns are managed effectively and promptly.
This guide reviews twelve common causes of prolonged menstrual bleeding and identifies possible solutions for each.
1. Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalance, particularly imbalance related to estrogen and progesterone, prolongs menstrual bleeding. Estrogen builds up the uterine lining, and progesterone stabilizes it. An imbalance of the two hormones can create turmoil in the body.
If there is too much estrogen or too little progesterone in the body, the lining of the uterus becomes too thick. This results in prolonged periods or heavy menstruation.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) and thyroid disorders occur due to the overproduction of androgens. It causes irregular ovulation and menstrual cycles. In both types of thyroid dysfunction, hypothyroidism, and hyperthyroidism, the reproductive hormones are imbalanced.
Interventions through medication are critical to treat this hormonal imbalance and maintain healthy menstrual cycles.
Read More: Top 8 Hormone-Balancing Foods: Supporting Women’s Hormonal Health
2. Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths that vary in size and number and may cause heavy and prolonged bleeding during periods. They distort the uterine cavity, and because of the increased surface area of the endometrium, there is excessive menstrual flow.
Pelvic pain, backache, frequent urination, and constipation are common symptoms.
A good gynecologist can diagnose uterine fibroids through a pelvic examination, ultrasound, or MRI. Diagnostic tests can determine the size, location, and number of fibroids, and determining these factors is required to curate a treatment plan for fibroids.
3. Polyps
Uterine polyps, also known as endometrial polyps, are small growths on the inner lining of the uterus. They come in different sizes and are usually attached to the uterus lining, thereby leading to irregular and prolonged bleeding during periods.
Polyps can make a period heavier or may cause bleeding between periods. Postmenopausal women with polyps may also experience bleeding. Other symptoms may include pelvic pain and infertility.
Diagnosing polyps correctly is essential as these symptoms may be confused with other conditions. Diagnostic tests include ultrasounds, hysteroscopies, and endometrial biopsies. Early detection and treatment are crucial to effectively managing the symptoms and preventing possible complications.
4. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a chronic disease where tissue similar to the inner lining of the uterus grows outside of the uterus and affects the ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and pelvic lining. It thickens, breaks down, and bleeds during each menstrual cycle, causing prolonged and heavy menstrual bleeding.
Endometriosis causes pelvic pain, especially during menstruation. Other symptoms include fatigue, infertility, and pain during intercourse, bowel movements, and urination. These symptoms are an indication that one needs medical attention.
Diagnosis typically requires pelvic exams, ultrasounds, or laparoscopy. Medication or surgery may also be considered.
Read More: 20 Natural Remedies For Endometriosis For Faster Relief
5. Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis is a disorder in which the tissue that usually lines the uterus (endometrium) begins to grow into the muscular walls of the uterus. The disorder causes prolonged periods of heavy bleeding, which can be accompanied by severe cramping and pelvic pain.
Diagnosis of adenomyosis typically includes examination of the patient’s medical history, pelvic examination, and imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI. In some cases, a biopsy of the uterine tissue may be required to provide a definitive diagnosis.
Adenomyosis treatment mainly consists of relief from symptoms and pain management with NSAIDs, hormonal therapy to regulate the menstrual cycle, and, in severe cases, surgeries like hysterectomy may be suggested.
6. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic inflammatory Disease, also referred to as PID, is an infection of female reproductive organs, usually due to sexually transmitted bacteria like chlamydia or gonorrhea. PID causes extended menstrual bleeding due to inflammation and damage to the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
Symptoms may include pelvic pain, especially during intercourse or urination, abnormal vaginal discharge, fever, and sometimes irregular intermenstrual bleeding. Treatment at an early stage is essential to prevent complications such as chronic pelvic pain, infertility, or ectopic pregnancy.
PID treatment includes a course of antibiotics to treat the infection. Early treatment by a good doctor is essential once PID is suspected. This reduces the long-term consequences of reproductive problems.
PID can be prevented by regular STI testing and safe sexual practices.
7. Blood Disorders
Blood disorders, especially clotting disorders like Von Willebrand’s disease, impact menstrual bleeding patterns. Von Willebrand’s disease causes difficulties in blood clotting and, therefore, may result in prolonged and heavy bleeding during menstruation.
Women with the disorder may suffer from excessive bleeding during menstrual cycles and even between periods. Diagnosis is done through blood tests to measure clotting factors and determine the time it takes to form a blood clot.
Medical examination is critical in early detection to manage these blood disorders effectively. Medication to improve clotting, hormonal therapies to regularize the menses, or even procedures to control bleeding in severe cases are part of the treatment plans. Women with blood disorders should work closely with an excellent doctor to ensure effective monitoring and maintenance of their menstrual health.
8. Medications
Some medications disrupt normal menses, resulting in prolonged bleeding. Anticoagulants such as aspirin and warfarin inhibit blood clotting mechanisms, making periods heavier and longer.
Hormonal treatments, including birth control pills and hormone replacement therapies, can either reduce or increase the duration of menstrual bleeding, depending on the dosage and hormonal balance they induce.
If there is abnormal uterine bleeding, a healthcare provider should be contacted. A qualified healthcare professional can adjust the dosages or find other forms of treatment to ensure proper management of your menstrual health. Close observation and communication about changes in menstrual patterns will ensure appropriate management of any possibility of complications due to medication-induced irregularity in the menses.
9. Intrauterine Device (IUD)

Both hormonal and non-hormonal intrauterine devices can affect menstrual bleeding patterns. Non-hormonal intrauterine devices, especially copper IUDs, may increase menstrual flow and cramping due to inflammation in the uterus.
Some of the side effects of hormonal IUDs include prolonged and heavy bleeding, severe cramps, and spotting between periods. While the condition is manageable, these symptoms must be addressed carefully.
If you are experiencing heavy bleeding that is soaking through pads or tampons quickly and experiencing cramps and spotting, seek medical care immediately. Your healthcare provider will be able to assess if it is due to an IUD or any other underlying problem that needs attention. Regular doctor check-ups and discussions with your doctor will ensure proper management of your chosen form of contraception and menstrual health.
10. Stress
Stress may impact menstrual health by causing prolonged periods of bleeding. When the body is subjected to stress, it produces hormones like cortisol that can interfere with the normal production of reproductive hormones like estrogen and progesterone. This alters the menstrual cycle, hence leading to prolonged bleeding.
Getting enough sleep, exercising regularly, meditating, and deep breathing help reduce your daily stress levels. In addition, maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains for a healthy body to regulate the menstrual cycle.
Stress management practices promote hormonal balance and may help alleviate the symptoms of prolonged menstrual bleeding. These self-care activities, along with professional support, can be extremely helpful in maintaining good menstrual health.
Read More: 20 Stress Relieving Foods Help You Reduce It Instantly
11. Weight Fluctuations
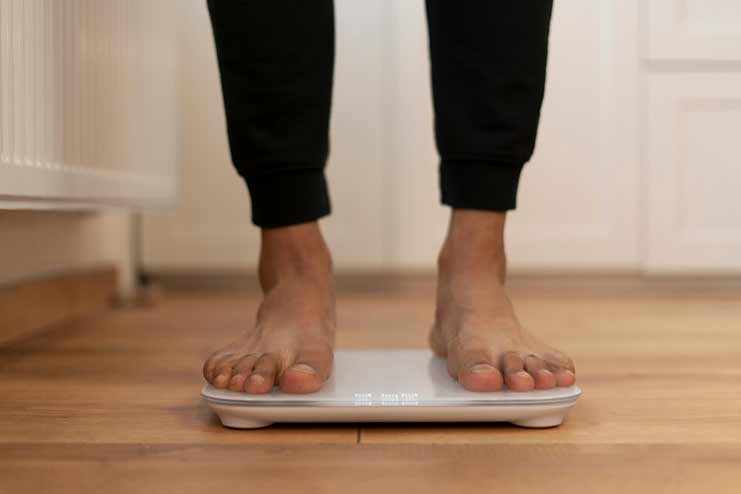

Menstrual changes fluctuate with weight gain or loss by disturbing the balance of hormones. Too much body fat increases estrogen production and may result in heavy or more frequent periods. On the other hand, extreme weight loss or very low body fat percentage reduces estrogen levels in a woman’s body, leading to irregular or absent periods.
Learn how to maintain a healthy weight with a balanced diet and good lifestyle habits, which are crucial in hormonal regulation and menstrual health. Maintaining the recommended BMI for your age and height can help you keep your menses regular.
A dietician can provide valuable, individualized advice on achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, promoting optimum menstrual function.
12. Cancer
In rare cases, prolonged menstrual periods can be indicative of certain underlying conditions, such as endometrial or cervical cancer. Indeed, abnormal bleeding is a symptom of endometrial cancer.
Early detection through regular screenings like Pap smears and pelvic exams is important to diagnose these conditions at an early stage.
For cervical cancer, the HPV vaccine provides preventive measures against strains of the virus known to cause cancer. Regular screenings can detect abnormalities indicating a cancerous or precancerous condition, thus allowing timely treatment measures.
Related Articles:
- 14 Early Signs Of Breast Cancer – Know The Risks Before
- 11 Measures To Prevent Cancer Risk – For the Better World
Conclusion
Abnormal or prolonged menstrual bleeding affects your menstrual health and knowing the root cause is important. It can be caused by hormonal imbalances and problems within the uterus, such as fibroids and polyps, infections, and, in the worst scenario, even cancer. These can be diagnosed by a thorough medical evaluation.
If you are bleeding more than usual, seek medical help immediately. Early diagnosis can help prevent potential complications.
Regular check-ups, screening, and communication with healthcare providers can help one manage menstrual health problems.
Remember that your menstrual cycle indicates your overall health. Never hesitate to seek medical advice for treatment options. Leading a balanced and healthy life and taking preventive measures can help you manage your reproductive health.
In this Article





















